4
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................................. 6
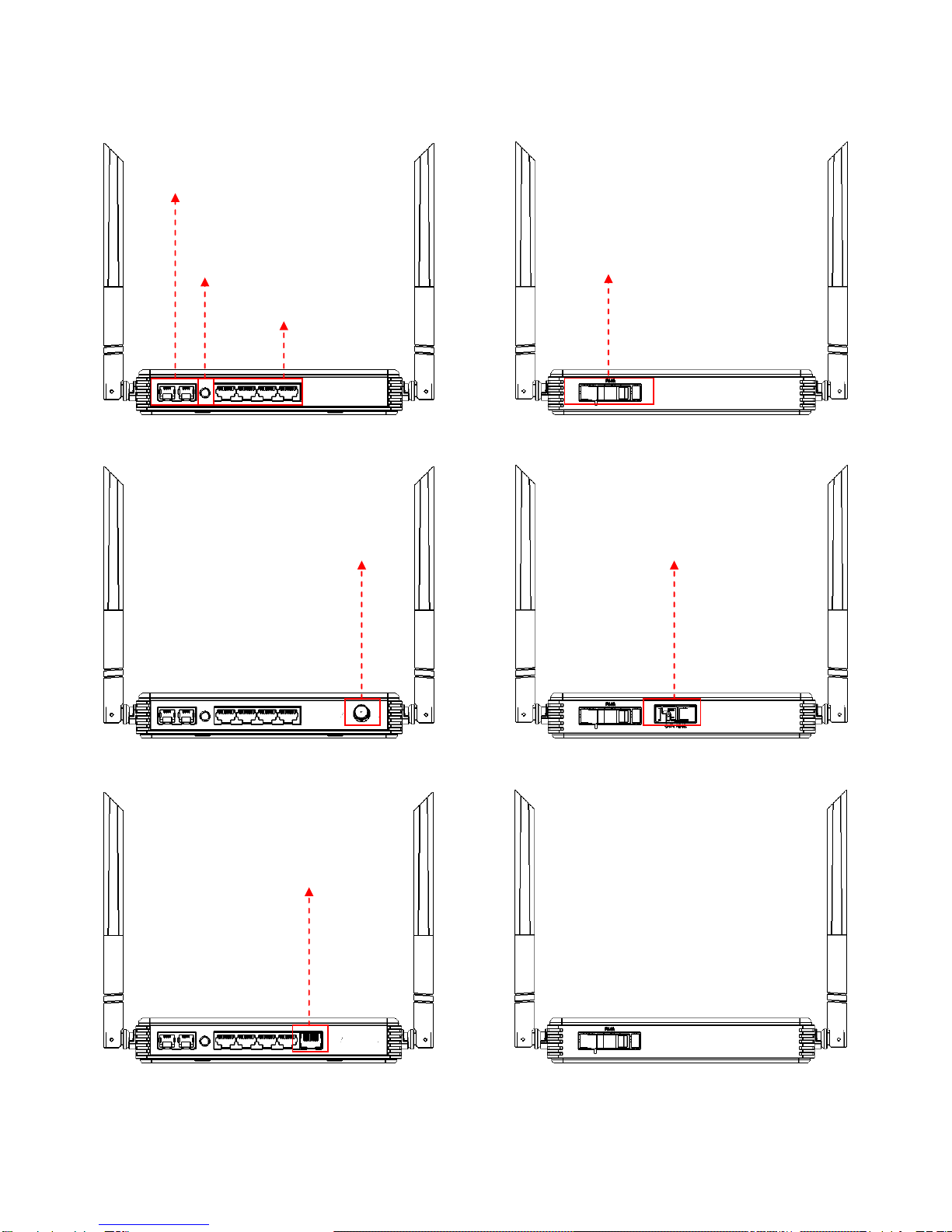
1.1 Front, Rear and Top-Front Panel............................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Management Options ............................................................................................................................................................ 10
1.2 Management Options ............................................................................................................................................................ 10
1.3 Interface Descriptions............................................................................................................................................................. 10
1.4 Connecting the Residential Gateway...................................................................................................................................... 11
1.5 RF over Fiber (With RF Receiver only) .................................................................................................................................... 12
1.6 LED Descriptions ..................................................................................................................................................................... 13
2. WEB MANAGEMENT ......................................................................................................................... 14
2.1 The Concept of IP address ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Start Configuring .................................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.3 Introduction to Sub-Menus..................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.4 Setup ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
2.4.1 System Information ........................................................................................................................................................ 19
2.4.2 Basic Setup ..................................................................................................................................................................... 21
2.4.3 DDNS............................................................................................................................................................................... 31
2.4.4 Network Setup................................................................................................................................................................ 33
2.4.5 Routing Setup ................................................................................................................................................................. 36
2.5 WiFi ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 38
2.5.1 Wireless Setup................................................................................................................................................................ 38
2.5.2 Wireless Security ............................................................................................................................................................ 43
2.5.3 MAC Access Filter ........................................................................................................................................................... 48
2.6 Security................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
2.6.1 Firewall ........................................................................................................................................................................... 50
2.6.2 Packet Filter.................................................................................................................................................................... 51
2.6.3 URL Filter ........................................................................................................................................................................ 55
2.6.4 VPN Passthrough ............................................................................................................................................................ 56
2.6.5 UPnP ............................................................................................................................................................................... 57
2.6.6 DDoS ............................................................................................................................................................................... 58
2.7 Application ............................................................................................................................................................................. 62
2.7.1 Port Forwarding.............................................................................................................................................................. 62
2.7.2 Port Triggering ................................................................................................................................................................ 64
2.7.3 DMZ ................................................................................................................................................................................ 66
2.8 QoS ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
2.8.1 QoS Priority .................................................................................................................................................................... 68
2.8.2 QoS Ratelimiter .............................................................................................................................................................. 73
2.9 SIP........................................................................................................................................................................................... 75
2.9.1 Basic Settings.................................................................................................................................................................. 75
2.9.2 Account Settings ............................................................................................................................................................. 77
2.9.3 Server Settings................................................................................................................................................................ 78
2.10 Voice ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 80
2.10.1 Voice Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 81
2.10.2 Call Service ................................................................................................................................................................... 83
2.10.3 FAX Port Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 85
2.10.4 FAX Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 87
2.10.5 General Dialing Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 88
2.10.6 Phone Book .................................................................................................................................................................. 90
2.10.7 Dialing Plan ................................................................................................................................................................... 91