Contents
ENGLISH
About Using the Manual
• This basic manual briefly introduce X Mark I Pro functions, specification
and usage precautions.
• To familiar with X Mark I Pro, you can read the Calculation Examples
for a series of examples, operation procedure’s; and the calculation
range of major functions.
Statistical Calculations
Statistical Type Selection......................................................P.16
Statistical Data Input.............................................................P.16
Editing Statistical Sample Data.............................................P.16
Statistical Calculation Screen ...............................................P.17
Statistical Menu ....................................................................P.17
Statistical Calculation Example.............................................P.18
Distribution Calculations .......................................................P.18
Advanced Scientific Calculations
Equation Calculations ..................................................... P.19-20
Solve Function ......................................................................P.20
CALC Function .....................................................................P.20
Differential Calculations ........................................................P.21
Integration Calculations ........................................................P.21
Matrix Calculations ...............................................................P.22
Vector Calculations...............................................................P.23
Inequality Calculations .........................................................P.24
Ratio Calculation ..................................................................P.25
Function (x, y) Table Calculation ..............................................P.25
Battery Replacement...................................................................P.26
Advice and Precautions .............................................................P.26
Specifications .............................................................................P.26
1
Getting Started
Power On, Off......................................................................... P.2
Display Contrast Adjustment ................................................. P.2
Mode Selection....................................................................... P.3
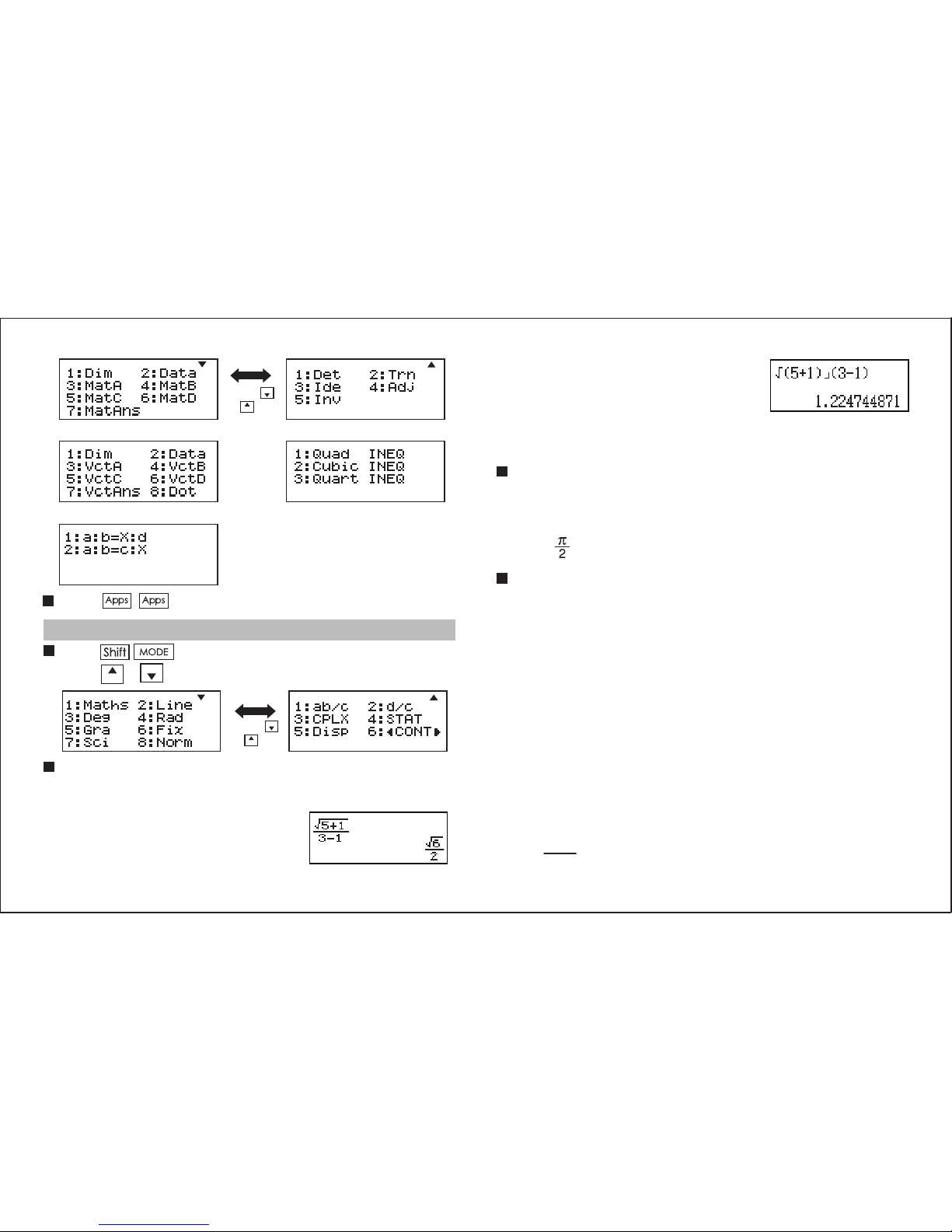
Application Function Menu ..................................................... P.3
Calculator Set-up Menu.......................................................... P.4
Before Using the Calculator.................................................... P.5
Inputting Expressions and Values
Input Capacity......................................................................... P.6
Input Editing ........................................................................... P.6
Inputting and Display Result in Mathematics Mode ................. P.6
Input Range and Error Messages .............................................. P.7
Order of Operations................................................................ P.7
Calculation Stacks .................................................................. P.7
Error Messages and Error Locator ......................................... P.7
Basic Calculations
Arithmetic Calculations ........................................................... P.8
Memory Calculations .............................................................. P.9
Fraction Calculations .............................................................. P.9
Percentage Calculations....................................................... P.10
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Calculations ................................ P.10
Replay & Multi-statements.................................................... P.10
Constant Value Calculations ................................................ P.11
Metric Conversions............................................................... P.11
Functional Scientific Calculations
Square, Root, Cube, Cube Root, Power, Power Root,
Reciprocal and Pi ................................................................. P.11
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm, Antilogarithm and Logab ....... P.12
Angle Unit Conversion.......................................................... P.12
Trigonometry Calculations.................................................... P.12
Permutation, Combination, Factorials and Random
Number Generation .............................................................. P.12
Least Common Multiple and Greatest Common Divisor ...... P.13
Prime Fractorization ............................................................. P.13
Quotient and Remainder Calculations.................................. P.13
Coordinate Conversion......................................................... P.14
Absolute Value Calculation................................................... P.14
Engineering Notation ............................................................ P.14
Display Values Exchange..................................................... P.14
Complex Number Calculations ............................................. P.14
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations...................... P.15