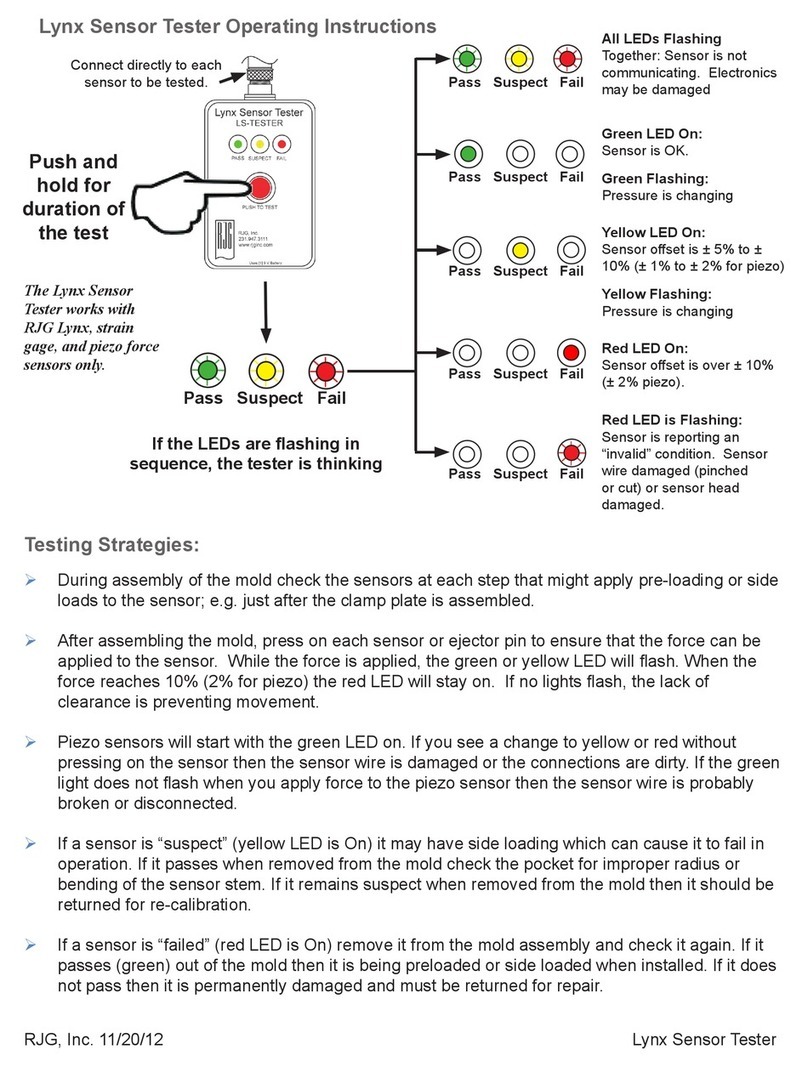
DGC ZM-DGC900 User manual

1
BGA Rework Station ZM-DGC900
SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS
Address: Office 12D Fuxin Building , 318 Fuhua Road , 558000, Shenzhen, China
Telephone: (86)0755-88360496 Fax:(86)0755-83292149
Http : //www.dragongroupchina.com
Contents
A. Company Profile
B. BGA Rework Station
C. Installation
D. Safety Cautions
E. Introduction of Structure
F. Operation Steps
G. PLC (Programmable logic Controller)
H. Curve Program Controller
I. Related information
J. Tips for operation
Appendix: Packing list.
2
A. Company Profile
DGC as quality control specialist in China started operations since 2007, with the Union of
intelligent human resources from China and Overseas, it has since then paved the way for Chinese
brand best products in outside markets, also promote and develop strategies for different products
according to languages and needs have been basic in DGC objectives. DGC now is involved
directly in the production of different lines for specific markets according to the conclusion of the
studies about each field, and the real needs for those.
Shenzhen Machine Co., Ltd. is located in one of the most prosperous parts—Xixiang, with
Shenzhen International Airport to its south and State Hwy. 107 as well as Shenzhen-Guangzhou
Superhighway to its north, enjoying convenient transportation.
Shenzhen Zhuomao Co., Ltd. aims to expand the market with advanced thinking and
pioneering philosophy; seizes the market with strong technical expertise; ensures the high quality of
the products with modern scientific management and mature advanced technology; and offers our
clients the best service with perfect sales network and high-quality staff.
We sincerely hope that our products will bring you more and more profits and wealth.
B. BGA Rework Station
1. Knowledge about BGA
BGA is short for Ball Grid Array. It is a kind of package method which use organic carrier in IC. It
has the following features:
Small①package area. Greater functions and more pins.②
Self③-centerize while PCB puddle welding, easy to put on tin. More reliable.④
Good conductivity and low overall cost.⑤
Memory which applies BGA can enlarge the memory capacity by 2 to 3 times
while the volume of memory remains the same. Compared with TSOP, BGA is much
smaller and better at radiating and conducting electricity.
2. Types and Features of BGA
a. Types
According to the encapsulation material, BGA can be classified into the following types:
(1)PBGA(Plastic BGA)
(2)CBGA(Ceramic BGA)
(3)CCBGA(Ceramic Column BGA)
(4)TBGA(Tape BGA)
(5)CSP (Chip Scale Package or MBGA)
b. Features
Compared with QFP, BGA has the following features:
(1) I/O terminal space is big (eg. 1.0mm, 1.27mm, 1.5mm), and it can accommodate
more I/O.
(2) More reliable package, low rate of welding defects and welding spot durable.
(3) Paraposition of QFP is usually observed with naked eyes. When the pin space is
smaller than 0.4mm, it is hard to paraposition and weld. While the pin space of
BGA is bigger, by applying the paraposition-amplification device, it is easy to
paraposition and weld.
(4) The welding coplanarity of BGA is better than QFP, because solder can make up
the flat error between BGA and PCB after melting.
(5)Good electrical property. The pins are small, the selfinductance and mutualinductance
of the conductivity is low, and the frequency characteristic is good.
3

(6)The tension between solder points produces good self-centration effect in solder-
reflow, allowing 5% error of patch precision.
(7)Compatible with original SMT mount technology and machines. The original
screen printer machine, mounter and solder-reflow machine all can be used. The
comparison between BGA and QFP is shown in Table 1. The main defect of BGA is
the necessity of X-ray detection after welding.
c. Welding of BGA
The success of welding BGA is affected by the assembly of PCB. So 3 key
factors must be considered in the layout of PCB.
Features BGA QFP
Package size S/m2525 1600
Pin space L/mm 1.27 0.50
fault rate (×10-6/ pcs)0.60 100
(1)Thermal management
Thermal management must be considered when we design the assembly of PCB.
If many pieces of BGA gather on a small area of PCB, it will cause the imbalance of
PCB in the reflow oven. If many big pieces of BGA gather on a certain area of PCB,
longer heating period will damage some of the BGA. The areas with fewer
components have reached the welding temperature, while those areas with BGA are
still in low temperature. So the welding period is over before the flux paste
withdraws from the welding spots, thus there may be poor soldering or no-melting
of welding balls.
(2)Rabbet
The design of rabbet on PCB should stick to relevant standards strictly. Any
rabbet near BGA welding pad must cover the solder mask very well. If not, the extra
welding paste will flow from the welding pad to the rabbet, then leads to short
circuit between welding pad and rabbets nearby.
The geometric shape and diameter of welding pad:
The compactness of pins has immediate impact on the geometric shape and
diameter of welding pad. Similarly, BGA has different sizes, shapes and complexity.
As the package size decreases, the geometric shape and diameter of the welding pad
calls for higher precision in detection.
3. Inspection standards of BGA
For BGA assembled on PCB, inspection standard is a very important issue.
Before BGA is applied to the PCB, most BGA manufacturers don't use X-ray in
process of inspection. Instead, they employ some traditional methods to test PCB,
such as automatic optical inspection, man-eye inspection or on-line function test.
However, these methods can't detect the invisible problems very exactly, such as
poor soldering, cold welding and bridging. The X-ray can discover these problems
very efficiently. At the same time, it can do live monitoring, guarantee the quality,
and realize the in-time feedback of the process control,
a. Evaluation of X-ray
When BGA is first used on BGA, X-ray can evaluate the solder-reflow according
to the situation of un-solder area or areas around it. Open-circuit, non-touching and
other similar situations show the solder paste has not reflow enough. Bridging may
result from the fact that the temperature is too high for the solder to liquefy. So the
solder flows from the pad to the interval between them, causing short-circuit.
Poor welding should be evaluated objectively: it is not so terrible; the key
4

point is that the welding spots can still be welded on the pad. The ideal situation is
no poor welding. Poor welding may be caused by pollution or the uneven
distribution of flux paste. What's more, warped PCB may also lead to poor welding.
Open-circuit welding spot may exist, too.
The quantity and size of poor welding are the key factors to decide whether it
will be accepted. Generally the size of single poor welding should be less than 50%
of the solder ball's diameter. If the ball is surrounded by reflow solder, BGA is able
to work. It is a very critical standard. The electrical properties may meet the
requirements but the mechanical strength will be affected.
PCB with BGA must use X-ray evaluation systems that can decern holes of less
than 100 µm diameter. The X-ray must be able to observe from top-down and tilt.
X-rays is a reliable guarantee of successful BGA welding,
b. Proposed inspection criteria
The inspection criteria will help X-ray inspection system confirm some typical
welding problems, which is related with the use of BGA device. It includes the
following factors:
(1)Poor welding
Poor welding results from the expansion of compounds in solder during the
heating of BGA. BGA with poor welding may cause some problems such as
ineffectiveness. The inspection criterias are as follows: the size of single poor
welding should be no more than 20% of the solder ball's diameter, with no single
poor welding on the surface; if many poor welding may exist, the total should be no
more than 20% of the solder ball's diameter.
(2)Desoldering spots
No desoldering spots.
(3)Bridging and short-circuit.
When there is extra solder or the solder is not put on the right place, bridging
and short-circuit may happen. So no bridging or short-circuit.
(4)None paraposition.
The X-ray image will show very clearly whether the BGA solder ball is aimed
at the welding pad on PCB.
(5)Broken circuit and cold welding
When solder don't touch the relevant pad or the solder doesn’t flow very well, there
will be broken circuit or cold welding. It is absolutely not allowed.
4. BGA rework process
Most of the semiconductor device’s heat-resistant temperatures are between
240°C and 600 °C. Therefore, the control of the temperature and uniformity are very
important to BGA rework systems. BGA rework process as follows:
a. Printed Circuit Board and BGA preheating
Printed Circuit Board and BGA’s preheating is meant to wipe off the moisture. If
the moisture was little, this step can be omitted.
b. Remove BGA
If the BGA will not be reused, and the PCB can endure high temperature, we can
use high temperature (shorter heating period) to remove it.
c. Clean the pad.
Pad cleaning is mainly clearing the solder paste and scaling powder remained on the
surface of PCB after BGA removal. For that process, it must use standard cleaning agent. To
ensure the reliability of the BGA solders, generally we cannot use the remained solder
paste in the pad, and we must clear away the used solder paste, except that solder balls reform on
the BGA. Because of the small size of BGA, especially CSP (or µBGA smaller), it is always
difficult to cleaning the pad, so when reworking CSP, it needs to use Rinse-free Flux if
5
Table of contents
Other DGC Test Equipment manuals
Popular Test Equipment manuals by other brands

Redtech
Redtech TRAILERteck T05 user manual

Venmar
Venmar AVS Constructo 1.0 HRV user guide

Test Instrument Solutions
Test Instrument Solutions SafetyPAT operating manual

Hanna Instruments
Hanna Instruments HI 38078 instruction manual

Kistler
Kistler 5495C Series instruction manual

Waygate Technologies
Waygate Technologies DM5E Basic quick start guide

StoneL
StoneL DeviceNet CK464002A manual

Seica
Seica RAPID 220 Site preparation guide

Kingfisher
Kingfisher KI7400 Series Training manual
Kurth Electronic
Kurth Electronic CCTS-03 operating manual

SMART
SMART KANAAD SBT XTREME 3G Series user manual

Agilent Technologies
Agilent Technologies BERT Serial Getting started