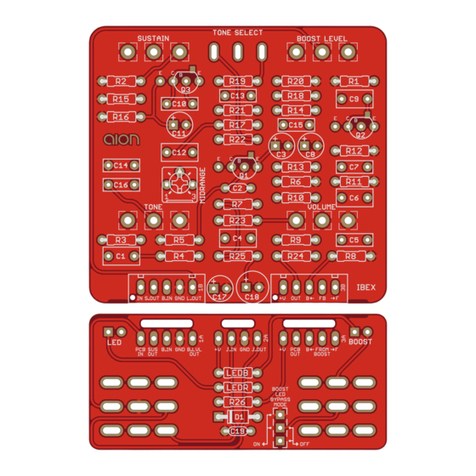
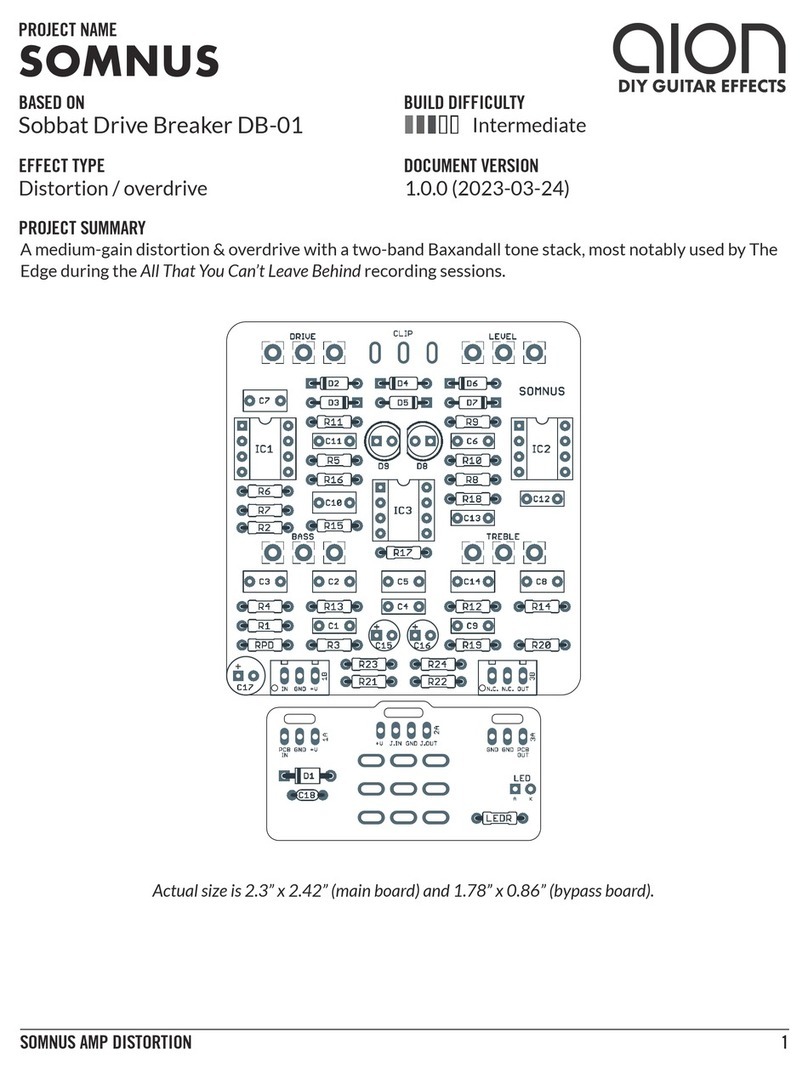
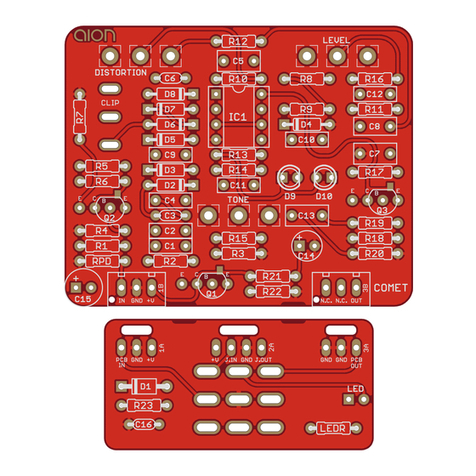
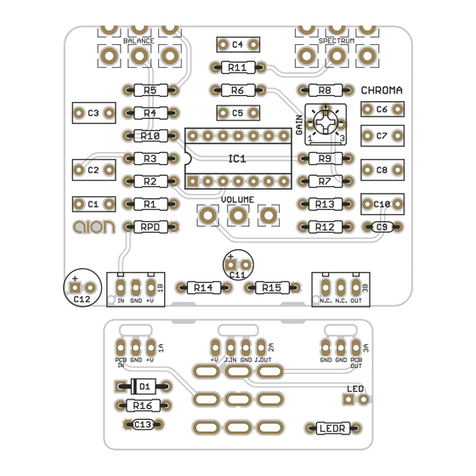
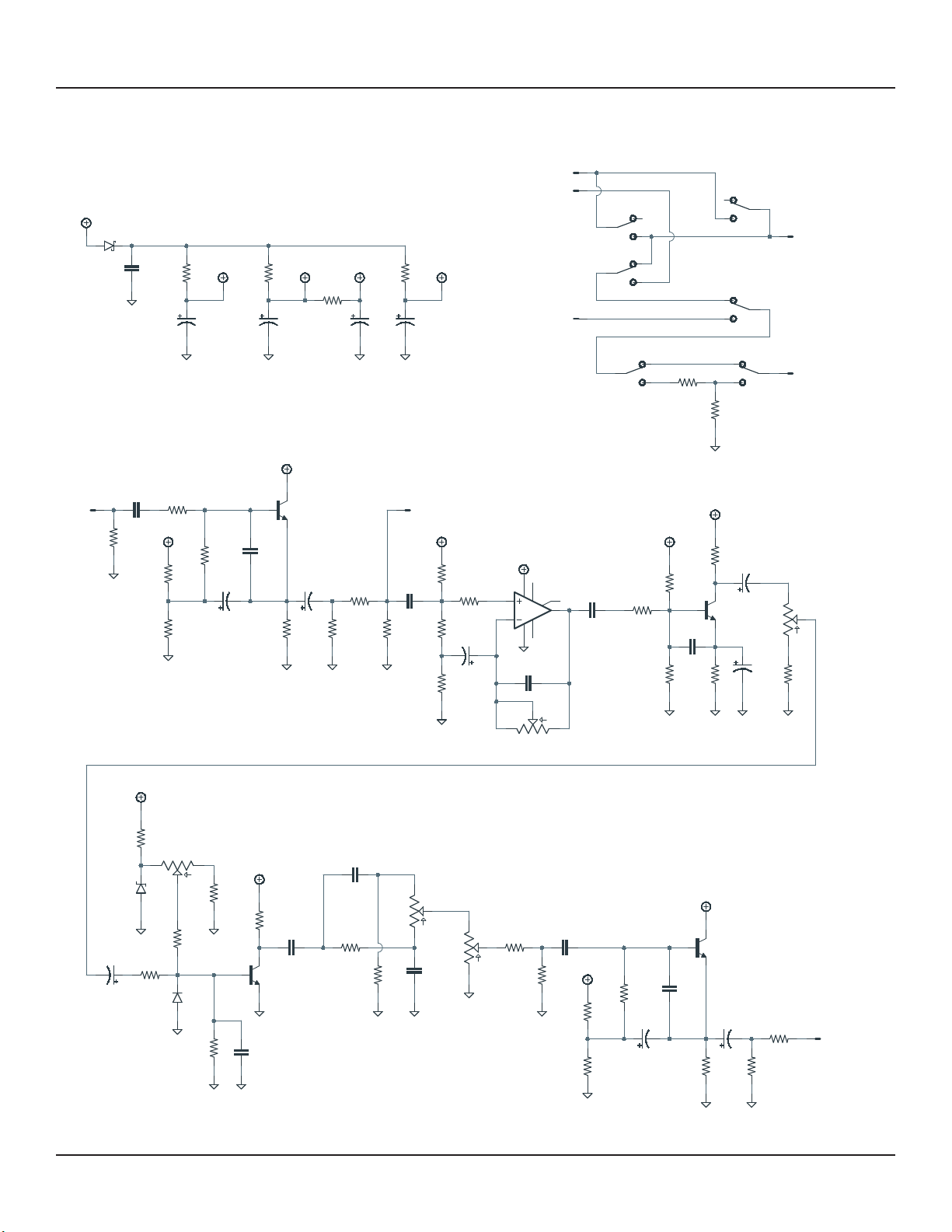
NYSIAD SILICON FUZZ 5
PARTS LIST, CONT.
PART VALUE TYPE NOTES
R33 5k1 Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R34 10k Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R35 91R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R36 100R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R37 150R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R38 150R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R39 150R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R40 91R Metal film resistor, 1/4W
R41 51k Metal film resistor, 1/4W
LEDR 10k Metal film resistor, 1/4W LED current-limiting resistor. Adjust value to change LED brightness.
C1 100n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C2 4.7uF Electrolytic capacitor, 4mm
C3 1n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C4 22uF Electrolytic capacitor, 5mm
C5 100n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C6 4.7uF Electrolytic capacitor, 4mm
C7 100pF MLCC capacitor, NP0/C0G
C8 220n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C9 1n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C10 22uF Electrolytic capacitor, 5mm
C11 4.7uF Electrolytic capacitor, 4mm
C12 4.7uF Electrolytic capacitor, 4mm
C13 1n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C14 220n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C15 10n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C16 10n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C17 100n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C18 1n Film capacitor, 7.2 x 2.5mm
C19 4.7uF Electrolytic capacitor, 4mm
C20 22uF Electrolytic capacitor, 5mm
C21 220uF Electrolytic capacitor, 6.3mm Power supply filter capacitor.
C22 220uF Electrolytic capacitor, 6.3mm Power supply filter capacitor.
C23 220uF Electrolytic capacitor, 6.3mm Power supply filter capacitor.
C24 220uF Electrolytic capacitor, 6.3mm Power supply filter capacitor.
C25 100n MLCC capacitor, X7R Power supply filter capacitor.
D1 1N5817 Schottky diode, DO-41
D2 1N914 Fast-switching diode, DO-35