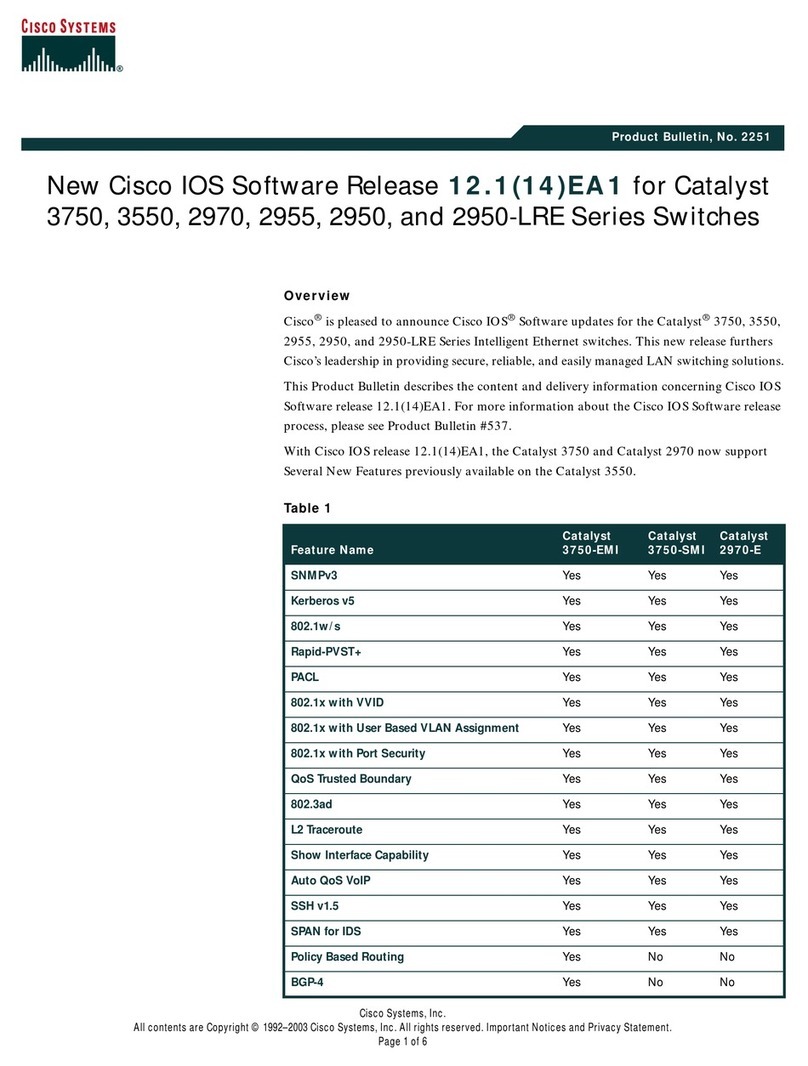
Data Sheet
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 22
Availability and Scalability
Superior Redundancy for
Fault Backup
●Cisco Uplink Fast and BackboneFast technologies help ensure quick failover recovery,
enhancing overall network stability and reliability.
●IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) provides rapid spanning-tree
convergence independent of spanning-tree timers and the benefit of distributed
processing.
●Per-VLAN Rapid Spanning Tree Plus (PVRST+) allows rapid spanning-tree
reconvergence on a per-VLAN spanning-tree basis, without requiring the implementation
of spanning-tree instances.
●Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is supported to create redundant, fail-safe
routing topologies.
●Command-switch redundancy enabled in Cisco Network Assistant software allows
designation of a backup command switch that takes over cluster-management functions
if the primary command switch fails.
●Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol (UDLD) and Aggressive UDLD allow
unidirectional links to be detected and disabled to avoid problems such as spanning-tree
loops.
●Switch port autorecovery (errdisable) automatically attempts to reenable a link that is
disabled because of a network error.
●Cisco RPS 2300 support provides superior internal power-source redundancy, resulting
in improved fault tolerance and network uptime.
●Equal cost routing (ECR) provides load balancing and redundancy.
●Bandwidth aggregation up to 8 Gbps through Cisco Gigabit EtherChannel technology
and up to 800 Mbps through Cisco Fast EtherChannel technology enhances fault
tolerance and offers higher-speed aggregated bandwidth between switches and to
routers and individual servers.
High-Performance IP Routing ●Cisco Express Forwarding hardware routing architecture delivers extremely high-
performance IP routing.
●Basic IP unicast routing protocols (static, RIPv1, RIPv2 and RIPng) are supported for
small-network routing applications.
●Advanced IP unicast routing protocols (OSPF, Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
[IGRP], EIGRP, Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 [BGPv4] and IS-ISv4) are supported
for load balancing and constructing scalable LANs. The IP Services license is required.
●IPv6 routing capability (OSPFv3, EIGRPv6) is support. IP Services license is required.
●Policy-Based Routing (PBR) allows superior control by enabling flow redirection
regardless of the routing protocol configured.
●Inter-VLAN IP routing provides for full Layer 3 routing between two or more VLANs.
●Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) for IP Multicast routing is supported, including PIM
sparse mode (PIM-SM), PIM dense mode (PIM-DM), and PIM sparse-dense mode. The
IP Services license is required.
●Fallback bridging forwards non-IP traffic between two or more VLANs.
Integrated Cisco IOS Software
Features for Bandwidth
Optimization
●Per-port broadcast, multicast, and unicast storm control prevents faulty end stations
from degrading overall systems performance.
●IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol support for redundant backbone connections and
loop-free networks simplifies network configuration and improves fault tolerance.
●PVST+ allows for Layer 2 load sharing on redundant links to efficiently use the extra
capacity inherent in a redundant design.
●IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) allows a spanning-tree instance
per VLAN, enabling Layer 2 load sharing on redundant links.
●ECR provides load balancing and redundancy.
●VPN routing/forwarding (VRF)-Lite enables a service provider to support two or more
VPNs, with overlapping IP addresses.
●Local Proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) works in conjunction with Private VLAN
Edge to minimize broadcasts and maximize available bandwidth.
●VLAN1 minimization allows VLAN1 to be disabled on anyindividual VLAN trunk link.
●VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) pruning limits bandwidth consumption on VTP trunks by
flooding broadcast traffic only on trunk links required to reach the destination devices.
●Internet Group Management Protocol v3 (IGMP) Snooping for IPv4 and IPv6 MLD v1
and v2 Snooping provide fast client joins and leaves of multicast streams and limits
bandwidth-intensive video traffic to only the requestors.
●IGMP filtering provides multicast authentication by filtering out nonsubscribers and limits
the number of concurrent multicast streams available per port.
●Multicast VLAN registration (MVR) continuously sends multicast streams in a multicast
VLAN while isolating the streams from subscriber VLANs for bandwidth and security
reasons.