CS-Lab CSMO IP-M User manual

4-axis CNC Ethernet controller
User guide
Applies to firmware version: v1.200
First edition
© Copyright 2012 – CS-Lab s.c.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 2
Index
1. General .................................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Signs used in this guide ................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Contents .......................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Standards compliance ..................................................................................................... 6
1.4 Specification .................................................................................................................... 6
2. Safety....................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Example of E-STOP signal connection ............................................................................. 8
3. Recommendation for mechanical installation ........................................................................ 9
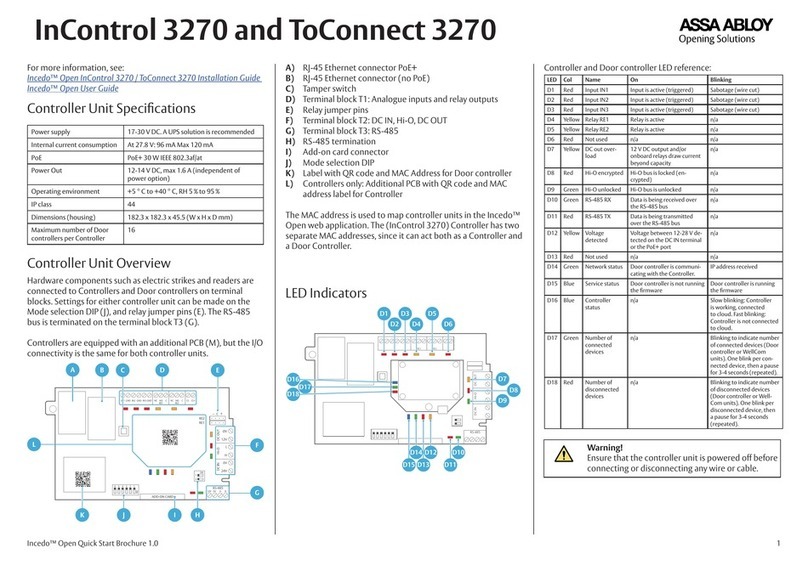
4. Connectors, controls and electrical installation of the device.............................................. 10
4.1 Arrangement of the connectors on the device ............................................................. 10
4.2 STEP/DIR controlling signals and digital outputs connector ......................................... 11
4.3 Digital inputs connector ................................................................................................ 13
4.4 Analog I/O connector .................................................................................................... 14
4.5 Expansion modules connector ...................................................................................... 14
4.6 Power connector ........................................................................................................... 15
4.7 Communication connector – Ethernet.......................................................................... 15
4.8 Recommended cables ................................................................................................... 16
4.9 Installation examples..................................................................................................... 17
4.9.1 The simplest connection of inverter with the use of analog output......................... 17
4.9.2 Illustrative diagram of XYZ plotter............................................................................. 18
4.9.3 Automatic control of drives power supply (HV)........................................................ 20
4.10 LED lights meaning ........................................................................................................ 21
5. Recommendations and drive selection (motor drives)......................................................... 22
6. Precise homing with use of the servo drive and the encoder INDEX signal.......................... 24
7. LAN connection and configuration........................................................................................ 26
7.1 PC direct connection ..................................................................................................... 26
7.2 Local network with router and DHCP............................................................................ 28
8. Mach3 program – general information................................................................................. 29
8.1 Recommended PC configuration................................................................................... 31
9. Software installation ............................................................................................................. 32
9.1 Mach3 installation......................................................................................................... 32
9.2 Microsoft® .Net installation (older operating systems) ................................................ 33
9.3 Installation of the plug-in for Mach3............................................................................. 33
9.4 Administrator rights in Windows® Vista and Windows® 7. .......................................... 34
10. Mach3 program configuration .......................................................................................... 35
10.1 Configuration profile ..................................................................................................... 35
10.2 The first run ................................................................................................................... 36
10.3 Configuration of axes used in the machine................................................................... 37
10.4 Configuration of the digital input signals ...................................................................... 38
10.5 Configuration of digital output signals .......................................................................... 40
10.6 Configuration of spindle and cooling controlling .......................................................... 42
10.7 Configuration of the resolution, speed and acceleration of the axes........................... 44
10.8 Configuration of motion directions, homing and software limits................................. 45
10.9 Additional configuration functions in the plug-in window............................................ 46

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 3
10.9.1 Servo drive fault signals......................................................................................... 46
10.9.2 Override sources tab, feed rate correction speed and spindle revs ..................... 47
10.9.3 Spindle tab, selection of analog output that controls the spindle revs ................ 47
10.9.4 Special functions tab, HVEnable and ServoReset.................................................. 48
10.10 Selection of inch/mm units ....................................................................................... 49
10.11 Parameters in the General Config window. .............................................................. 49
11. First tests ........................................................................................................................... 51
11.1 Checking the input signals............................................................................................. 51
11.2 Verification of axes scaling and motion directions ....................................................... 52
11.3 HOMING and software limit switches test.................................................................... 53
11.3.1 First homing........................................................................................................... 53
11.3.2 SoftLimit switches.................................................................................................. 53
11.4 Test of spindle and cooling............................................................................................ 54
12. Sample processing step by step ........................................................................................ 55
12.1 Preparation of project and G-Code files........................................................................ 55
12.2 Preparation of the machine and the Mach program .................................................... 59
12.3 We begin the work ........................................................................................................ 61
13. A few practical notes about Mach3 program and CSMIO/ IP-M....................................... 63
14. VisualBasic® macros ........................................................................................................... 65
14.1 Automatic tool-length measurement............................................................................ 65
14.1.1 Configuration......................................................................................................... 65
14.2 Automatic tool change macro ....................................................................................... 67
15. Addition A – CSMIO/IP-M software updates..................................................................... 68
15.1 How to check your software version............................................................................. 68
15.2 Updating application (uploader) ................................................................................... 68
15.3 Plugins file update ......................................................................................................... 69
15.4 Checking the update...................................................................................................... 69

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 4
1. General
CSMIO/IP-M product was designed for customers, who are looking for a compromise between
advanced CSMIO/IP-S controller and a simple LPT based device. The biggest advantage if the
CSMIO/IP-M controller is its reasonable price.
The main designing assumption was working stability – hence the PC connection via Ethernet (its
physical layer is galvanically isolated and protocols we use ensure reliable and fast transmission even
in tough industrial environment). Practically any others interfaces do not provide the continuity and
reliability of transmission on such a high level as the ETHERNET. That is why it is currently the
worldwide standard for high-speed digital communication
Another important assumption was simplicity of installation. CSMIO/IP-M does not require any
external electronics for proper operation. Inputs/outputs signals are inside optically isolated, filtered,
protected against short circuit, overheating etc. All signals are adjusted to
.
industry standard 24V. The
device is enclosed in a compact
CSMIO/IP-M product works with Mach3 program because of its low price, popularity and
enormous
cover, mounted on a DIN-rail, what makes that the mechanical and
electronic installation in the control cabinet takes less time and is even simpler.
ability to adapt to specific requirements. As a drives control interface the choice was a
popular step/direction (step / dir) standard. It allows controlling both the stepper motor drives and
the most modern servo drives. Max. frequency of stop signal is 125 kHz
so it is sufficient value for
many uses. What is important the controller is responsible for pulses generation, the same it ensures
that the signal is stable in the frequency domain and its fulfillment is 50%. This enables a greater
culture of machine work than it is while using LPT based controller.
1.1 Signs used in this guide
__________________________________________________________________________________
Potential danger, possible injury risk.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Useful information, tips.
__________________________________________________________________________________
Warning, failure to comply with these warnings may lead to inappropriate functioning or
damage of the device.
__________________________________________________________________________________

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 5
1.2 Contents
CSMIO/IP-M device is placed in the cartoon box with the DB->Terminal Block adapters1
•CNC CSMIO/IP-M Controller
for easier
wires connection in the control cabinet. More content details below:
•1xDB25 -> Terminal Block adapter
•1xDB25 + 1xDB9 -> Terminal Block adapter
•Ethernet connection wire
•2xDB25 connection tape
•1xDB9 connection tape
•1x„Phoenix” 3 pin power plug
•CD with electronic version of the user guide and
software
In case of lack of any elements listed above, please contact your distributor.
1CSMIO/IP-M can be bought without the DB->Terminal Block adapter.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 6
1.3 Standards compliance
CSMIO/IP-M controllers were designed and made in accordance with the national and international
standards
•Detailed requirements for programmable controllers: working
for industrial control systems based on electronic components:
characteristics, shock
resistance, safety
•
etc. EN61131-2 (IEC1131-2), CSA 22.2, UL508
Compliance with European Guidelines (low voltage, the level of electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic Compability),
•
the CE marking.
Electrical and non-combustible properties of insulation materials
•The Product
: UL 746C, UL 94, etc.
made in lead-free technology
, RoHS compliant.
1.4 Specification
Parameter
Value
Number of digital inputs 12
Number of digital outputs 4
Number of analog inputs
2
Number of analog outputs
2
Supply voltage
2
Power consumption
24VDC +/-10%
Maximum voltage on the in/out lines
5W
Maximum load of output line
30VDC
The voltage range of analog inputs
250mA
Maximal load of analog output 0-10VDC
Axis Drives control type 5mA
Maximum frequency of the STEP signal (STEP/DIR)
Fill factor of the STEP signal 125kHz
PC connection 50%
Ambient temperature range Ethernet 10/100Mb
Relative humidity 0
o
C to +60
o
C
Number of digital inputs 10% to 95%
(without condensation)
The STEP outputs signals frequency are in no way limited by the „Kernel speed” settings in Mach3
program. While using the CSMIO/IP-M controller this Mach’s configuration parameter is unused and
can be set on any value
.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 7
2. Safety
The CSMIO / IP-M device is powered by 24V safe voltage. I / O control lines are optically isolated, also
the PC connection is galvanically isolated. The device does not constitute a direct threat to the health
and life of the user.
Designing a complete control system (control cabinet), you should draw attention to several issues,
so that the entire system does not pose any hazard during use
.
Always use the NC contacts for limit switches and safety switch. Thanks to it - a wiring fault or i.e.
plug-ins disconnection will stop the machine
.
Pay special attention to the emergency stop circuit. The control system must be designed in such a
way that when you press the emergency stop mushroom, controlled machine stops immediately in
all axes. You should also take into account the possibility of failure of particular system components
such as the main controller, or axis drives
.
Best way is, to use for that purpose a standard safety relay (i.e. from PILZ Company). The safety
switch mushroom, FAULT signals of the drives and inverter and eventually other alarm signals – you
should connect to the input circuits. The output or outputs should be connected to the CSMIO/IP-M
controller, and defined as the emergency stop. Outputs of the security module should be also
connected to the axis drives, inverters, etc. This way we get double protection – if, by inappropriate
configuration or CSMIO/IP-M controller failure - the emergency would not work, the information
goes to the axis drives, which can properly respond to it. It works both sides: if the drives would not
react, you always have the controller
.
CSMIO-IP/M Controller in the active state on the input line - defined as E-Stop, blocks the STEP
signals within 0.000! s. It happens autonomously, without Mach3 program and thus the machine
stops very fast. The same happens with reaction
to signals from limit switches.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 8
2.1 Example of E-STOP signal connection
The simple example above shows the E-Stop signal connection to the CSMIO/IP-M controller and to
the axis drives, using Pilz company safety relay (PNOZ X7 24V symbol). S1 is a reset button (safety
relay switching on), S2 is an emergency stop
.
This module has one input, and due to it, all the alarm sources are connected to this input (A1). In
addition to the mentioned emergency stop (S2) there are NC contacts - NC1 and NC2, which may be,
i.e. opening sensors for the cover and the control cabinet. Moreover, there are drives’ FAULT signals
connected in series. Two outputs of the safety relay were used as an E-Stop signal for the CSMIO/IP-
M controller and axis drives
.
This combination assures the machine stops in case of failure on any axis (FAULT signals of the
drives), by pressing emergency stop mushroom and opening of the cabinet or cover. Separation of
the safety relay output channels gives double protection for the system and significantly increases
the reliability of the entire system.
PILZ
PNOZ X7 24 V

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 9
3. Recommendation for mechanical installation
CSMIO/IP-M controller and DB->Terminal block - connection modules were designed to be installed
on standard DIN-rail. It is the quickest and best way of installation.
The Controller uses a small amount of electricity and creates a negligible amount of heat.Aluminum
housing provides adequate cooling for the electronics inside, even if the ambient temperature
reaches 40OC.
As for the same controller, there are no special precautions for ventilation and the minimum
distances. However, usually, next to the controller in the control cabinet, there are also inverters,
power supplies, motor drives - these components emit a lot of heat, so you should always remember
about their proper location and proper ventilation of the cabinet
.
Here is an example - components arrangement in the control cabinet
.
Caution is advised during the mechanical and electrical installation. Poorly tightened cable may cause
many problems, it is also very difficult to find such a defect while launching/using the system.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 10
4. Connectors, controls and electrical installation of the device
4.1 Arrangement of the connectors on the device
Detailed description of signals on individual connectors is placed in next sections.
DB->Terminal block modules have the same pin numbers as DB connectors in CSMIO/IP-M device.
In example: 15 pin of DB25 connector match with the 15 pin on the terminal block.
Signals that control the drives (STEP/DIR)
and digital outputs (relays either)
Analo inputs and outputs (0-10V)
Expansion modules connector
Power connector
Digital inputs Communication
connector (ETHERNET)

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 11
4.2 STEP/DIR controlling signals and digital outputs connector
While connecting the STEP/DIR signals to the drive (both servo and stepper drives) pay attention
which STEP edge is active. The active edge in the CSMIO/IP-M is the growing edge – namely change
of the STEP+ signal from the logic “0” state (0V) to logic “1” (5V).
PIN number Description
1
DIR[0]+
2
STEP[0]+
3
DIR[1]+
4
STEP[1]+
5
DIR[2]+
6
STEP[2]+
7
DIR[3]+
8 STEP[3]+
9 24V power supply for 0..3 outputs
10 0 output
11 2 output
12 4 output (NO1 relays)
13 5 output (NO2 relays)
14 DIR[0]-
15 STEP[0]-
16
DIR[1]-
17
STEP[1]-
18
DIR[2]-
19
STEP[2]-
20
DIR[3]-
21
STEP[3]-
22
0V power supply for 0..3 outputs
23 1 output
24 3 output
25 Common PIN for relay outputs 4
and 5
The differential outputs, which are
available on this connector, have low
permissible load (50mA) and serves
only to control the LEDs in the
optically isolated inputs of motor
controller.
Pay special attention during
connection because STEP/DIR signals
are not protected against short
circut and voltage higher than 5V!
Digital
outputs have 250mA
permissible load. Pay attention - if
you connect large inductance you
may need to use an additional surge
led, preferably as close to the coil as
possible.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 12
During launching the machine it is worth to check if step signal is polarized properly. The easiest
way is to make the reference, next to ride on zero point and do the mark e.g. on the axis of motor or
on the cover. Now prepare and run a test g-code, it should consist of short rides for test axis. For X
axis it will look like below:
G0 X0
G1 X5 F4000
G1 X0
G1 X5
…
G1 X0
M30
These rides should be as much as making of the track would last at least 10 minutes. Next, you
should check if the marks line up on the motor shaft and the cover. If the marks do not match it may
mean improper polarization of the STEP signal. You should change the polarization in the Mach3
program (menu Config/Ports & Pins/Motor Outputs - select/deselect „STEP Low Active”) and run the
test again. Of course, you can also use appropriate measurement tools instead.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 13
4.3 Digital inputs connector
PIN number Description
1
0 (+) Input
2
1 (+) Input
3
2 (+) Input
4
3 (+) Input
5
4 (+) Input
6
5 (+) Input
7
6 (+) Input
8
7 (+) Input
9
8 (+) Input
10 9 (+) Input
11 10 (+) Input
12 11 (+) Input
13 GND
14 0 (-) Input
15
1 (-) Input
16
2 (-) Input
17
3 (-) Input
18
4 (-) Input
19
5 (-) Input
20
6 (-) Input
21
7 (-) Input
22 8 (-) Input
23 9 (-) Input
24 10 (-) Input
25 11 (-) Input
Pay special attention to not exceed
the permissible voltage (30VDC) on
the inputs lines. It may cause the
device damage.
The GND Signac is not used in this
case and it should not be connected.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 14
4.4 Analog I/O connector
4.5 Expansion modules connector
PIN number
Description
1
0 analog output
2 GND
3
1 analog input
4 -
5 10V (max. 50mA)
6 1 analog output
7 0 analog input
8 GND
9
-
PIN number
Description
1
CAN H
2
RS232 RxD
3
RS232 TxD
4
-
5
GND
6 CAN L
7 RS485 B-
8 RS485 A+
9 -
Pay special attention to not exceed the permissible voltage (10VDC) on the inputs
lines. It may cause the device damage.
10V output has 50mA load and serves only to supply the potentiometers, if you
want to connect the potentiometers, such as regulation of feed rate or spindle
speed correction.
Connector serves only for CS-Lab s.c. expansion modules. Do not plug it into any
other devices, PC, etc.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 15
4.6 Power connector
4.7 Communication connector – Ethernet
PIN number
Description
1
Power – 24V DC
2 GND
3
Ground
PIN number
Description
1
TX+
2
TX-
3
Rx+
4 -
5 -
6 RX-
7 -
8 -
View of the plug from the
side of connecting wires
Pay special attention to not exceed the permissible voltage (30VDC) on the inputs
lines. It may cause damage of the device.
If you use in the system such inductive loads as electromagnets, solenoids,
electromagnetic clutches – it’s recommended to use a separate 24V power supply
for the above receivers and separate for CSMIO / IP-M.
It’s recommended to use wire-screen FTP or STP cat.6.
The network interface has no Auto MDI-MDIX function. So, while connecting
CSMIO/IP-M directly to a computer we should use so-called crossover cable. If
you connect it to the network switch or router - use a non-crossover cable.
In the purchase set crossover cable is attached.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 16
4.8 Recommended cables
Connections type Recommended cable
Digital In/out
Minimum cross-section 0,25mm2
Analog In/out Cross-section 0,25mm
2
best - shielded or pair of signal-to-
mass weirs twisted together along the entire length
Drives controlling (STEP/DIR)
Cross-section 0,25mm2; shielded–twisted. You can possibly
use the FTP computer cable. Please note that pairs of signals
(e.g., STEP + / STEP-) you should always lead by twisted pair
of cables.
Ethernet Communication wire
Standard Power cable, shielded - FTP, cat. 6.
Power
Min. Cross-section 0,5mm2
CAN expansion modules If modules are mounted on the same DIN rail, next to the
controller you can use DB9 plugins clenched on the 9-wire
tape (if further – shielded twisted pair).
During mechanical and electrical montage – particular caution is adviced. Poorly tightened
cable may cause many troubles, it’s also very difficult to find such a defect while
launching/using the system.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 17
4.9 Installation examples
4.9.1 The simplest connection of inverter with the use of analog output.
This example above shows the simplest connection of the inverter to operate
e.g. spindles in the
engraving plotter.
CSMIO/IP-M used outputs:
CSMIO/IP-M signal
Connector on CSMIO/IP-M
PIN number in
CSMIO/IP-M connector
Inverter function
Analog mass
connection
DB9 – Analog I/O 2
mass –reference potential for analog input of the
speed command
0 analog output DB9 – Analog I/O 1 Voltage input 0-10V of the speed command
Common PIN for relay
outputs 4 and 5
DB25 – Digital outputs 25
Output 24V for controlling signals
4 relay output
DB25 – Digital outputs
12
Right revs switching
5 relay output DB25 – Digital outputs 13 Left revs switching
Do no forget to set the configuration parameters of the inverter properly. Incorrect settings may
cause - in the best case - an inverter error, at worst - the spindle motor would becomes
permanently damaged (such damage is not covered under warranty
).
Mach3 program configuration, concerning use of the spindle with speed control was described
in a chapter 10 - "Mach3
Configuration".
Due to the variety of inverters, to facilitate the connection, in the CSMIO / IP-M controller there
are two relay outputs that can control both positive, negative potential and the potential
brought by the inverter.
In the example above the 24
V potential brought by the inverter was used.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 18
4.9.2 Illustrative diagram of XYZ plotter

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 19
A scheme presented in this section is the simplest implementation of 3axis plotter (XYZ).
Two power supplies were used: 24V to supply the CSMIO/IP-M controller and 80V for the stepper
motors drives. Switches used: NC switches for axis homing (HOME) and limit switches (LIMIT). In
practice, it is necessary to build more comprehensives systems, however the example above shows
the main rule.

CS-Lab s.c. –CNC CSMIO/IP-M controller
Page 20
4.9.3 Automatic control of drives power supply (HV)
CSMIO/IP-M controller allows for automatic control of drives power supply and some other devices.
Switching on this function was described in 10th Chapter. The logic of the output working, define as
so called „HV Enable” is very easy. The voltage is switched ON at the moment of requesting “Reset”
by Mach program. It stays ON until one of the following conditions exists:
•FAULT signal from any axis drive
•E-Stop signal (the emergency stop mushroom pressing)
•Turning on the limit switch
•Loss of communication with the Mach3 program
•Error of inside position/speed regulators in CSMIO/IP-M
Here is an example of connected outputs used as „HV Enable”. The output number is irrelevant, it is
defined in the configuration window of the Mach3 program.
When you use large contactors for switching off the power, check if the coil doesn’t take more than
250mA. If so, use smaller transmitter and turn on the bigger one with it. With a large contactor it’s
good to have a diode and noise-suppression condenser to eliminate the overvoltages generated
during switching off the coil.
CSMIO/IP-M controller makes the "HV Enable" voltage control function automatically. Response time
for the events that cause the disconnection is less than 0,0001s.
Do not forget that digital outputs of the CSMIO/IP-M are fully isolated so they need separate power
supply (9 and 23 PIN on a STEP/DIR & Digital Outputs connector).
Table of contents
Other CS-Lab Controllers manuals
Popular Controllers manuals by other brands

GESTRA
GESTRA TA 7 Installation and service instructions

Linear Technology
Linear Technology LT8570 Demo Manual

Hydrocom
Hydrocom Water Controller II user manual

Keysight Technologies
Keysight Technologies M9038A Startup guide

White Rodgers
White Rodgers UNIVERSAL INTEGRATED FURANCE CONTROL... installation instructions
FANOX
FANOX ES400-45 instructions