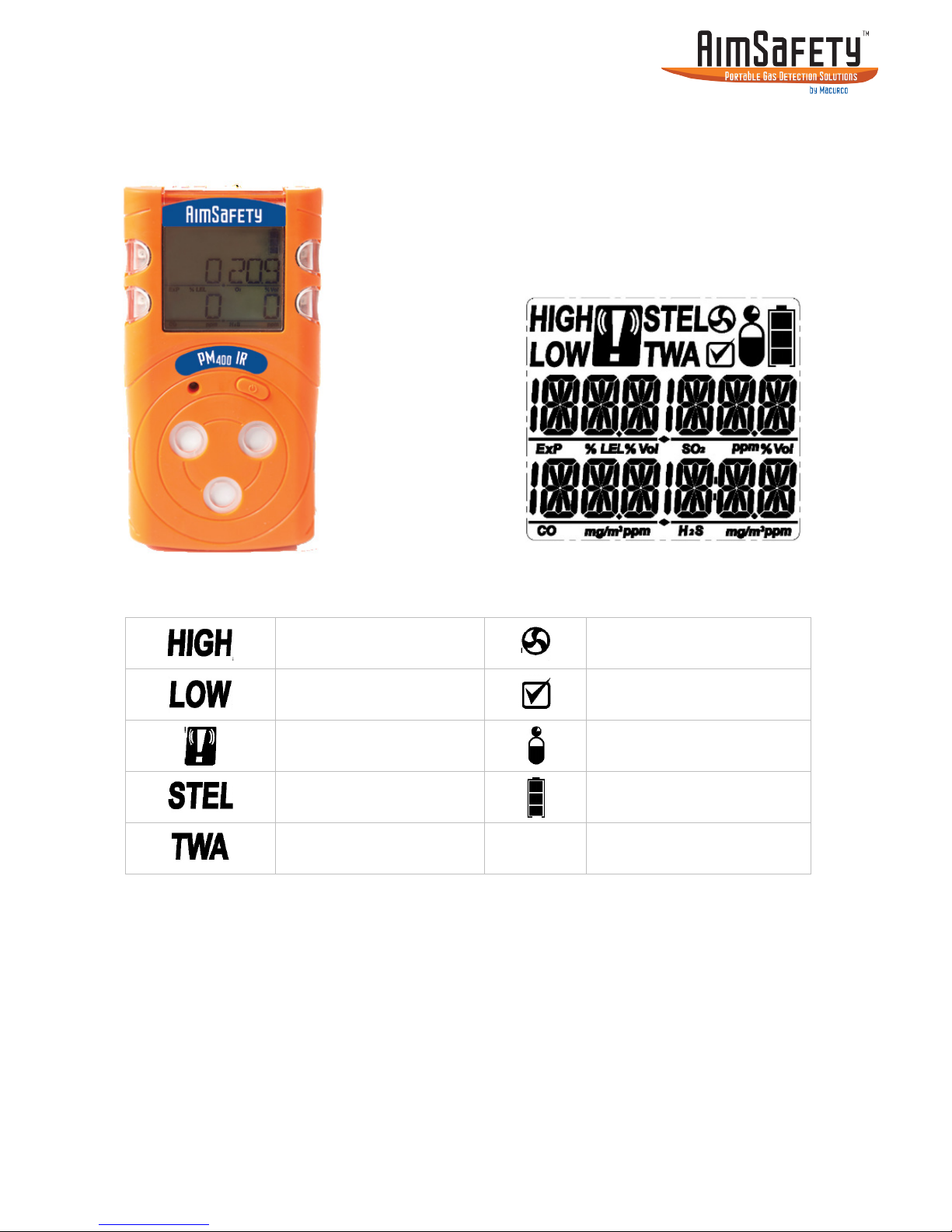
2.2.2 Disadvantages of Catalytic Bead technology
The Catalytic sensor can be “poisoned”: Certain chemicals will damage the internal
elements and cause the sensor to lose sensitivity. Common poisons are chemicals
which contain silicon (found in hand lotions and industrial lubricants) and Sulfur
compounds, which can be released with gases. Chlorine (found in many cleaning
products) and heavy metals can also poison a catalytic sensor. This list is by no means
comprehensive.
The Catalytic Bead sensors require oxygen to detect gases: Because a Catalytic Bead
sensor burns the sample of gas, oxygen is required for the monitor to detect the
presence of combustible gases.
The Catalytic Bead sensor can burn out:Exposure to high concentrations of gas can
completely disable the sensor. See section 2.1 Over Range Alert Function
The Catalytic Bead sensor is more prone to sensor drift: These sensors typically
require more frequent calibration. See section 8. Calibration
The Catalytic sensor requires more power: Due to the sensor design, the Catalytic
Bead sensor requires more power to operate, thus shortening the runtime of the
monitor.
2.3 Non-Dispersive Infra-Red (NDIR) technology (PM400 IR)
Overview
2.3.1 Disadvantages of NDIR technology
Doesn’t detect certain combustible (LEL) gasses: Gases such as hydrogen and
acetylene go undetected by NDIR sensors.
Be sure the safety of your users isn’t dependent on detecting hydrogen
and/or acetylene. The PM400 IR does NOT detect these gases.
2.3.2 Advantages of NDIR technology
The NDIR sensor does not require oxygen to detect gases: Because the NDIR sensor
uses absorbed light spectrum technology to detect combustible gases, the sensor does
not require oxygen to operate, making it ideal for inert and oxygen deficiency
applications.
The NDIR is more durable:Cannot be inhibited, poisoned by external chemicals and
gases.
The NDIR sensor is more stable: Requires minimal recalibration and is typically stable
even after extended storage.
The NDIR sensor has a longer lifespan: The sensor has a life expectancy of up to 10
years.
The NDIR sensor requires less power: Due to the sensor design the NDIR sensor
requires less power to operate, thus allowing for extended runtimes compared to the
Catalytic Bead sensor.