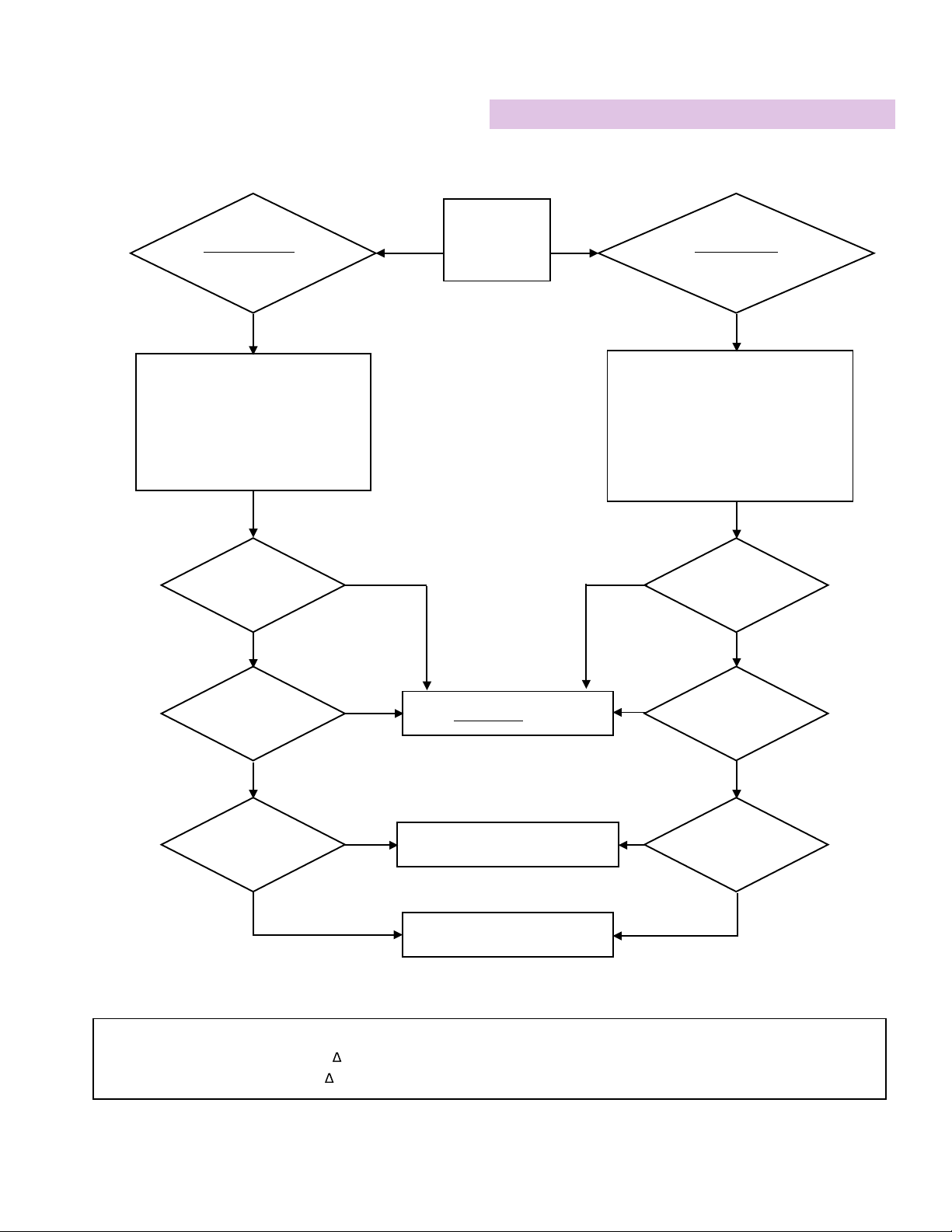
GENERAL RULES
• HFJV ΔP (PIP - PEEP) is the primary determinant of PaCO2. HFJV I-time and Rate are secondary.
• Resting lung volume (FRC supported by set PEEP) and mean airway pressure (MAP) are crucial determinants of PaO2.
• Avoid hypercarbia and hypoxemia by using optimal PEEP (see “When to Raise” PEEP below).
• Minimize IMV at all times, using very low rates (typically 0 – 5 bpm), unless IMV is being used to recruit lung volume or
stabilize FRC. In general, keep CV PIP at a level necessary to achieve a moderate chest rise.
• To overcome atelectasis, IMV rates up to 5 bpm can be used for 10 – 30 minutes. Thereafter, IMV rate should be dropped
back to as close to 0 as possible.
• If lowering CV rate worsens oxygenation, PEEP may be too low. Higher PEEPs and lower CV rates reduce risk of lung injury.
• Lower FiO2before PEEP when weaning until FiO2is less than 0.4.
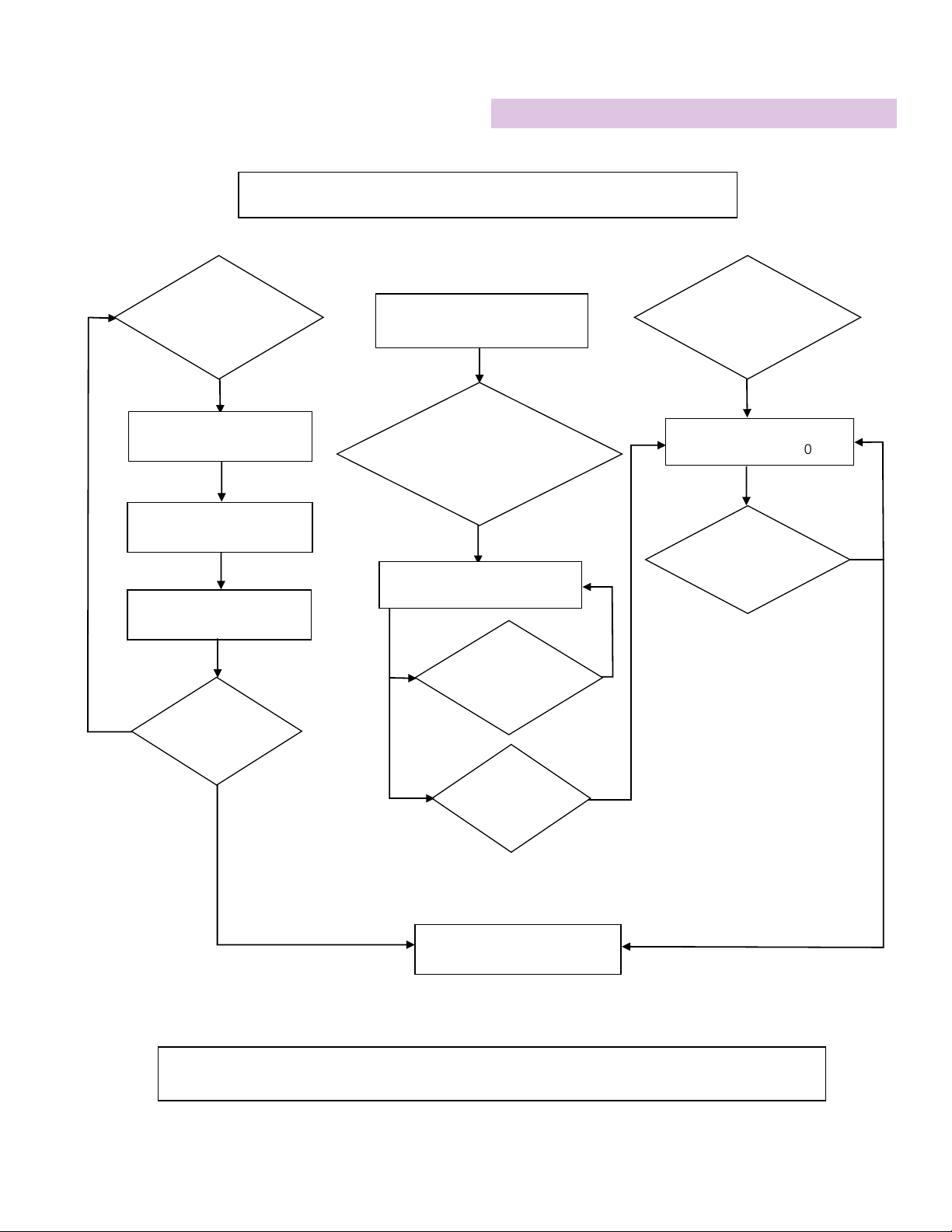
Patient Management During HFJV
SETTING INITIAL WHEN TO RAISE WHEN TO LOWER
HFJV PIP Whatever produces
desired PaCO2
To decrease PaCO2
To increase PaCO2 (Raise PEEP if nec-
essary to keep SpO2constant)
HFJV Rate 420 bpm (neonates)
300 bpm (peds)
To decrease PaCO2in smaller pa-
tients with low compliance
To eliminate inadvertent PEEP or
hyperinflation by lengthening exhala-
tion time or to increase PaCO2when
weaning
HFJV I-TIme 0.020 seconds To increase delivered tidal volume
and lower PaCO2
0.020 is the minimum
CV Rate 0 - 5 bpm To reverse atelectasis as a temporary
recruitment maneuver (3 – 5 bpm)
To minimize volutrauma, especially
when air leaks are present, or to de-
crease hemodynamic compromise
CV PIP
PIP necessary to
achieve moderate
chest rise
To reverse atelectasis or stabilize lung
volume; PIP typically < HFJV PIP
To minimize volutrauma, especially
when air leaks are present, or to de-
crease hemodynamic compromise
CV I-Time 0.4 seconds To reverse atelectasis or stabilize lung
volume
To minimize volutrauma, especially
when air leaks are present, or to de-
crease hemodynamic compromise
PEEP
7 – 12 cm H2O
(Neonates)
10 – 15 cm H2O
(Peds)
To improve oxygenation and de-
crease hyper-ventilation
To find optimal PEEP:
Raise PEEP until SpO2stays constant
when switching from IMV to CPAP
Lower PEEP only
• when it appears that cardiac out-
put is being compromised; or
• when oxygenation is adequate
• FiO2< 0.4, and
• when lowering PEEP doesn’t de-
crease PaO2
FiO2As needed Raise as needed after optimizing
PEEP
Lower FiO2in preference to PEEP when
weaning until FiO2< 0.4
Special Air Leak Considerations:
1. Minimize IMV by using HFJV and adequate CPAP.
2. If oxygenation is compromised AND expiratory time has been optimized, raise PEEP, even if the lungs appear to be over-
expanded on x-ray.
5