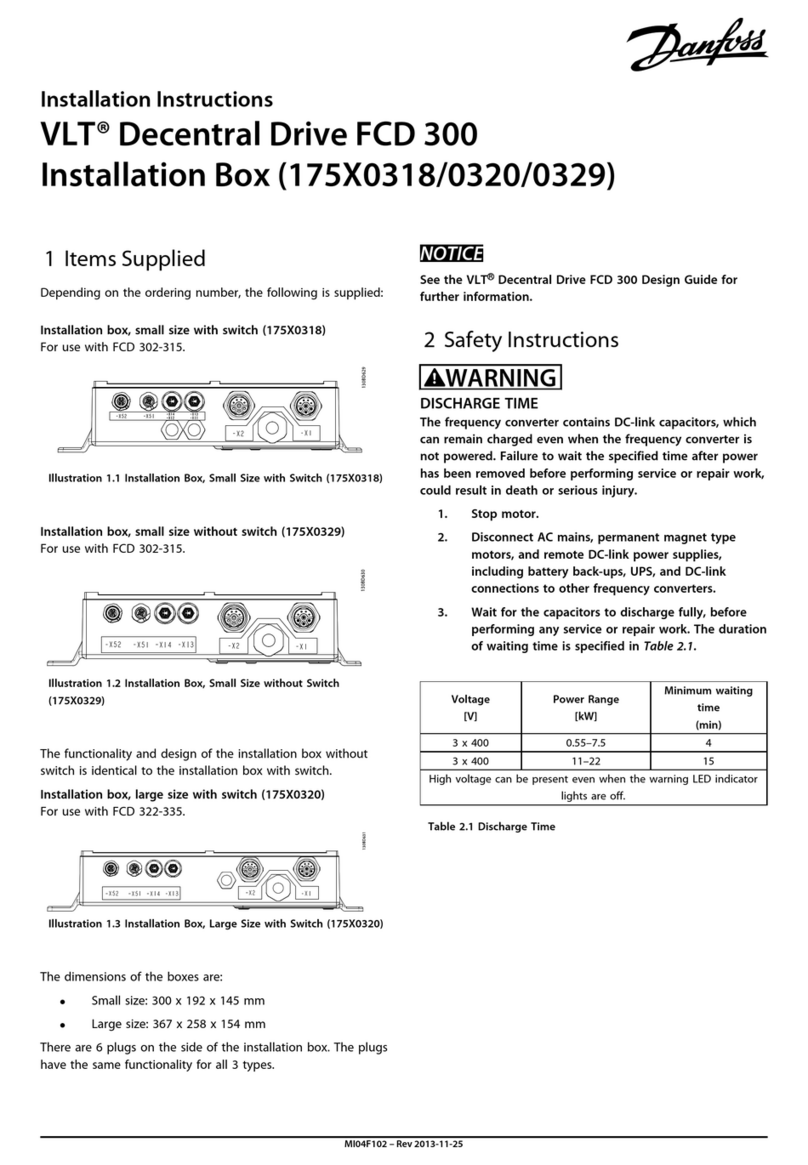
1.4.5 Miscellaneous
Analog inputs
The analog inputs are used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
There are 2 types of analog inputs:
•Current input, 0–20 mA and 4–20 mA
•Voltage input, 0–10 V DC.
Analog outputs
The analog outputs can supply a signal of 0–20 mA, 4–20
mA, or a digital signal.
Automatic Motor Tuning, AMT
AMT algorithm determines the electrical parameters for the
connected motor at standstill.
Brake resistor
The brake resistor is a module capable of absorbing the
brake power generated in regenerative braking. This
regenerative brake power increases the DC-link voltage,
and a brake chopper ensures that the power is transmitted
to the brake resistor.
CT characteristics
Constant torque characteristics used for all applications
such as conveyor belts, displacement pumps, and cranes.
Digital inputs
The digital inputs can be used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
Relay outputs
The frequency converter features 2 programmable relay
outputs.
ETR
Electronic thermal relay is a thermal load calculation based
on present load and time. Its purpose is to estimate the
motor temperature.
Initializing
If initializing is carried out (parameter 14-22 Operation
Mode), the programmable parameters of the frequency
converter return to their default settings.
Initializing parameter 14-22 Operation Mode does not
initialize communication parameters.
Intermittent duty cycle
An intermittent duty rating refers to a sequence of duty
cycles. Each cycle consists of an on-load and an o-load
period. The operation can be either periodic duty or none-
periodic duty.
LCP
The local control panel makes up a complete interface for
control and programming of the frequency converter. The
control panel is detachable and can be installed up to 3 m
from the frequency converter, that is, in a front panel with
the installation kit option.
lsb
Least signicant bit.
MCM
Short for Mille Circular Mil, an American measuring unit for
cable cross-section. 1 MCM ≡0.5067 mm2.
msb
Most signicant bit.
On-line/O-line parameters
Changes to on-line parameters are activated immediately
after the data value is changed. To activate changes to o-
line parameters, press [OK].
PI controller
The PI controller maintains the speed, pressure,
temperature, and so on, by adjusting the output frequency
to match the varying load.
RCD
Residual current device.
Set-up
Save parameter settings in 2 set-ups. Change between the
2 parameter set-ups and edit 1 set-up, while another set-
up is active.
Slip compensation
The frequency converter compensates for the motor slip by
giving the frequency a supplement that follows the
measured motor load keeping the motor speed almost
constant.
Smart logic control (SLC)
The SLC is a sequence of user-dened actions executed
when the associated user-dened events are evaluated as
true by the SLC.
Thermistor
A temperature-dependent resistor.
STW
Status word.
FC standard bus
Includes RS485 bus with FC protocol.
Trip
A state entered in fault situations, for example, if the
frequency converter is subject to an overtemperature or
when the frequency converter is protecting the motor,
process, or mechanism. Restart is prevented until the cause
of the fault has disappeared and the trip state is canceled
by activating reset or, sometimes, by being programmed to
reset automatically. Do not use trip for personal safety.
Trip lock
A state entered in fault situations when the frequency
converter is protecting itself and requiring physical
intervention, for example, if the frequency converter is
subject to a short circuit on the output. A trip lock can
only be canceled by cutting o mains, removing the cause
of the fault, and reconnecting the frequency converter.
Restart is prevented until the trip state is canceled by
activating reset or, sometimes, by being programmed to
reset automatically. Trip lock may not be used for personal
safety.
Introduction Design Guide
MG02K402 Danfoss A/S © 01/2016 All rights reserved. 7
11