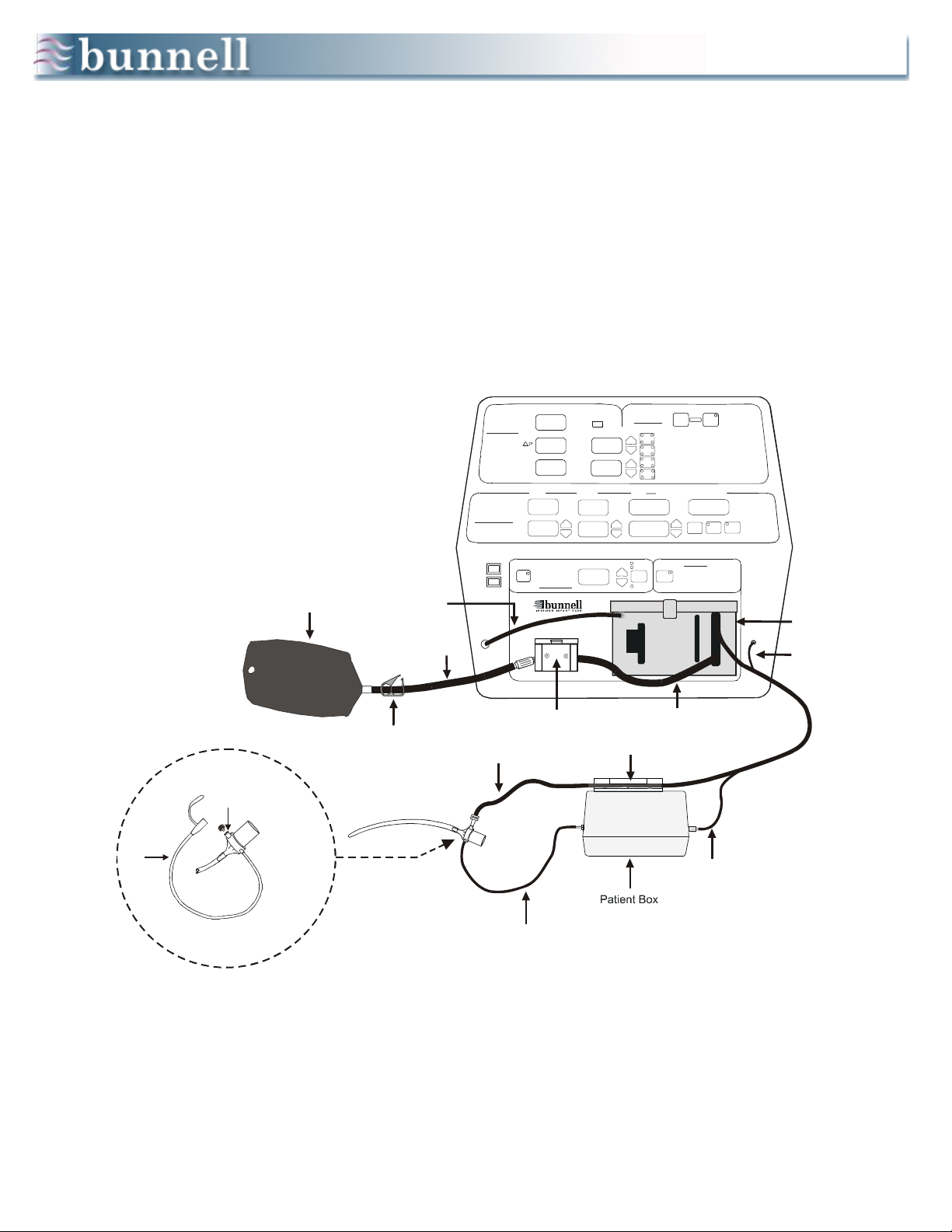
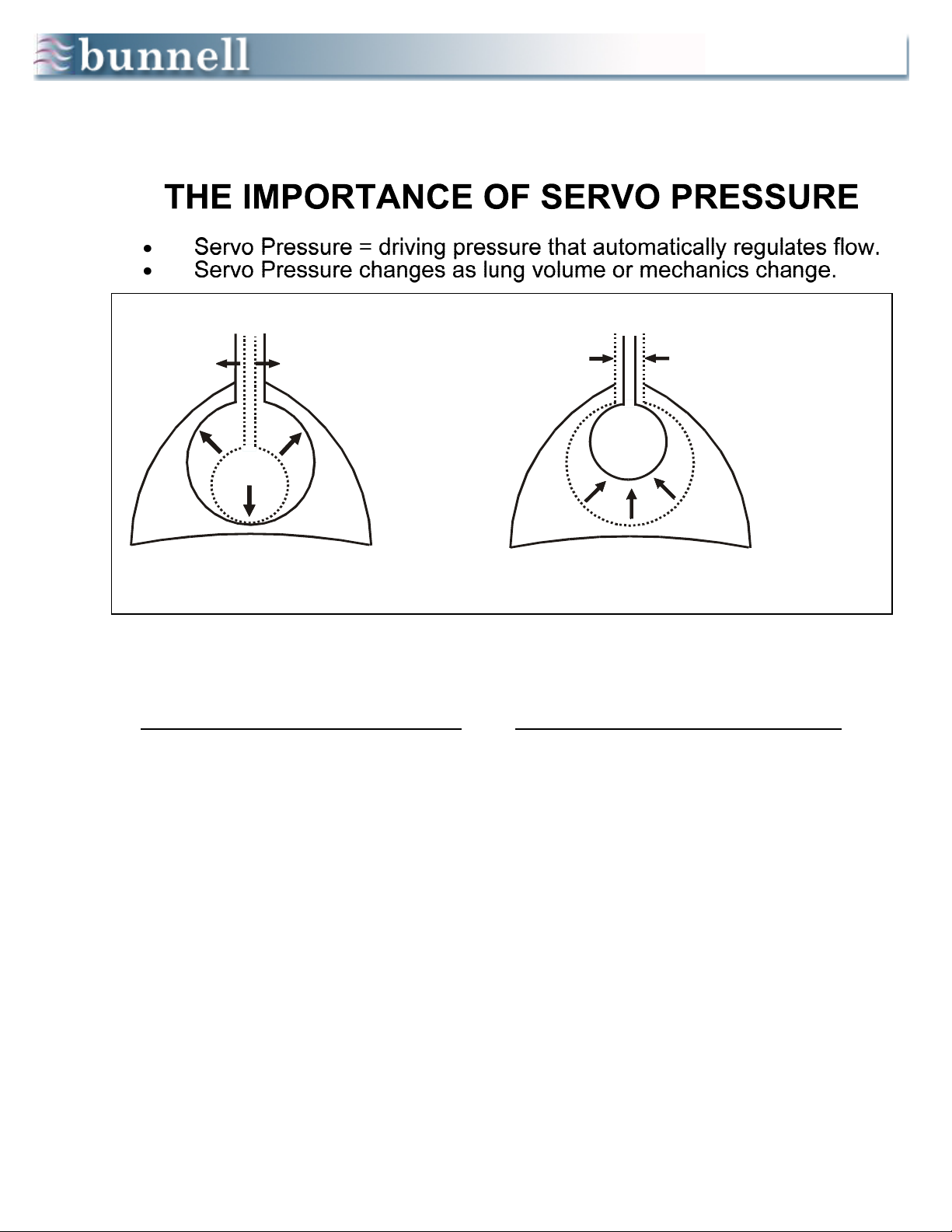
4
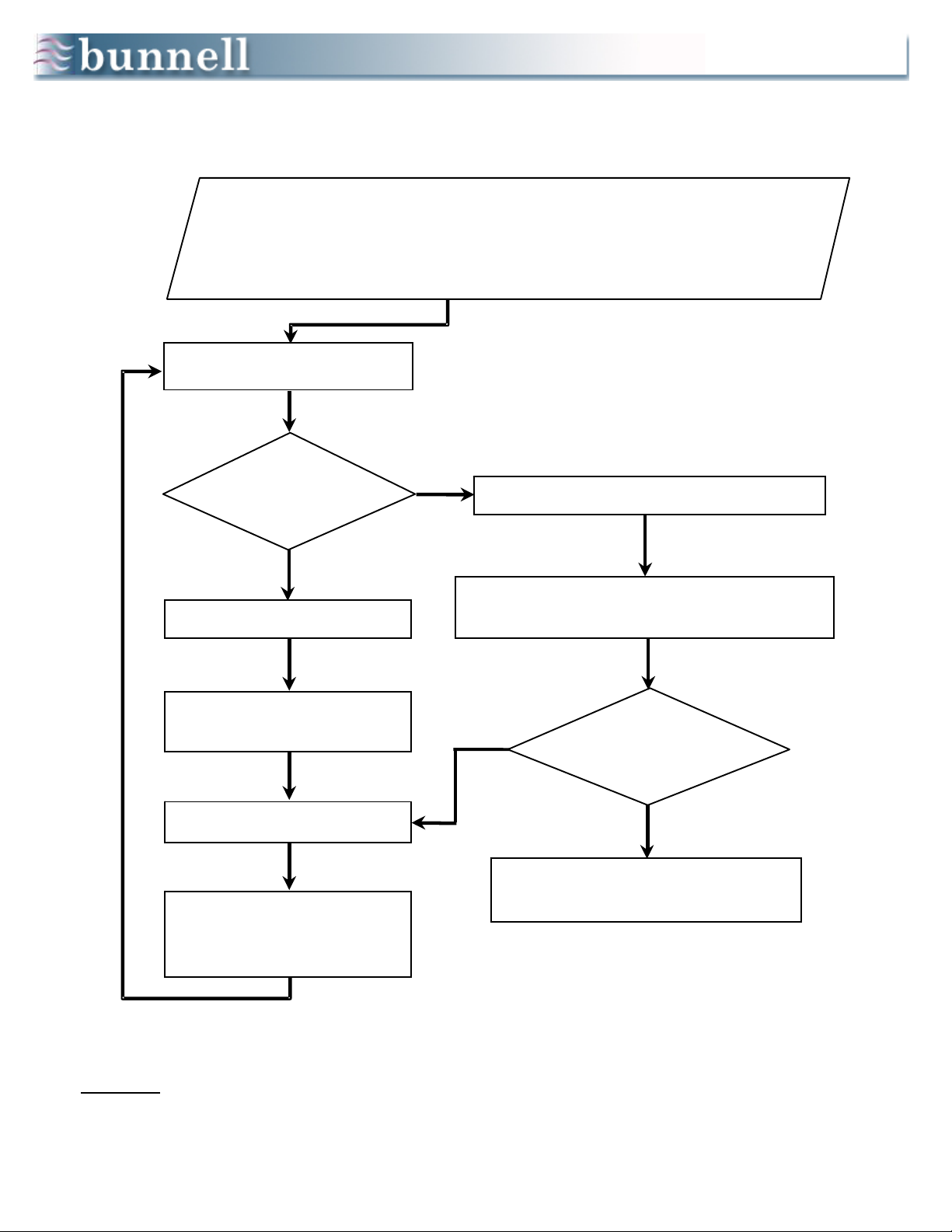
Patient Management During HFV
1. HFV ΔP (PIP - PEEP) is the primary determinant of PaCO2. HFV rate is secondary.
2. Resting lung volume (FRC supported by set PEEP) and mean airway pressure are crucial determinants of PO2.
3. Avoid hyperventilation and hypoxemia by using optimal PEEP. (See When to Raise PEEP below.)
4. Minimize IMV at all times, using very low rates (typically 0 – 3 bpm), unless IMV is being used to dilate airways or
temporarily to recruit collapsed alveoli. In general, keep IMV PIP 20 – 50% < HFV PIP.
5. To overcome atelectasis, IMV rates up to 10 bpm can be used for 10 – 30 minutes. Thereafter, IMV rate should be
dropped back to 0 – 3 bpm. In general, keep IMV I-time = 0.4 – 0.6 sec.
6. If lowering IMV rate worsens oxygenation, PEEP is probably too low. Higher PEEPs and lower IMV rates reduce the
risk of iatrogenic lung injury.
7. Lower FIO2 before PEEP when weaning until FIO2 is less than 0.53.
SETTING USUAL WHEN TO RAISE WHEN TO LOWER
HFV PIP
whatever
produces
desired
PCO2
To lower PCO2.
To raise PCO2.
(Raise PEEP simultaneously to keep MAP and
PO2 constant.)
HFV Rate
420 bpm
(neonates)
300 bpm
(peds)
To decrease PCO2 in smaller
patients; or
To increase MAP and PO2.
To eliminate inadvertent PEEP by lengthening
exhalation time or
To increase PCO2 when weaning.
HFV
I-Time 0.02 sec
To enable Jet to reach PIP at low
HFJV rates in larger patients ( >
15 kg).
Keep at the minimum of 0.02in almost all
cases.
IMV Rate 0 – 3 bpm
To reverse atelectasis or dilate
restricted airways
(5-10 bpm)
To minimize volutrauma, especially when air
leaks are present, or
To decrease hemodynamic compromise.
IMV PIP
PIP
necessary to
get adequate
chest rise
To reverse atelectasis or
dilate airways; PIP may be >
or < HFJV PIP.
To minimize volutrauma, especially when air
leaks are present, or
To decrease hemodynamic compromise.
IMV
I-Time 0.4 sec To reverse atelectasis or
dilate airways.
To minimize volutrauma, especially when air
leaks are present, or
To decrease hemodynamic compromise.
PEEP
7 – 12
cm H2O
(Neonates)
10 – 15
cm H2O
(Peds)
To improve oxygenation and
decrease hyperventilation.
To find optimal PEEP:
Raise PEEP until SaO2 stays
constant when switching from
IMV to CPAP.
Lower PEEP only:
–when it appears that cardiac output is being
compromised; or
–when oxygenation is adequate and
–when lowering PEEP doesn't decrease PaO2.
FIO2< 0.60 Raise as needed after optimizing
PEEP.
Lower FIO2 in preference to PEEP when
weaning until FIO2 < 0.3.
Special Air Leak Considerations
1. Minimize IMV by using HFV + adequate CPAP.
2. If oxygenation is compromised, raise PEEP, even if the lungs are overexpanded on xray.
(Rationale: you are going to have to raise something, and PEEP is less hazardous than IMV breaths.
It may also help interstitial gas find its way out of the lungs via more patent airways.)