Programming Manual UDP3000S Series
Instruments.uni-trend.com 3/ 49
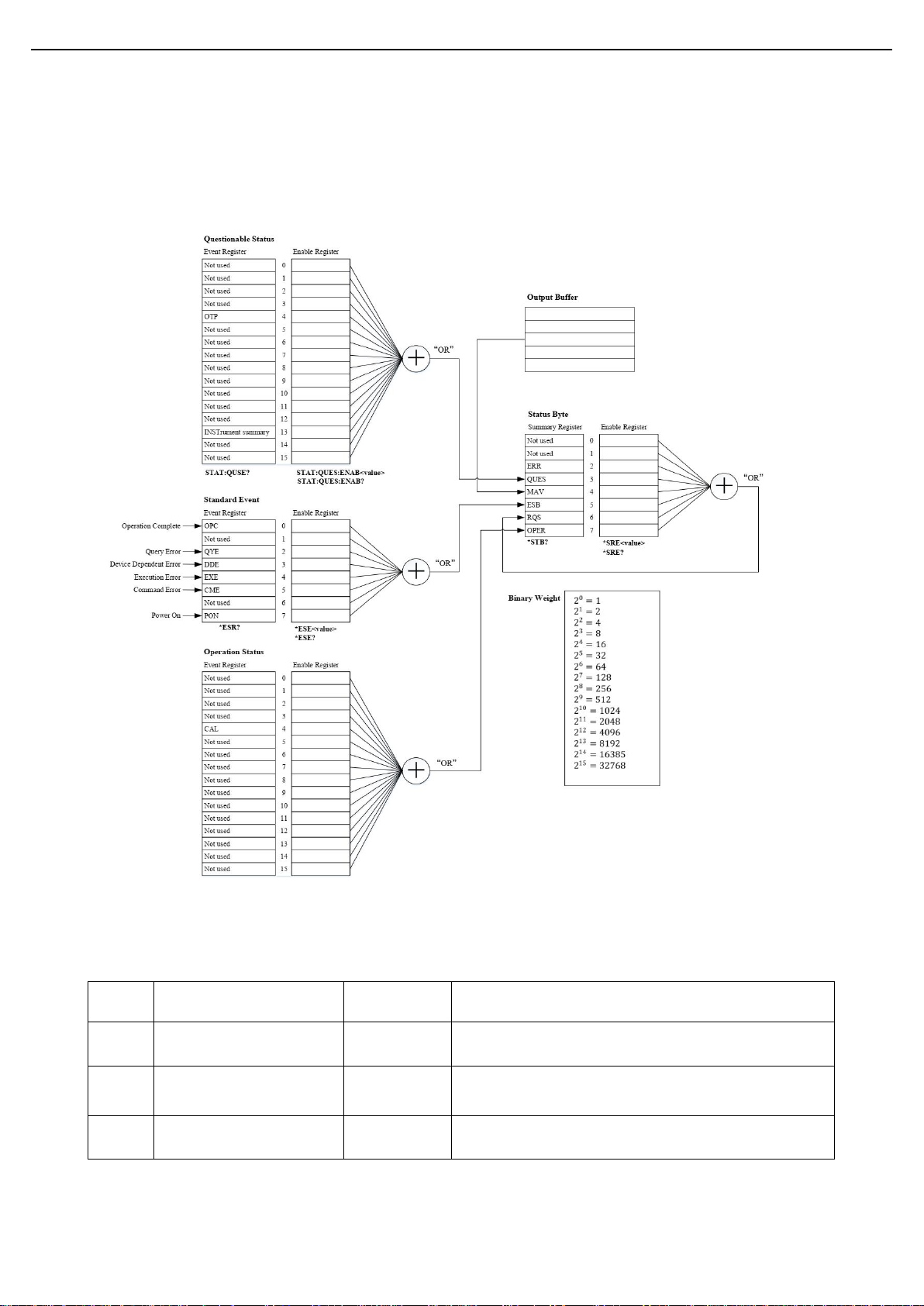
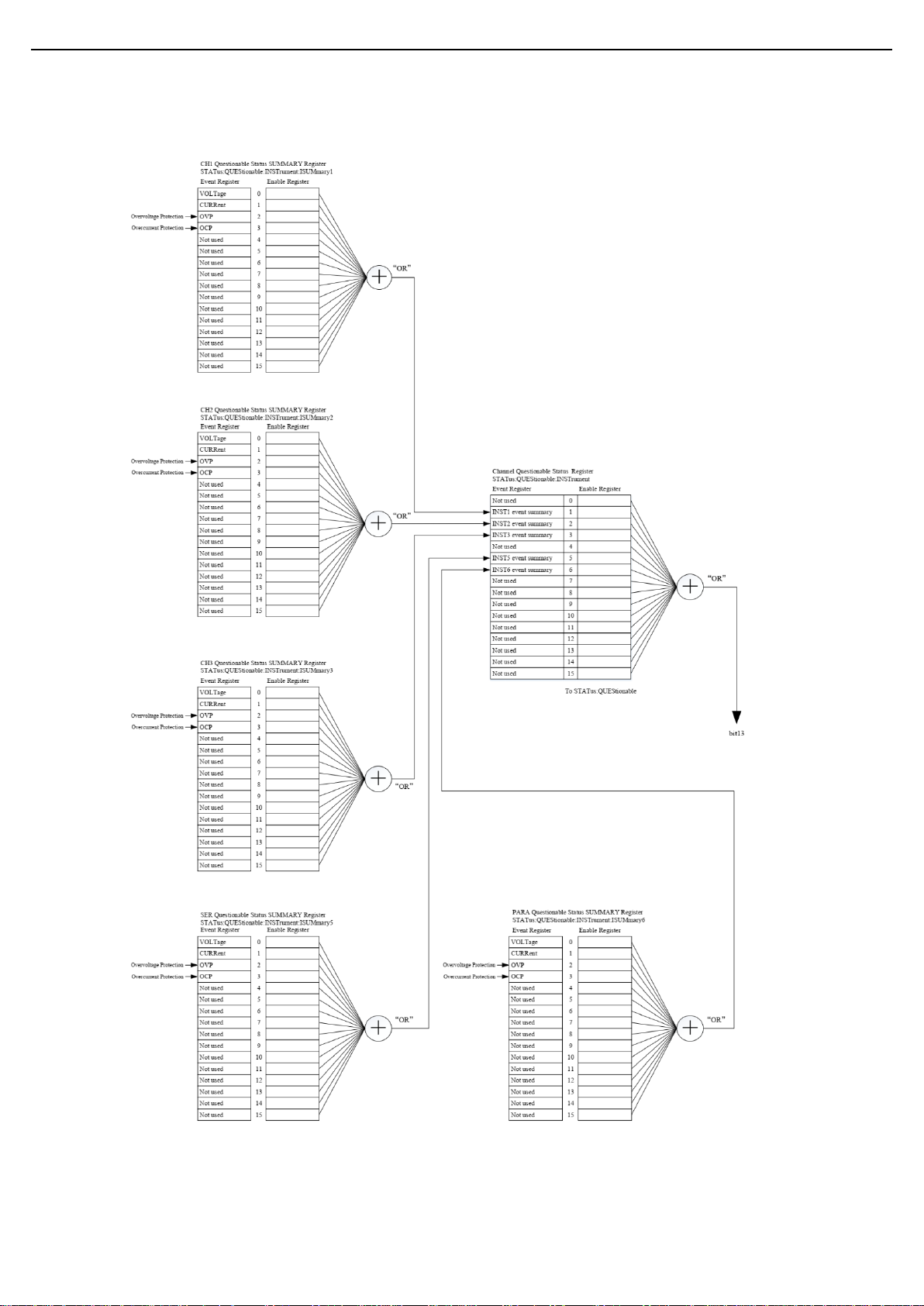
SCPI
SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments) is a standard command set based on the existing
standards IEEE 488.1 and IEEE 488.2. And follow the IEEE754 standard floating-point arithmetic rules, ISO646
information exchange 7 bits code symbol (equivalent to ASCII programming) and other standard standardized
instrument programming language.
This section describes the format, symbols, parameters, and abbreviation rules of the SCPI command.
Instruction Format
The SCPI command is a tree-like hierarchy consisting of multiple subsystems, each consisting of a root
keyword and one or more hierarchical key words.
The command line usually begins with a colon ":"; Keywords are separated by the colon ":", followed by optional
parameter settings. The command keyword is separated by spaces from the first parameter. The command
string must end with a newline <NL> character. Add the question mark "? " after the command line. It is usually
indicated that this feature is being queried.
Symbol Description
The following four symbols are not part of SCPI command, it cannot send with the command. It usually used as
supplementary description of command parameter.
Braces { }
usually contains multiple optional parameters, it should select one parameter when send command.
For example, INSTrument[:SELEct] {CH1|CH2|CH3|SER|PARA}
Vertical bar |
used to separated multiple parameters, it should select one parameter when send command.
For example, INSTrument[:SELEct] {CH1|CH2|CH3|SER|PARA}
Square Brackets [ ]
the contents in square brackets (command keywords) can be omissible. If the parameter is ignored, the
instrument will set the parameter as the default value.
For example, for the command : INSTrument[:SELEct] {CH1|CH2|CH3|SER|PARA}, [:SELEct] can be ignored.
Triangular Brackets < >
the parameter in the brackets must be replaced with a valid value.
For example, :LISTout:TEMPlet:POINTs <point>
:LISTout:TEMPlet:POINTs 20
Parameter Description
The parameter in this manual can divide into five types: Boolean, Integer, Real, Discrete and ASCII string.
Boolean
Parameter value can set “ON” (1) or “OFF” (0).