8
Infrared Thermometer Model CA870
CHAPTER 4
OPERATION
4.1 Measurement Considerations
MEASUREMENT THEORY: Every object emits infrared (IR) energy pro-
portional to its temperature. By measuring the amount of this radiant
energy, it is possible to determine the temperature of the emitting object.
Infrared radiation is invisible light (electromagnetic radiation), which easily
travels through air and is easily absorbed by solid matter. An IR thermom-
eter, which operates by detecting infrared radiation, can accurately mea-
sure an object surface temperature without touching it and independently
of the air temperature or the measurement distance.
Infrared radiation, which is emitted from the object, is focused into an infra-
red radiation sensor through an optical system. This system includes an
optical lens, which is transparent to infrared radiation, and a 5.3μm cut
offlter.Theoutputsignalfromtheinfraredradiationsensorisinputtoan
electronic circuit, along with the output signal from a standard temperature
sensor, to calculate the temperature and display it on the meter display.
4.2 Recommendations before Operating
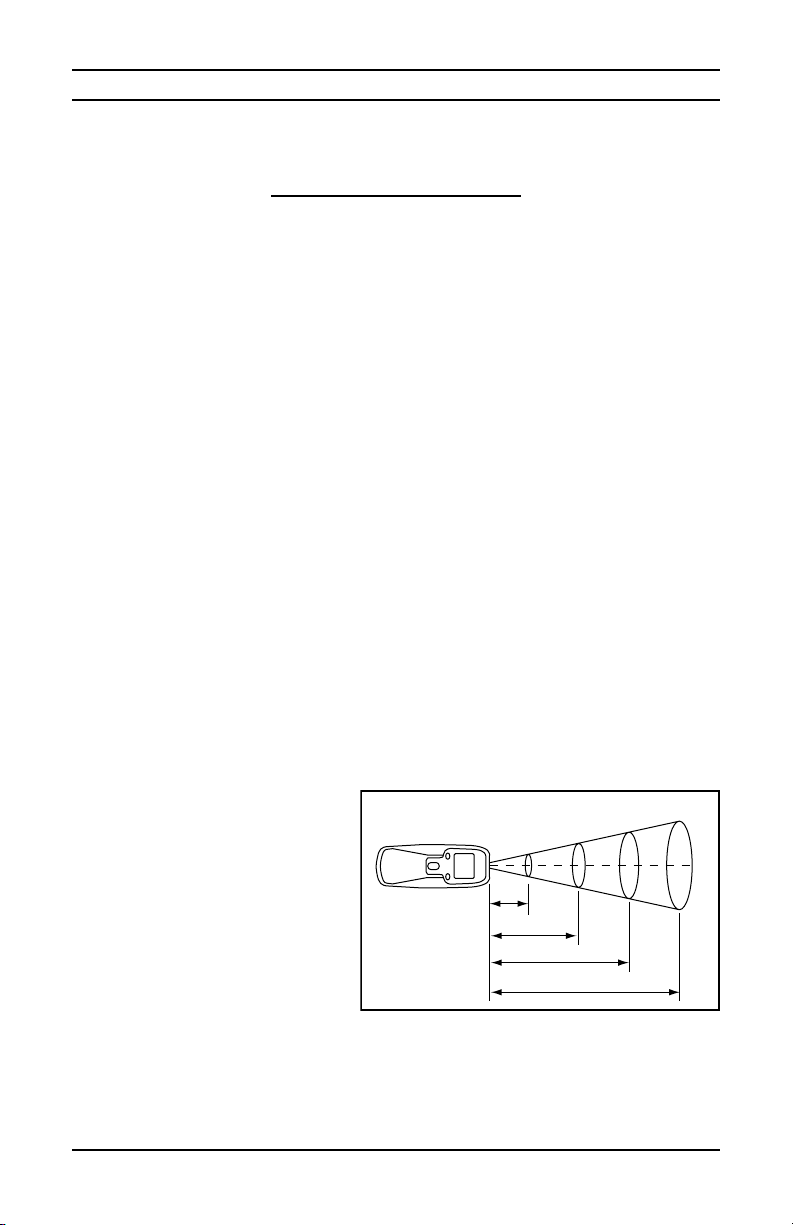
• If the measured surface target diameter is less than 2"/50mm Ø, then
place the sensor as close as possible to the target surface (<20"/50cm
away).SeeFieldofView(FOV)informationunderSpecications.
• If the target surface is covered with frost or any matter, clean it before
taking a measurement.
• Ifthetargetsurfaceishighlyreectiveputsomemattetape,ormatte
paint, over it before measuring.
• If the Thermometer is erratic, or seems not to be measuring properly,
make sure that the sensor is clean and not covered by condensation.