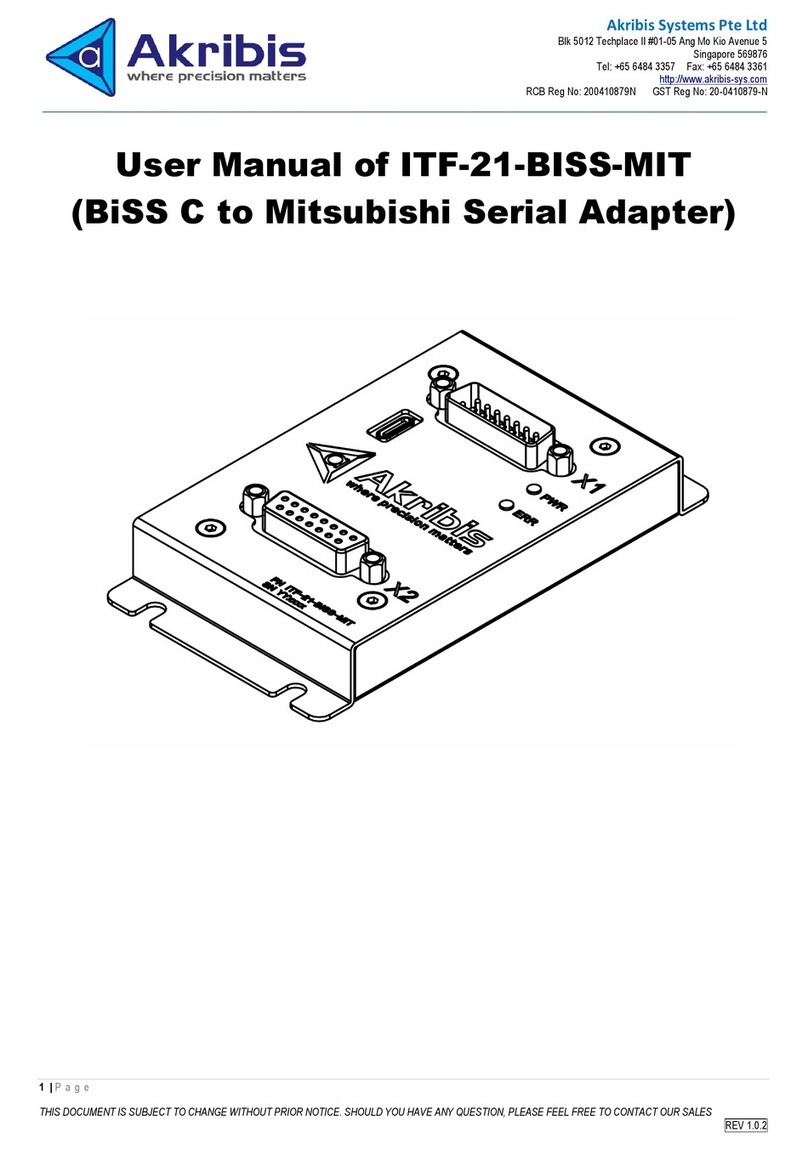
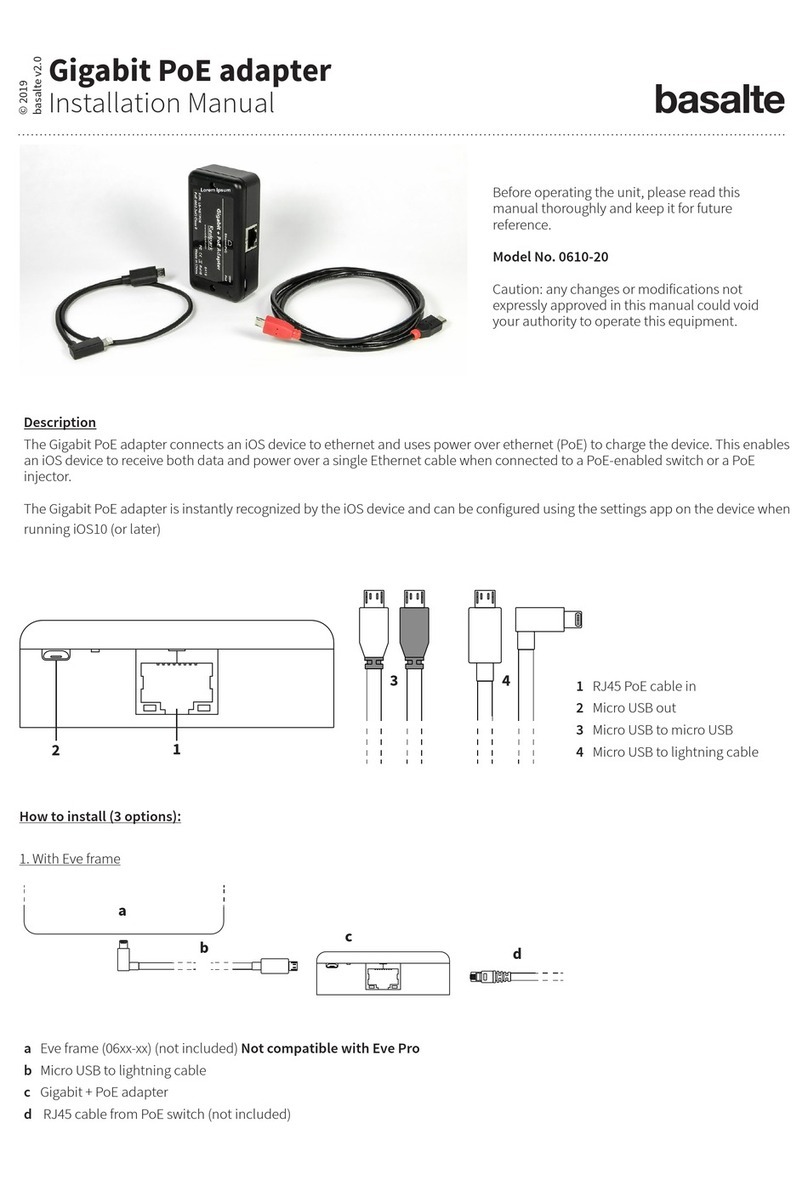
Software Configuration: Intel EtherExpress Pro/10+ PCI LAN Adapter
Overview | Microsoft®Windows®95 | Manually Adding an Adapter in Windows 95 | Windows NT®4.0 | Windows NT 3.51 | MS-DOS®and Windows 3.xfor
Novell®NetWare®Clients | Other Operating Systems
Overview
PCI systems automatically detect and configure PCI-compliant adapters. It is not necessary to run a configuration program. Start the system and it automatically
configures the adapter while it boots. If there is an error, see PCI Common Solutions.
Microsoft Windows 95
1. After installing the adapter in the computer, turn on the system.
2. At the New Hardware Found dialog box, click Driver From Disk Provided by Hardware Manufacturer and then click OK.
If the New Hardware Found dialog box does not appear, see Manually Adding an Adapter in Windows 95.
3. Insert the Intel configuration and drivers diskette in the diskette drive, type a: in the Path box, and click OK.
Windows 95 copies the driver files to the computer.
4. Restart the computer when prompted.
5. Click on the Network Neighborhood icon to see if the computer is connected to the network.
Manually Adding an Adapter in Windows 95
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the System icon.
3. Click the Device Manager tab, double-click Other Devices, and double-click PCI Ethernet Controller.
4. Click the Driver tab, and then click Change Driver.
5. Click Network Adapters and click OK.
6. Click Have Disk, insert the Intel configuration and drivers diskette in the diskette drive, and click OK.
7. Restart the computer when prompted.
Windows NT 4.0
1. After installing the adapter in the computer, turn on the system.
2. Insert the Windows NT CD into the CD-ROM drive.
3. Click Start, point to Settings, and click Control Panel.
4. Double-click the Network icon.
5. Click Add.
A list of adapters appears.
6. Click Intel EtherExpress PRO/10+ PCI Adapter and click OK.
The Intel drivers and the PROSet utility are installed, and PROSet launches. You can use PROSet to configure and test your adapter and display the resources assigned when the
adapter was installed.
7. Click OK in the PROSet window to return to Windows NT.
The Intel adapter appears on the list in the Network window.
8. Click Close.
9. Restart when prompted.
Windows NT 3.51
1. After installing the adapter in the computer, turn on the system.
2. Double-click the Control Panel icon in the Main window.
3. Double-click the Network icon.
4. Click Add Adapter.
A list of adapters appears.
5. Click <Other> Requires Disk From Manufacturer.
6. Insert the Intel configuration and drivers diskette in the diskette drive and click OK.
The Intel drivers and the PROSet utility are installed, and PROSet launches. You can use PROSet to configure and test your adapter and display the resources assigned when the
adapter was installed.
7. Click OK in the PROSet window to return to Windows NT.
8. Click OK in the Network Settings window and remove the diskette.
9. Restart the system when prompted.