DM9000A
APPLICATION NOTES
Preliminary 2
Version: DM9000A-AN-V121
November 27, 2007
1INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................6
1.1 General Description..................................................................................................................6
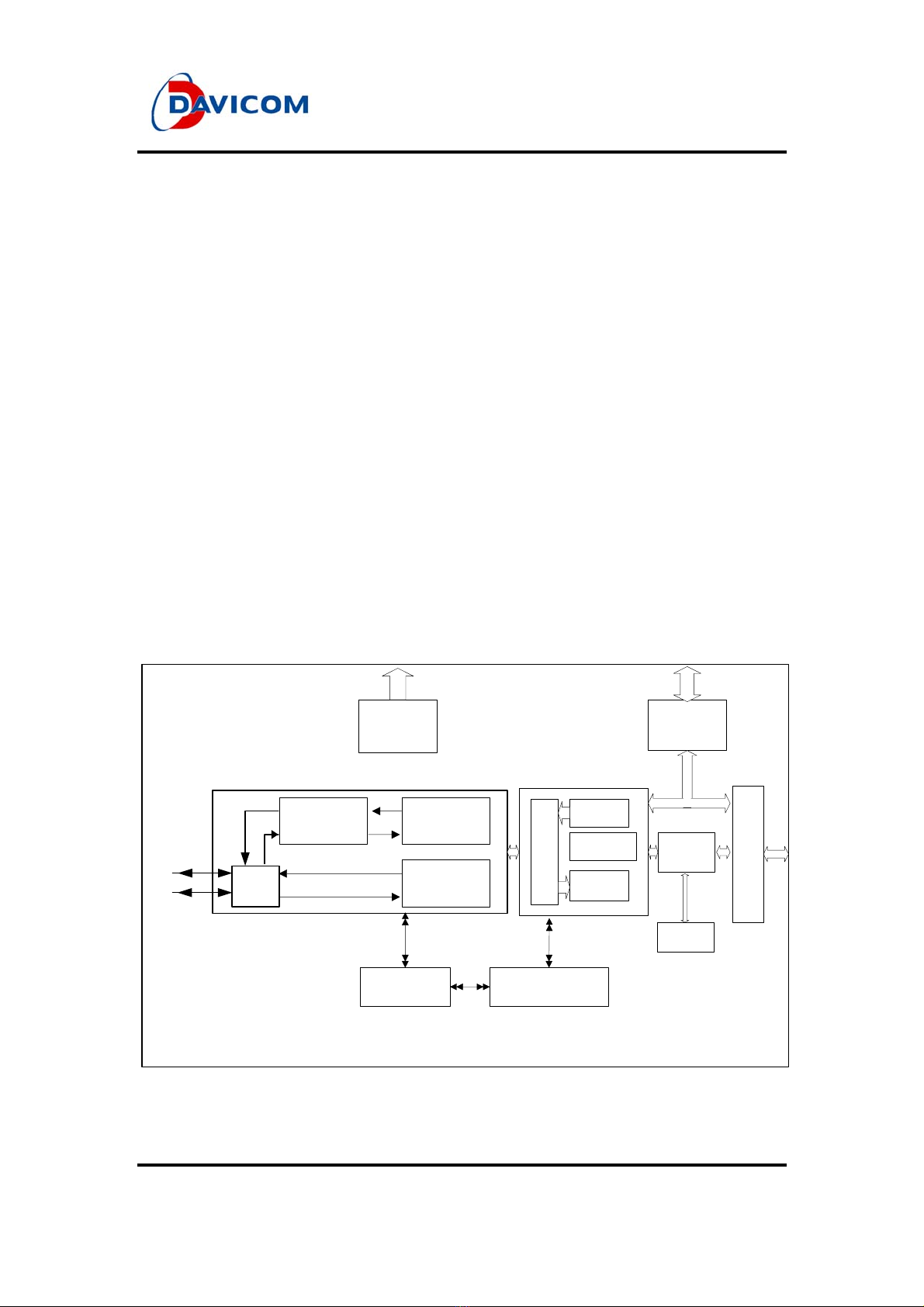
2GENERALPROCESSOR BUS DESCRIPTION...............................................7
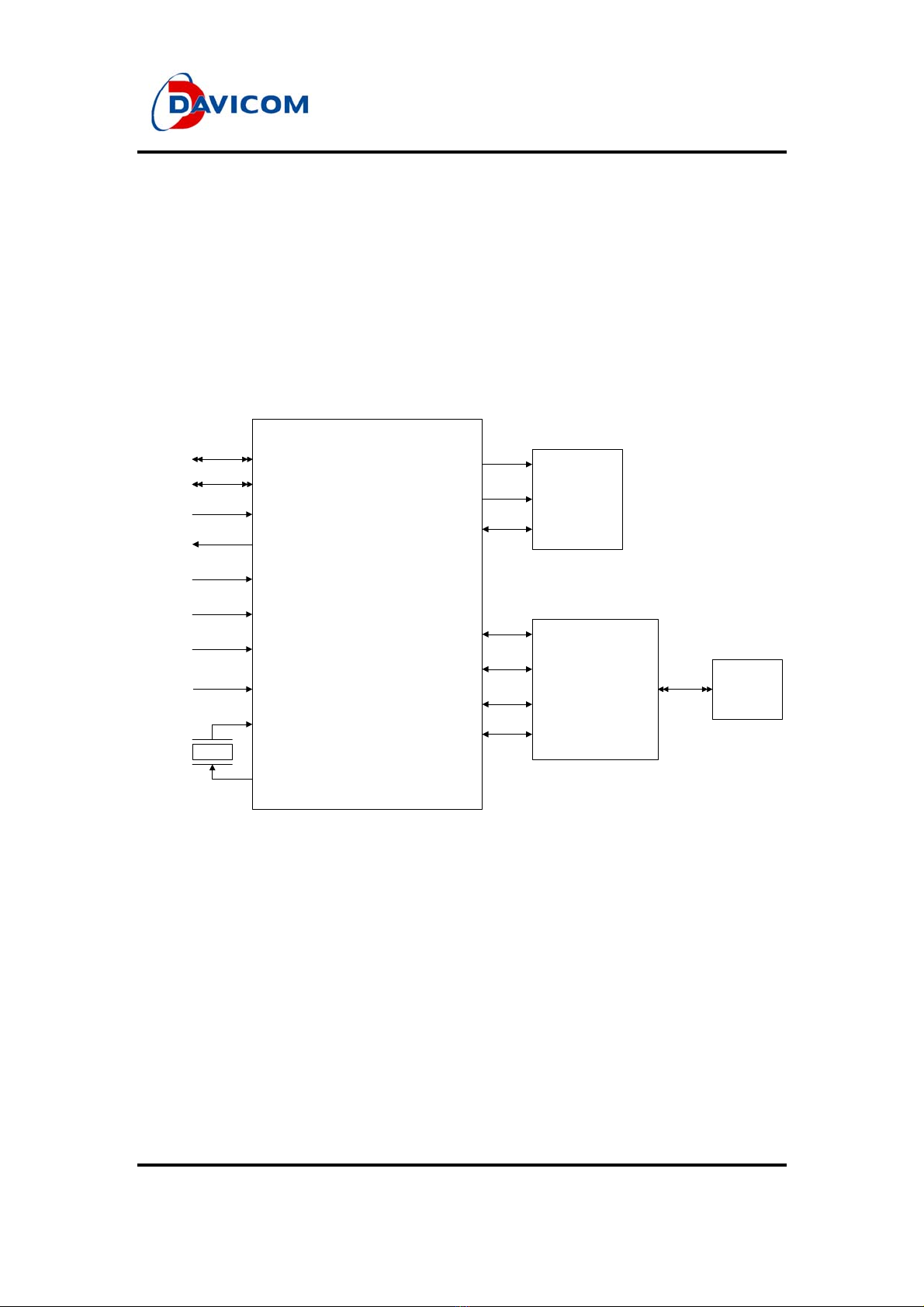
2.1 Typical Signal Connection with Processor Bus.........................................................................7
2.1.1 Pin Function Table.............................................................................................................8
2.1.2 Processor Parallel Bus 8/ 16-Bit Mode Setting..................................................................8
2.1.3 Command Type...................................................................................................................9
3SYSTEM HARDWARE DESIGN......................................................................10
3.1 How to Select Chip..................................................................................................................10
3.2 Strap Pins Setting....................................................................................................................10
3.3 Serial EEPROM Operation.....................................................................................................10
3.3.1 EEPROM Format.............................................................................................................11
3.4 GPIO Pins Setting...................................................................................................................15
3.5 Schematic Reference Design...................................................................................................17
3.5.1 Application Schematics for 8-Bit and 16-Bit....................................................................17
4RESETOPERATIONAND PHYPOWER-DOWN MODE...........................19
4.1 Power On Reset.......................................................................................................................19
4.2 Software Reset.........................................................................................................................19
4.3 PHY Power Down Mode.........................................................................................................19
4.3.1 GPR PHYPD Setting........................................................................................................20
4.3.2 PHY Register Setting........................................................................................................20
5HOWTO PROGRAM DM9000A......................................................................21
5.1 How to Read/ Write DM9000A Register .................................................................................21
5.2 Driver Initializing Steps..........................................................................................................22
5.3 How to Read/ Write EEPROM Data .......................................................................................23
5.3.1 HOWTO Read EEPROM Data ......................................................................................23
5.3.2 HOWTO Write EEPROM Data......................................................................................24
5.4 How to Read/ Write PHY Register ..........................................................................................26
5.4.1 HOWTO Read PHY Register..........................................................................................26
5.4.2 HOWTO Write PHY Register .........................................................................................27
5.5 How to Transmit Packets ........................................................................................................28