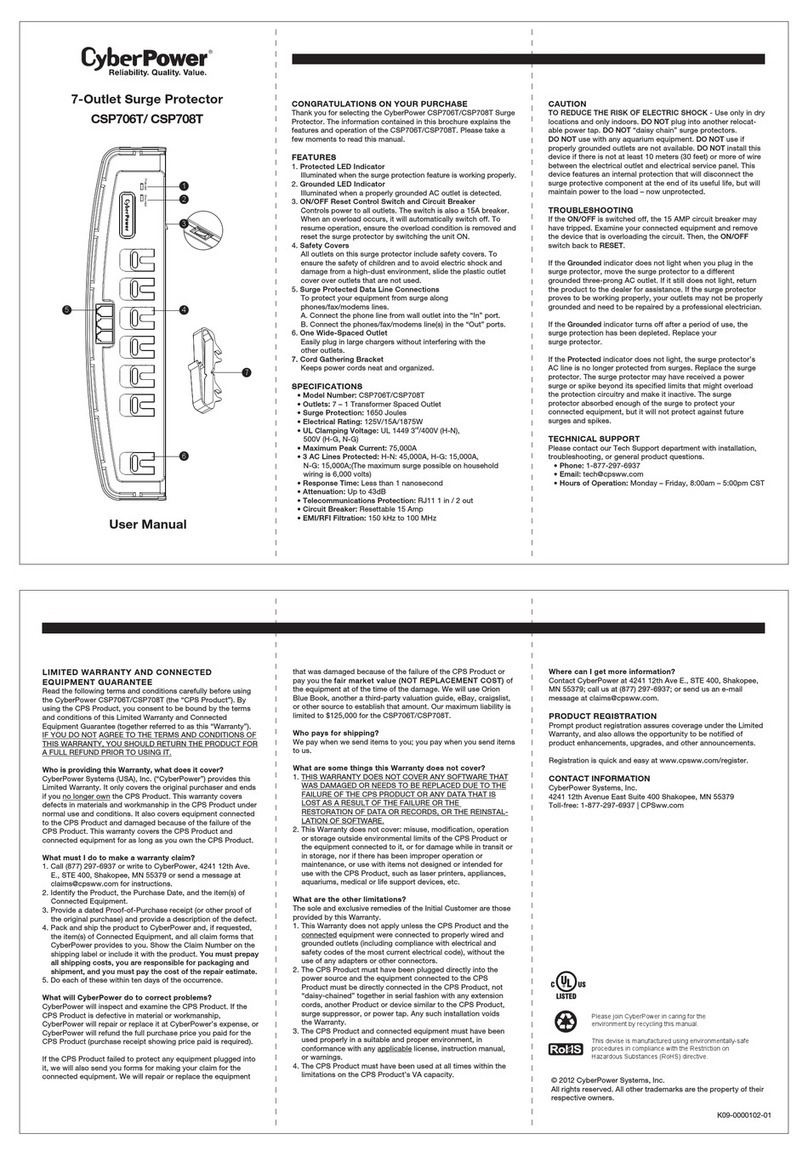
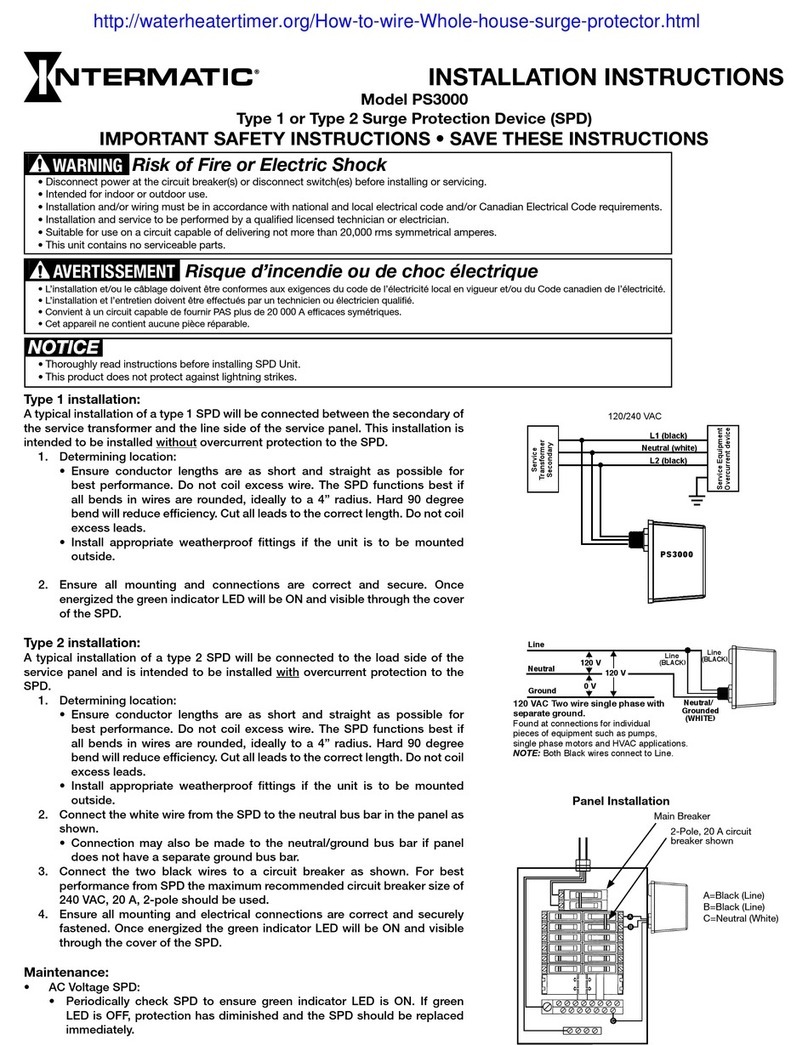
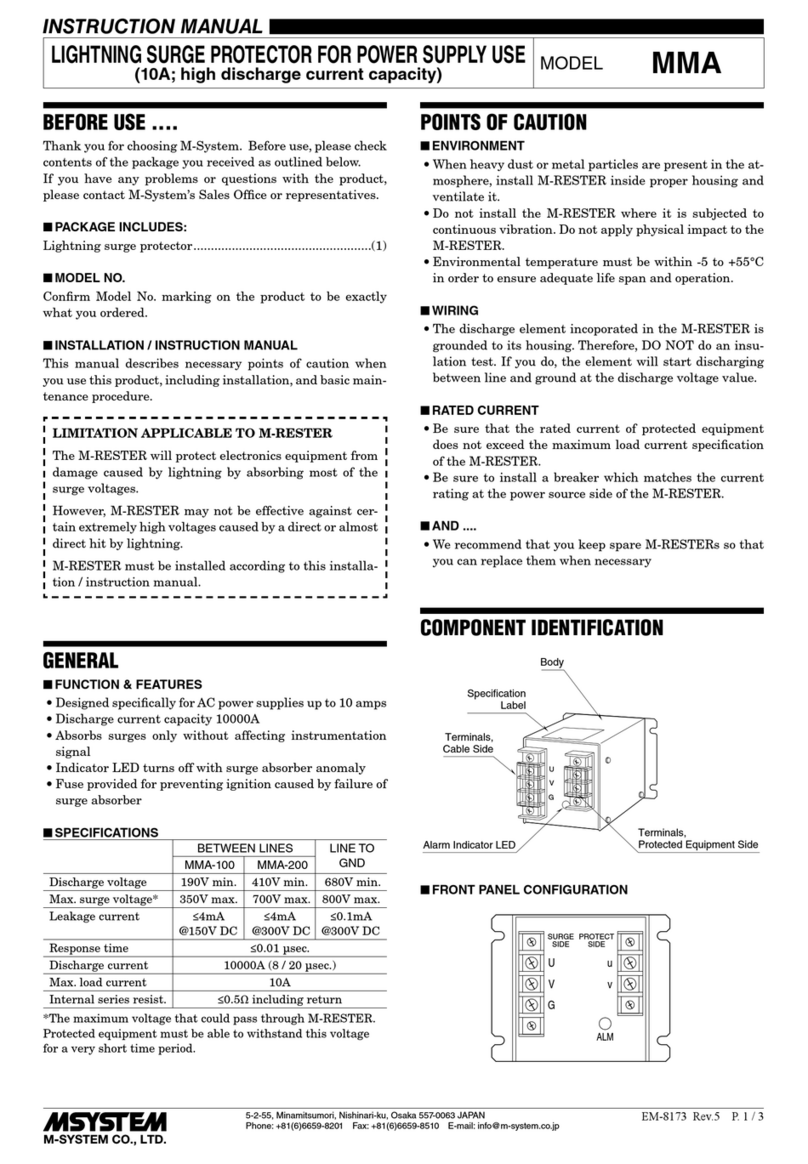
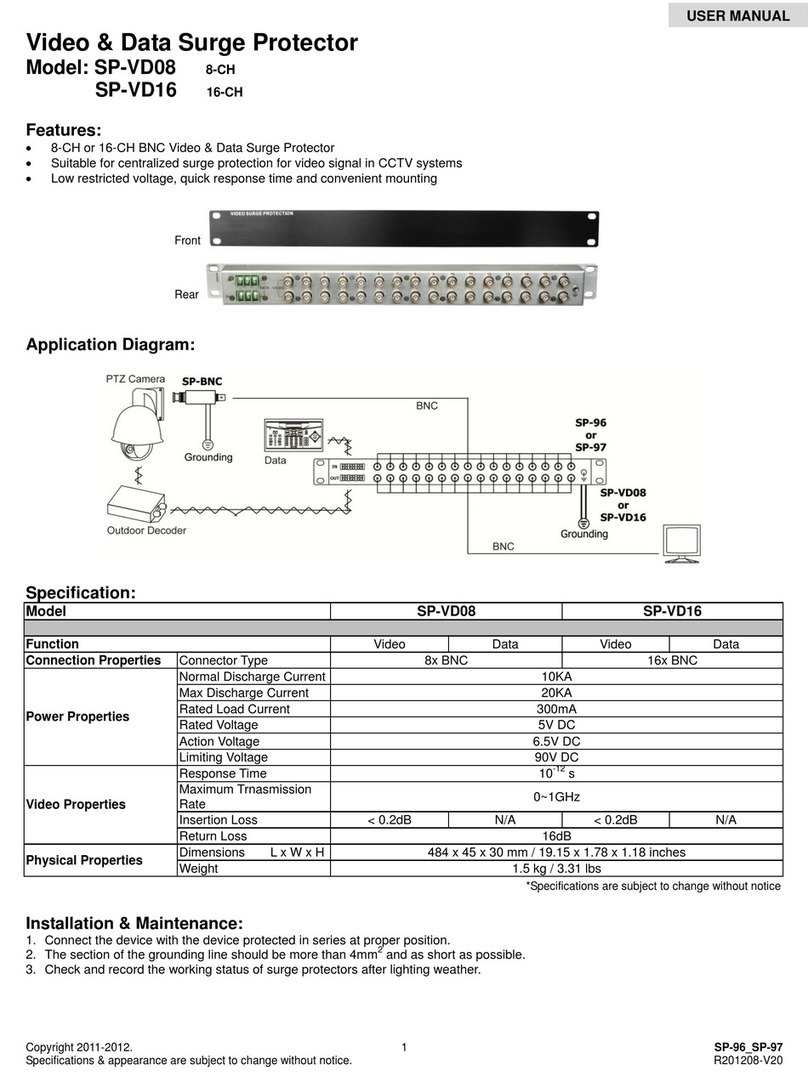
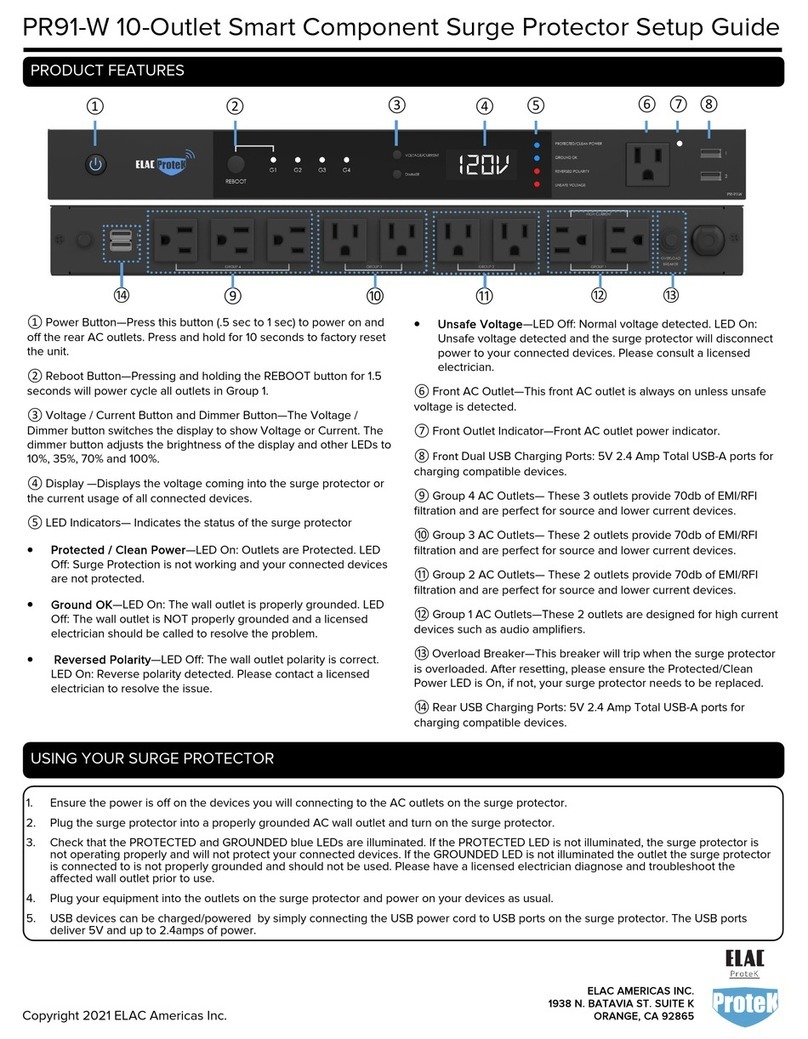
5
SPDs for ungrounded systems can be installed on grounded
systemswith a clamping performancepenalty. However,SPDs
for grounded systems installed on ungrounded systems are
almost certainly destined for premature failure. CallAPT Tech
Support at (800) 237-4567 for further information.
Circuit Breaker and Disconnect Switch
This HP and HPS SPDs are tested and qualified as
Type 2 SPDs per UL 1449 Third Edition and 2008 NEC
®
.
This SPD can be installed on the load side of the service
overcurrent device per 2008 NEC
®
Article 285.
Whenconnected onloadside ofmaindisconnect, wesuggest
connecting via a 60A circuit breaker. The circuit breaker is
the intended disconnect switch and provides short circuit
protection to the connecting conductors. The HP and HPS
Series have internal overload protection elements within
the product. A breaker or disconnect is not required for the
SPD’s overcurrent protection. HP and HPS SPDs have
demonstrated 200kAShort Circuit Current Ratings (SCCR).
Confer to label on unit.
Terminals
Terminals will accept 14 - 2 AWG conductor and are provided
for line (phase), neutral (if used), and equipment safety ground
connections. 8 AWG is the minimum recommended wire size
becauseULtestingandevaluation wasperformedusing 8AWG.
Wire Size and Installation Torque
Thisis a parallel-connected SPD; it isnotseries-connected.
The size of the SPD wiring is independent of the ampere
rating of the protected circuit. Recommended wire is 6
AWG for phase, neutral and ground connections. Torque
connections to 18 inch-pounds. Conductor length should
be as short as possible.
If other wire sizes are used, we recommend that all
conductors be the same gauge. Note that larger conductor
might appear to be benecial; however, it tends to have
the same inductance as smaller conductor and is more
difcult to work with.
Terminals accept 14 - 2 AWG conductor with 6 AWG being
preferred. Coordinate conductor size and overcurrent
protection per applicable codes.
System Grounding
An equipment grounding conductor must be used on
all electrical circuits connected to the SPD. For the best
performance, use a single point ground system where the
service entrance grounding electrode system is connected
to and bonded to all other available electrodes, building
steel, metal water pipes, driven rods, etc. (for reference
see: IEEE Std 142-2007).
For sensitive electronics and computer systems, we
recommend that the ground impedance measurement be
as low as possible. When metallic raceway is used as an
additional grounding conductor, an insulated grounding
conductor should be run inside the raceway and sized per
theNEC®.Adequate electricalcontinuitymust bemaintained
at all raceway connections. Do not use isolating bushings
to interrupt a metallic raceway run.
A separate isolated ground for the SPD is NOT
recommended.Properequipmentconnectionsto grounding
system and ground grid continuity should be veried via
inspections and testing on a regular basis as part of a
comprehensive electrical maintenance program.
On4-Wire Power Systems,neutraltoground bonding (Main
Bonding Jumper) must be installed per the NEC®. Failure
to do so WILL damage SPDs.
Internal Mounting of XR and XW Component SPD
XTE versions of the HP and HPS families are essentially
TE/HPSswithout enclosures. XTE/HPs and XTE/HPSs are
intended for installation within host electrical equipment
having suitable enclosures.
The experienced integrator will appreciate the simplicity
of XTE/HP and XTE/HPS. XTE/HP and XTE/HPS are
Type 4 SPDs that have been evaluated by UL for use as
Type 2 SPDs when installed in appropriate enclosures.
All UL required safety testing is complete without needing
additional safety apparatus. Contact factory for UL le
Engineering Considerations. Mount SPD in appropriate
enclosure,mount Diagnostic Display in appropriatelocation
andfollow appropriate instructions includingshortleads.UL
evaluation within your completed product should be easy
and trouble free. Do not Hi-Pot test with SPD in circuit.
In many instances, a disconnecting means is appropriate
for future service. A breaker serves this function, as well
as provides overcurrent protection to the connecting
conductors. If a breaker is not used, consider a disconnect
or safety switch having appropriate SCCR rating including
any required overcurrent protection. Please contact APT
Technical Support as appropriate.
Mounting Diagnostic Display: Mount Display in a user
friendly location, with considerations to weather and
vandalism. Dimensions are in Table 2. A Display with a
6’ connector cable is typically included. Longer lengths
are available. The Display features a UL 94-5VA and UL
746C(f1) polymeric label.A gasket is included.This same
display & gasket are used in the TE/HP and TE/HPS
series and UL has Listed them with an enclosure rating
of Type 1/12/3R/4.
UL 1283 required language concerning the installation
of EMI Filters
a) An insulated grounding conductor that is identical in size
and insulation material and thickness to the grounded and
ungroundedcircuit supply conductors,exceptthatit is green
with or without one or more yellow stripes, is to be installed
as part of the circuit that supplies the lter. Reference should
be made to Table 250-122 of the National Electrical Code
regarding the appropriate size of the grounding conductor.
b) The grounding conductor mentioned in item “a” is to
be grounded to earth at the service equipment or other
acceptablebuilding earth ground suchasthebuildingframe
in the case of a high-rise steel-frame structure.
c) Any attachment-plug receptacles in the vicinity of the
lter are to be of a grounding type, and the grounding
conductors serving these receptacles are to be connected
toearth ground attheservice equipment orotheracceptable
buildingearthground such as the building frame in thecase
of a high-rise steel-frame structure.
d) Pressure terminal or pressure splicing connectors and
soldering lugs used in the installation of the lter shall be
identied as being suitable for the material of the conductors.
Conductors of dissimilar metals shall not be intermixed in a
terminalor splicingconnectorwherephysical contactoccurs
between dissimilar conductors unless the device is identied
for the purpose and conditions of use.