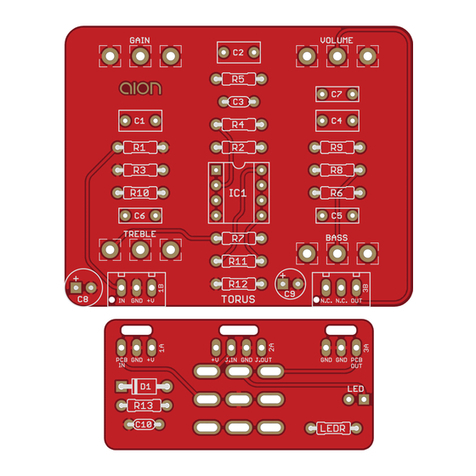
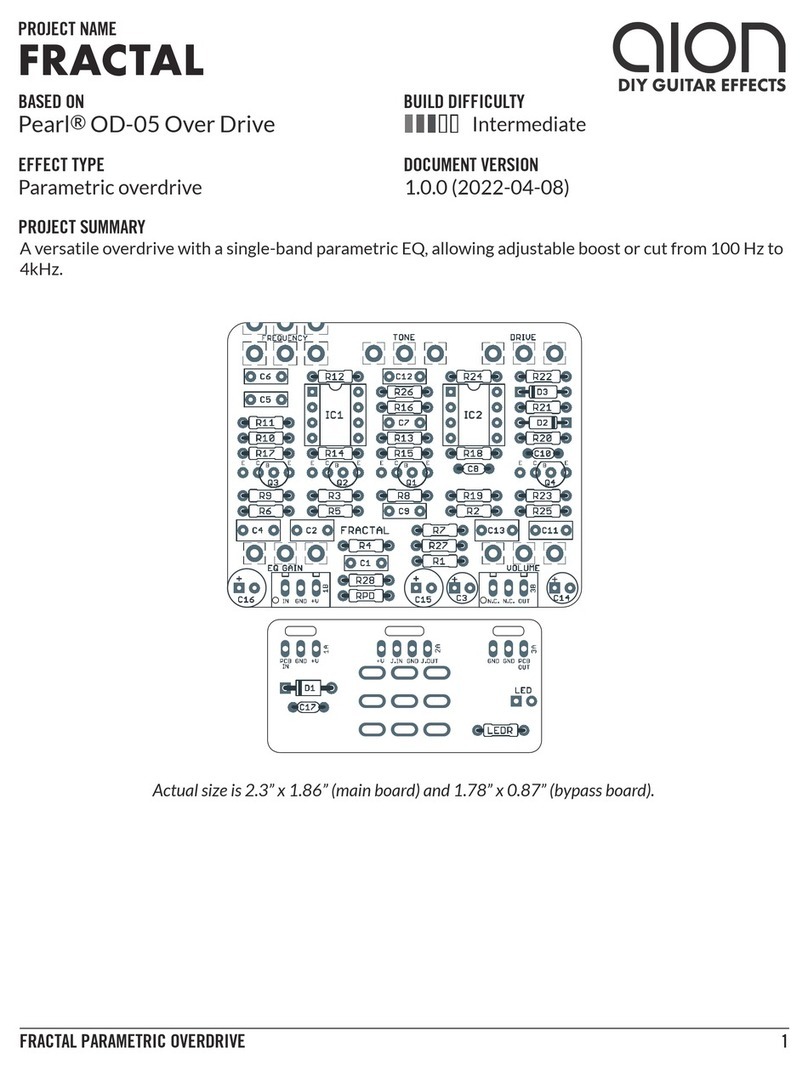
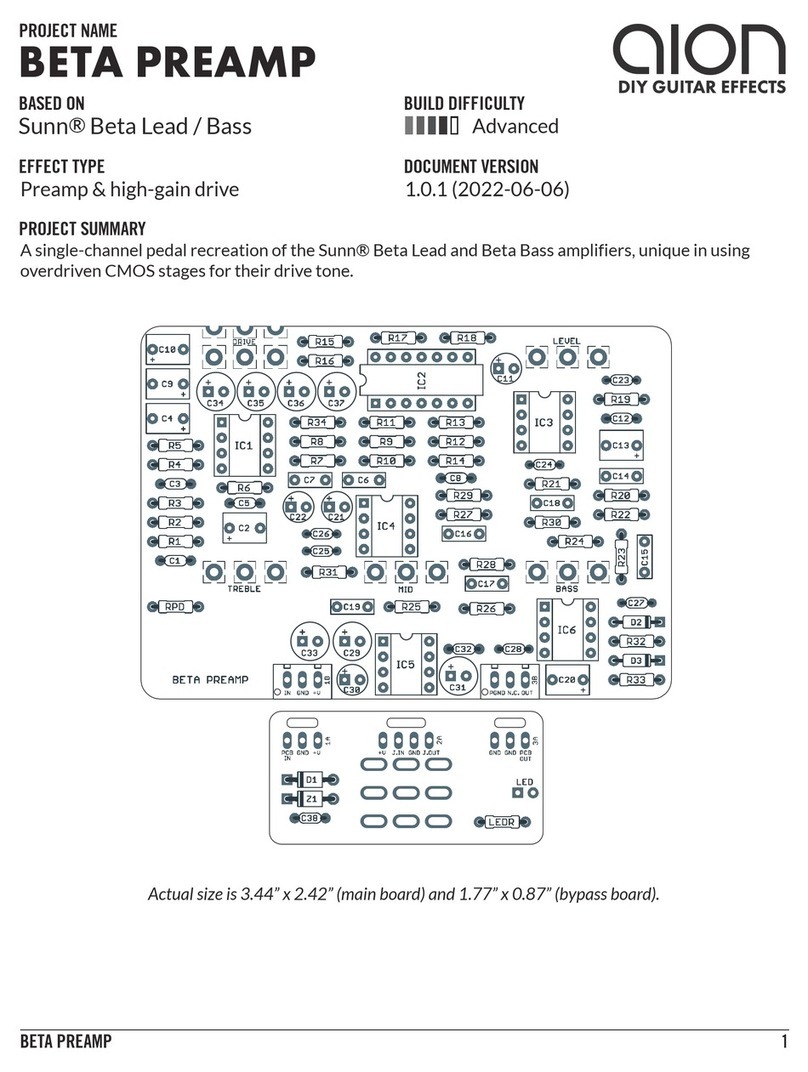
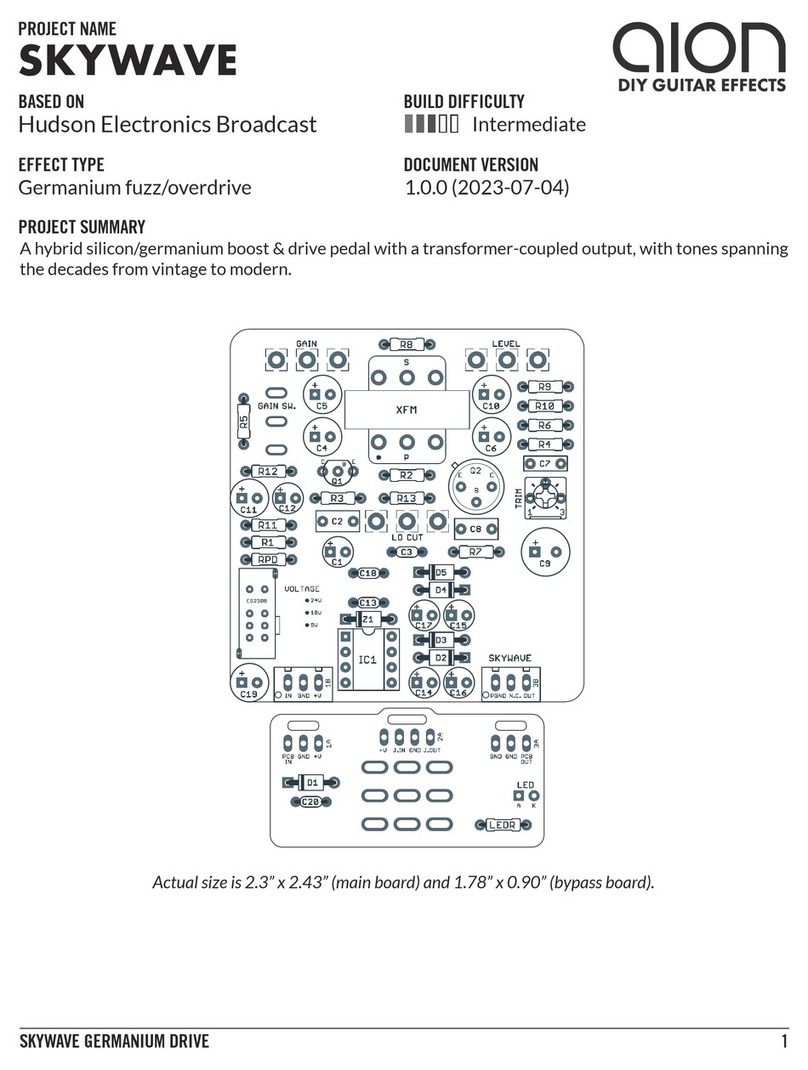
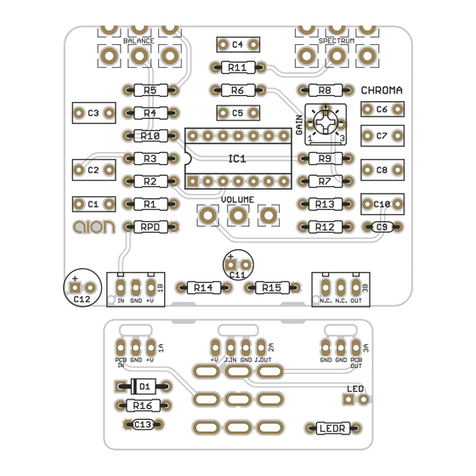
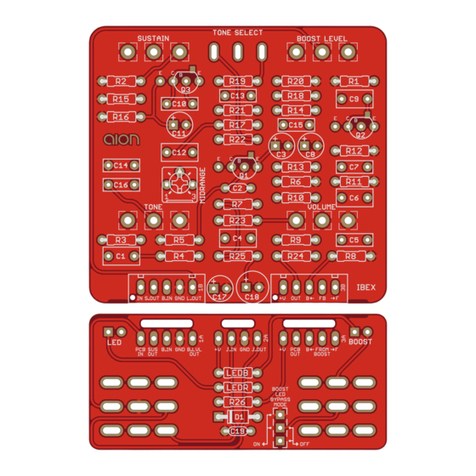
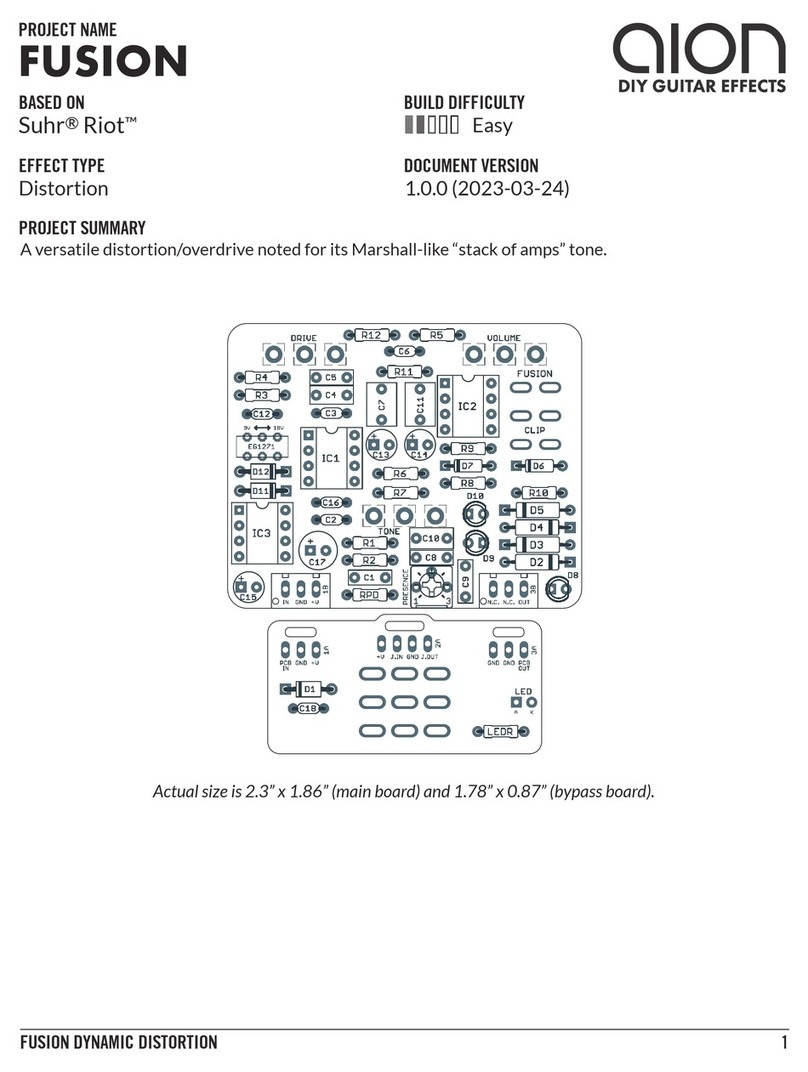
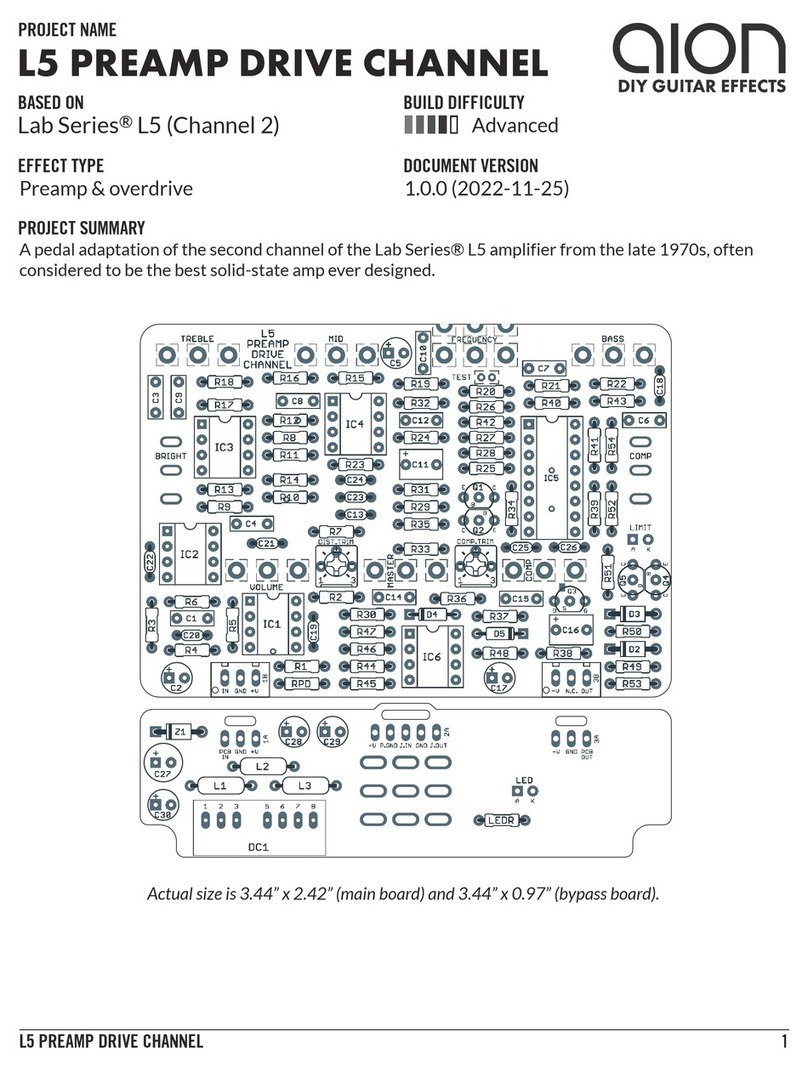
PHOBOS GERMANIUM FUZZ 3
INTRODUCTION
If this is your first pedal, welcome to the hobby and thank you for choosing Aion FX. You’ve just joined
a community of over 40,000 people around the world with a passion for building homemade noise
machines using obsolete electronics technologies, and we’re glad to have you!
If you’ve done this before, it’s great to see you again and we’re confident you’ll find this build experience
an enjoyable one.
Aion FX kits are designed to empower anyone to build a high-quality pedal, no matter the skill level.
The pedalbuilding hobby has traditionally had a steep learning curve, but don’t be overwhelmed—we’ve
done all the hard work for you. All you need to do is follow these instructions and you’ll be on your way
to transforming your tone.
There are a few things to go over before you get started.
• You’re going to have to get your hands dirty—there’s no way around it. Nothing here comes
preassembled, and you’ll have to learn the skills to put it all together. This document will walk you
through everything you need, but be prepared to learn a few things along the way.
• This will take time. Plan on about two hours start to finish. It may take even longer if it’s your first
time building. Don’t rush it. If you find yourself getting frustrated or overwhelmed, take a break
and come back in a couple of hours or the next day.
• No direct technical support is offered. There are several DIY forums and Facebook groups with
thousands of members who enjoy troubleshooting and teaching. But please be sensitive to the
fact that the staff at Aion FX is minimal, and every minute spent helping individuals in private is
time that can’t be spent on new project development.
• There is no implied guarantee of a final product. Aion FX provides the ingredients and the recipe,
but you are responsible for putting everything together to make it work. We’ve tried to make the
process as clear and accessible as possible, but it must be expressly stated that purchasing the kit
is not a guarantee that you will end up with a working pedal.
It’s recommended to read through all of the instructions before you start, particularly if you’ve never
built a pedal before. If you familiarize yourself with the entire process ahead of time and you know what
the goal looks like, each step will make more sense.
Now, on to the fun stuff!