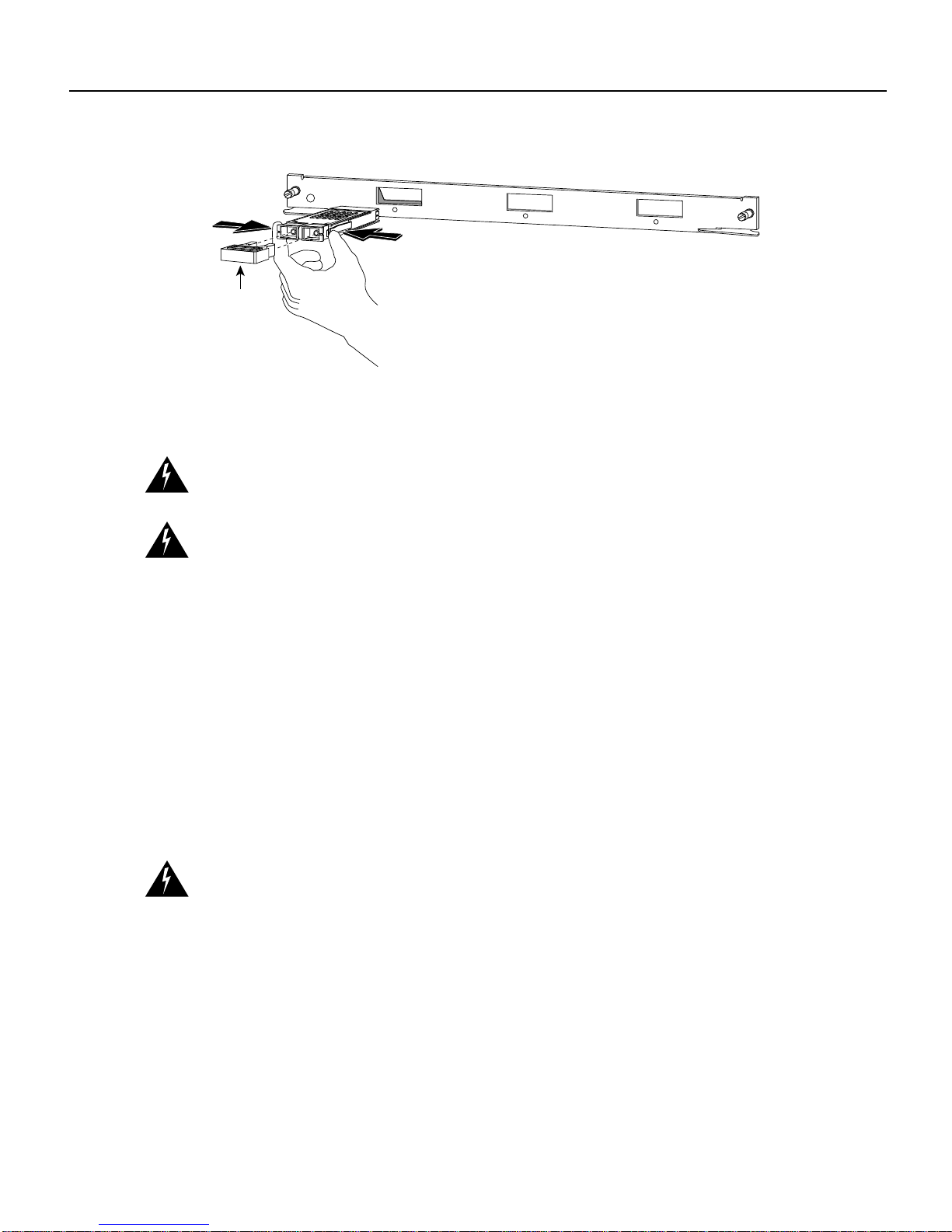
Gigabit Interface Converter Installation Note 9
Documentation CD-ROM
Documentation CD-ROM
Ciscodocumentationand additional literature are available in a CD-ROMpackage,whichshipswith
your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated
monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies
of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service.
The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription. You can also
access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com,
http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments
electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the
form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the Catalyst 4000, 5000, or 6000 Family Installation Guide.
Access Registrar, AccessPath, Any to Any, AtmDirector, CCDA, CCDE, CCDP, the CCIE logo, CCNA, CCNP, CD-PAC, Centri, the Cisco Capital logo, CiscoLink, the Cisco Management
Connection logo, the Cisco NetWorks logo, the Cisco Powered Network logo, the Cisco Press logo, the Cisco Technologies logo, ClickStart, ControlStream, DAGAZ, Fast Step, FireRunner,
IGX, IOS, JumpStart, Kernel Proxy, LoopRunner, MGX, Natural Network Viewer, NetRanger, NetRanger Director, NetRanger Sensor, NetSonar, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Point
and Click Internetworking, Policy Builder, Precept, RouteStream, Secure Script, SMARTnet, SpeedRunner, Stratm, StreamView, The Cell, TrafficDirector, TransPath, ViewRunner,
VirtualStream, VlanDirector, Workgroup Director, and Workgroup Stack are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Empowering the Internet Generation, The
Internet Economy, and The New Internet Economy are service marks; and BPX, Catalyst, Cisco, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Systems, the Cisco Systems logo, Enterprise/Solver,
EtherChannel, FastHub, ForeSight, FragmentFree, IP/TV, IPX, LightStream, LightSwitch, MICA, Phase/IP, Registrar, StrataSphere, StrataView Plus, and SwitchProbe are registered
trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. in the U.S. and certain other countries. All other trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.(9902B)
Copyright © 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved. Printed in USA.