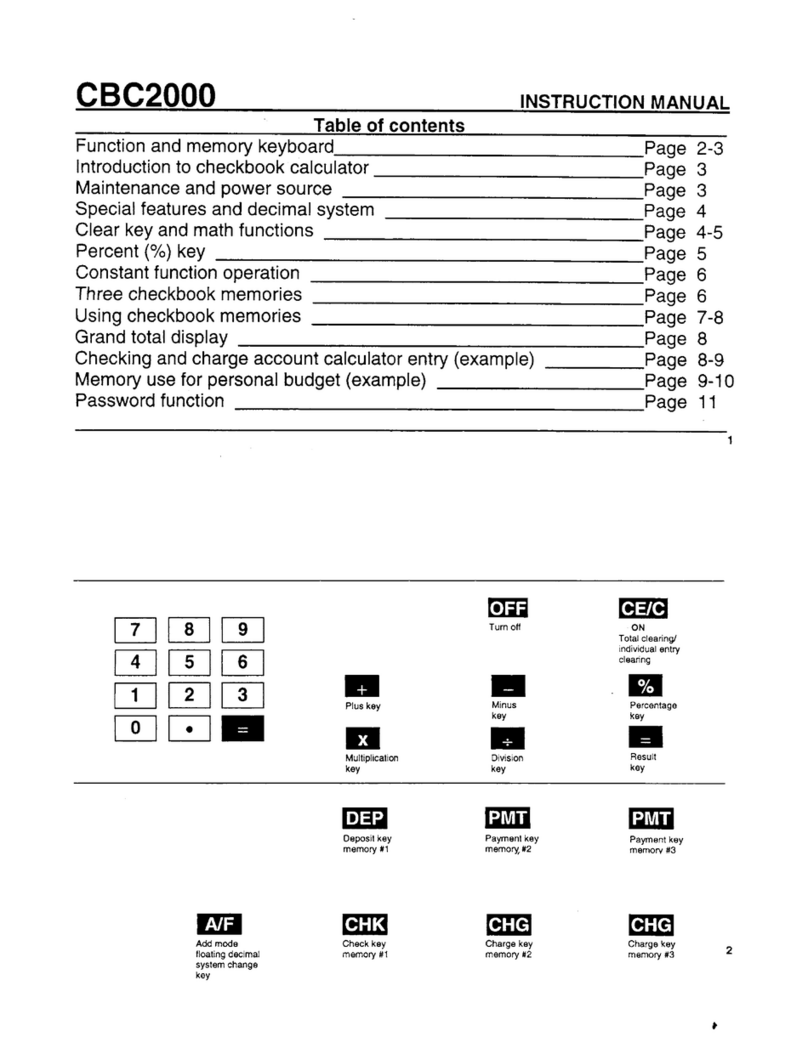
Sub-Total Recall Memory Key
This key is used to recall the memory
intermediately. The contents in the memory
are printed with Ssign, but the memory is
not cleared.
Accumulation Key
An automatic accumulation key used in
calculating sums and differences of pro-
ducts and quotients. This key locks when
depressed; to release, depress once more.
EB Non-Add Key
This key is used for printing figures
unrelated to the calculations, such as serial
numbers or dates. When entering figures
and depressing this key, the figures are
printed together with #sign. The next
calculation can be performed without the
(clear) key just after the unrelated
figures are printed.
Clear Key
When this key is depressed, all the registers
except the memory register are cleared,
and Csign is printed.
Clear Entry Key
This key is used for clearing entries as in
the following cases;
(1) When wrong numerals are entered by
mistake.
(2) When adouble entry occurs.
(3) When numerals entered overflow.
If this key is depressed after afunction key
(i.e. 5) J(&), the calculating
registers are cleared and Csign is printed.
‘CS’ Memory Lamp
This lamp lights when figures are entered
in the memory, and indicates that the
memory concerned is in use.
ODigit Indicators
These show how many digits have been
entered. If an overflow condition or a
double entry occurs, all the digit indicators
flash continuously.
Decimal Point Selector
Preselects the decimal point in the results
or the entries except multipliers and
divisors. It specifies the decimal point at
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6decimal digits. When the
key is locked, the decimal point of the
divisors in divisions is fixed to the pre-
selected decimal digit.
~~ Round-Off Switch
Gives automatic round-off (5/4) or drop-
off (3).
[ERE Power Switch
Power flows when this is turned ON, and
all circuits are automatically cleared for
immediate use.
EmiPaper Feed Lever
Press this lever for continuous printing
paper feed.