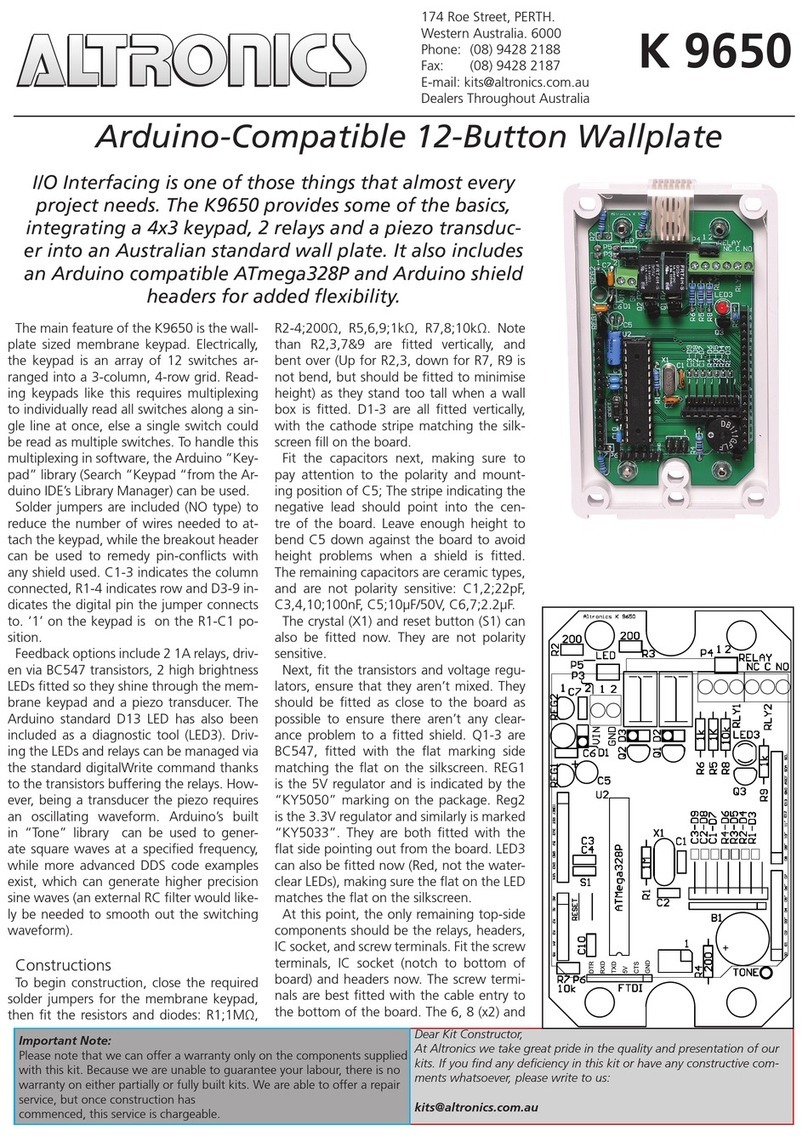
CR1000 Table of Contents
v
10. CRBASIC Programming Instructions .................10-1
10.1 Program Declarations....................................................................... 10-1
10.2 Data Table Declarations ................................................................... 10-3
10.2.1 Data Table Modifiers.............................................................. 10-3
10.2.2 On-Line Data Destinations ..................................................... 10-3
10.2.3 Data Storage Output Processing ............................................. 10-4
10.2.3.1 Single-Source................................................................ 10-4
10.2.3.2 Multiple-Source ............................................................ 10-5
10.2.4 Histograms..................................................................................... 10-6
10.3 Single Execution at Compile ............................................................ 10-6
10.4 Program Control Instructions ........................................................... 10-7
10.4.1 Common Controls................................................................... 10-7
10.4.2 Advanced Controls.................................................................. 10-9
10.5 Measurement Instructions .............................................................. 10-10
10.5.1 Diagnostics............................................................................ 10-10
10.5.2 Voltage.................................................................................. 10-11
10.5.3 Thermocouples...................................................................... 10-11
10.5.4 Bridge Measurements............................................................ 10-11
10.5.5 Excitation .............................................................................. 10-12
10.5.6 Pulse...................................................................................... 10-12
10.5.7 Digital I/O ............................................................................. 10-13
10.5.8 SDI-12................................................................................... 10-14
10.5.9 Specific Sensors .................................................................... 10-14
10.5.10 Peripheral Device Support .................................................. 10-15
10.6 Processing and Math Instructions................................................... 10-17
10.6.1 Mathematical Operators........................................................ 10-17
10.6.2 Logical Operators.................................................................. 10-19
10.6.3 Trigonometric Functions....................................................... 10-19
10.6.3.1 Derived Functions.............................................................. 10-19
10.6.3.2 Intrinsic Functions.................................................................... 10-20
10.6.4 Arithmetic Functions............................................................. 10-21
10.6.5 Integrated Processing ............................................................ 10-23
10.6.6 Spatial Processing ................................................................. 10-23
10.6.7 Other Functions..................................................................... 10-24
10.7 String Functions ............................................................................. 10-25
10.7.1 String Operations .................................................................. 10-25
10.7.2 String Commands.................................................................. 10-25
10.8 Clock Functions.............................................................................. 10-27
10.9 Voice Modem Instructions ............................................................. 10-28
10.10 Custom Keyboard and Display Menus......................................... 10-30
10.11 Serial Input / Output..................................................................... 10-31
10.12 Peer-to-Peer PakBus Communications......................................... 10-32
10.13 Variable Management .................................................................. 10-35
10.14 File Management.......................................................................... 10-35
10.15 Data Table Access and Management............................................ 10-37
10.16 Information Services .................................................................... 10-38
10.17 Modem Control ............................................................................ 10-40
10.18 SCADA ........................................................................................ 10-40
10.19 Calibration Functions ................................................................... 10-41
10.20 Satellite Systems Programming.................................................... 10-42
10.20.1 Argos................................................................................... 10-42
10.20.2 GOES .................................................................................. 10-42
10.20.3 OMNISAT .......................................................................... 10-43
10.20.4 INMARSAT-C.................................................................... 10-43