2
Table of Contents
1. Radio Frequency Immunity (RFI) Scanning Outline ........................................................ 3
Configuration Diagram....................................................................................................................................... 3
Main Components of RFI Scanning ............................................................................................................... 3
Diagram of RFI measurement wiring........................................................................................................... 5
2. RFI Scanning Operation Procedures................................................................................... 5
Setup test environment ..................................................................................................................................... 5
Create a project..................................................................................................................................................... 5
Capture the DUT image...................................................................................................................................... 8
Define probe Z offset........................................................................................................................................... 8
Define a reference point to get DUT height and calibrate probe XY offset................................... 9
Define scan area and scan height.................................................................................................................11
Check instrument and SmartScan software connection ....................................................................11
Open “Instrument Settings” window and set parameters.................................................................12
Run measurement..............................................................................................................................................13
List of Figures
Figure 1: Block diagram of RFI scanning. ................................................................................. 3
Figure 2: Measurement setup diagram of RFI scanning. ......................................................... 5
Figure 3: Create a new workspace.............................................................................................. 6
Figure 4: Name the workspace and save in a directory. ........................................................... 6
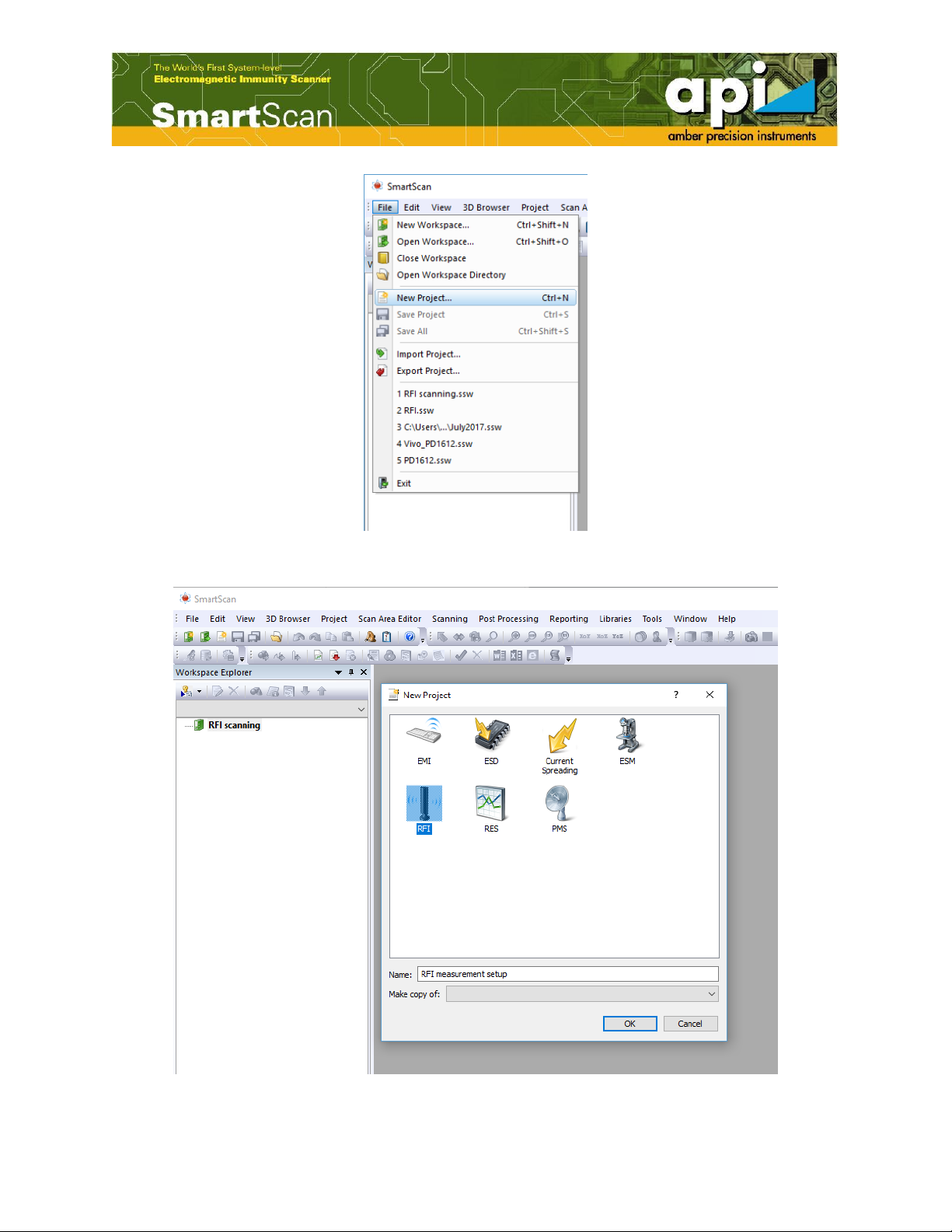
Figure 5: Create a new RFI project. ........................................................................................... 7
Figure 6: Name the RFI project. ................................................................................................. 7
Figure 7: Capture DUT image..................................................................................................... 8
Figure 8: Probe Z offset icon........................................................................................................ 8
Figure 9: Probe Z offset calibration window.............................................................................. 9
Figure 10: Reference point........................................................................................................... 9
Figure 11: Detect DUT height by touch sensor........................................................................ 10
Figure 12: Get DUT height manually........................................................................................ 10
Figure 13: Calibrate probe XY offset........................................................................................ 10
Figure 14: Probe XY offset calibration window....................................................................... 11
Figure 15: Open “Options” window.......................................................................................... 11
Figure 16: Signal generator communication setting window. ................................................ 12
Figure 17: Instrument settings................................................................................................... 12
Figure 18: Run measurement. ................................................................................................... 13