ACR122U – Application Programming Interface info@acs.com.hk
Version 2.04 www.acs.com.hk
Page 2 of 49
Table of Contents
1.0. Introduction .............................................................................................................4
1.1. Features.................................................................................................................................4
1.2. USB Interface ........................................................................................................................5
2.0. Implementation........................................................................................................6
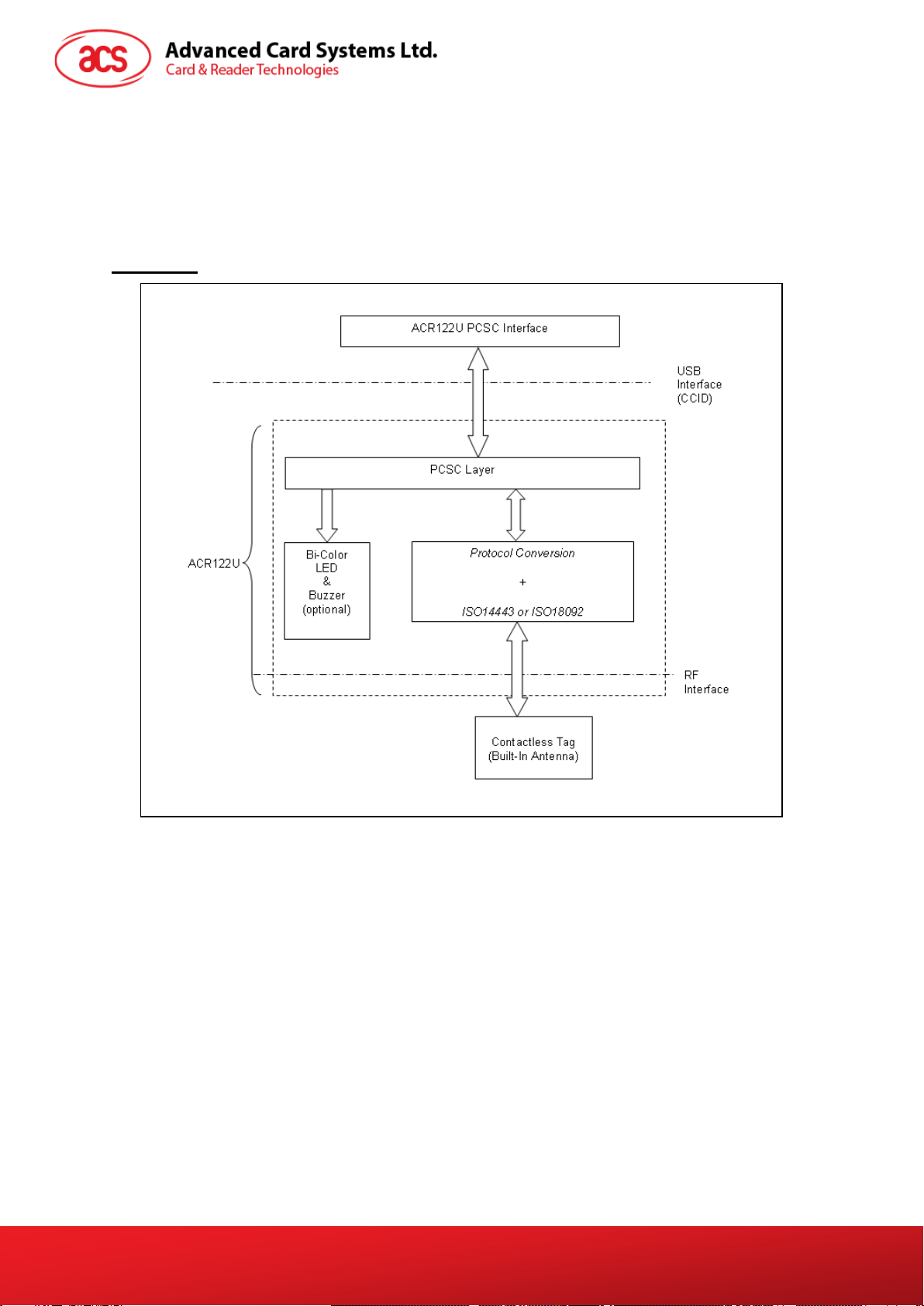
2.1. Communication Flow Chart of ACR122U..............................................................................6
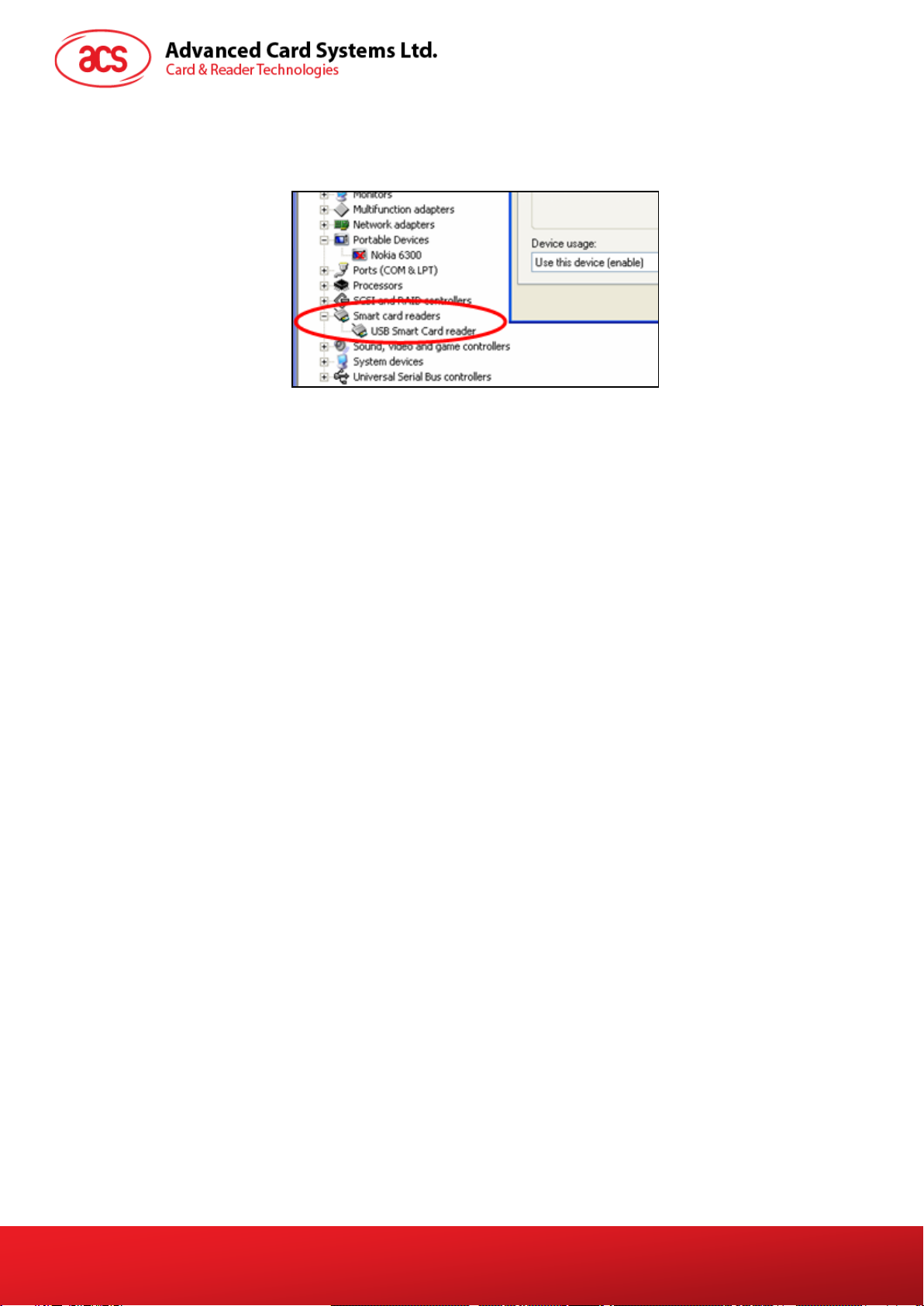
2.2. Smart Card Reader Interface Overview ................................................................................7
3.0. PICC Interface Description .....................................................................................8
3.1. ATR Generation.....................................................................................................................8
3.1.1. ATR format for ISO 14443 Part 3 PICCs......................................................................8
3.1.2. ATR format for ISO 14443 Part 4 PICCs......................................................................9
4.0. PICC Commands for General Purposes ..............................................................11
4.1. Get Data...............................................................................................................................11
5.0. PICC Commands (T=CL Emulation) for MIFARE Classic Memory Cards..........12
5.1. Load Authentication Keys....................................................................................................12
5.2. Authentication......................................................................................................................13
5.3. Read Binary Blocks .............................................................................................................16
5.4. Update Binary Blocks ..........................................................................................................17
5.5. Value Block Related Commands.........................................................................................18
5.5.1. Value Block Operation ................................................................................................18
5.5.2. Read Value Block........................................................................................................19
5.5.3. Restore Value Block....................................................................................................20
6.0. Pseudo-APDU Commands....................................................................................21
6.1. Direct Transmit ....................................................................................................................21
6.2. Bi-color LED and Buzzer Control.........................................................................................22
6.3. Get firmware version of the reader......................................................................................24
6.4. Get the PICC operating parameter......................................................................................25
6.5. Set the PICC operating parameter ......................................................................................26
6.6. Set Timeout Parameter........................................................................................................27
6.7. Set buzzer output during card detection..............................................................................28
7.0. Basic Program Flow for Contactless Applications .............................................29
7.1. How to access PC/SC-compliant tags (ISO 14443-4)?.......................................................31
7.2. How to access MIFARE DESFire tags (ISO 14443-4)? ......................................................32
7.3. How to access FeliCa tags (ISO 18092)? ...........................................................................34
7.4. How to access NFC Forum Type 1 Tags (ISO 18092)?......................................................35
7.5. Get the current setting of the contactless interface.............................................................37
Appendix A. ACR122U PC/SC Escape Command........................................................38
Appendix B. APDU Command and Response Flow for ISO 14443-Compliant Tags..41
Appendix C. APDU command and response flow for ISO 18092–compliant tags .....42
Appendix D. Error Codes...............................................................................................43
Appendix E. Sample codes for setting the LED ...........................................................45
List of Figures
Figure 1 : Communication Flow Chart of ACR122U ..............................................................................6
Figure 2 : Smart Card Reader Interface on the Device Manager ..........................................................7