Epson LQ-1170 Dimensions
Other Epson Printer manuals

Epson
Epson AcuLaser M2000D User manual

Epson
Epson Stylus Pro 4800 Portrait Edition User manual

Epson
Epson WorkForce Pro WP-4023 Manual

Epson
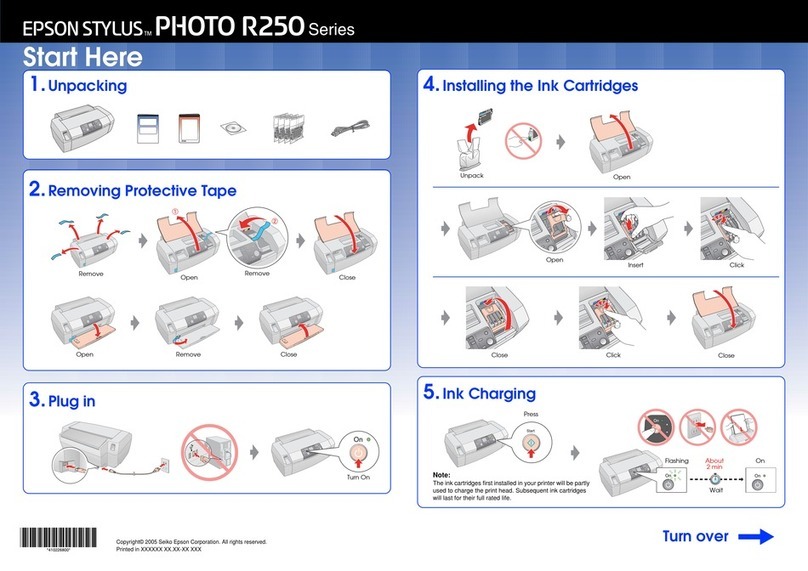
Epson Stylus Color 440 User manual
Epson
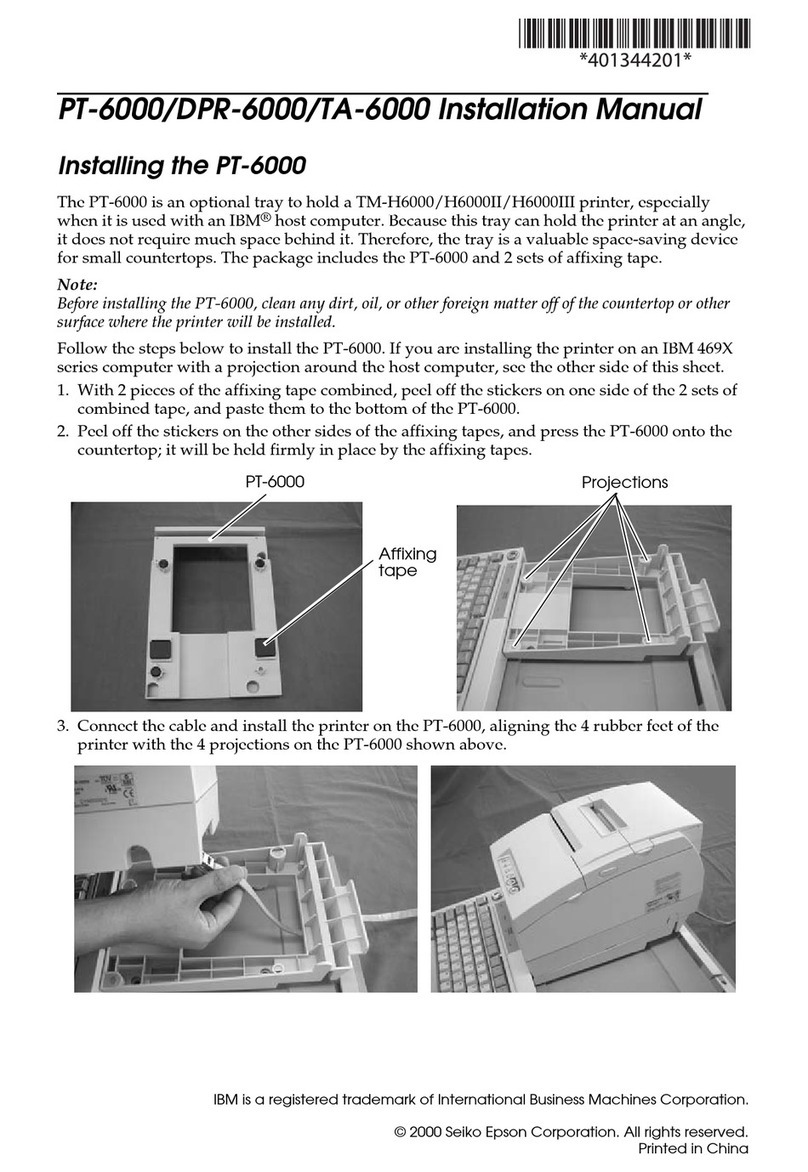
Epson PT-6000 User manual

Epson
Epson TM-T81 User manual

Epson
Epson Stylus Photo 1500W User manual

Epson
Epson Stylus Photo PX830FWD Assembly instructions
Epson
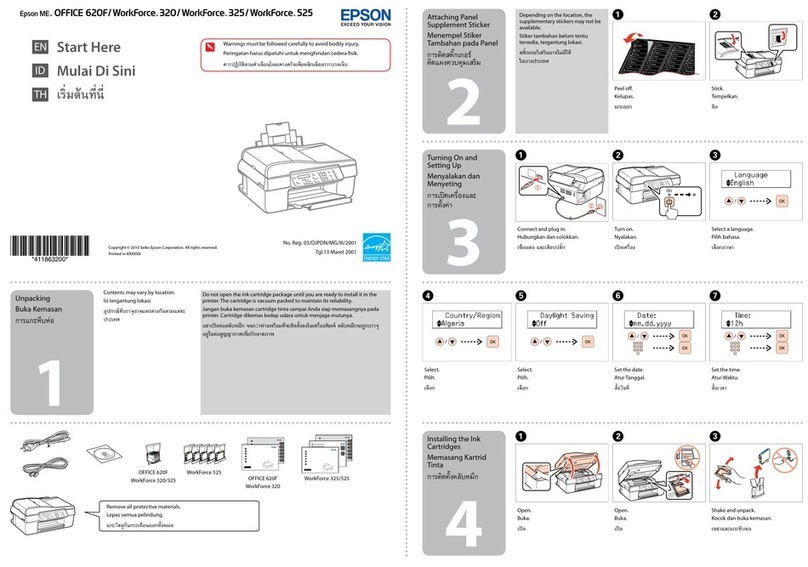
Epson WorkForce 320 Instruction Manual

Epson
Epson ET-3700 User manual

Epson
Epson Stylus Office BX630FW Assembly instructions

Epson
Epson TM-T70II User manual

Epson
Epson tm-m30 Use and care manual

Epson
Epson ET-M16680 Series Instruction Manual
Epson
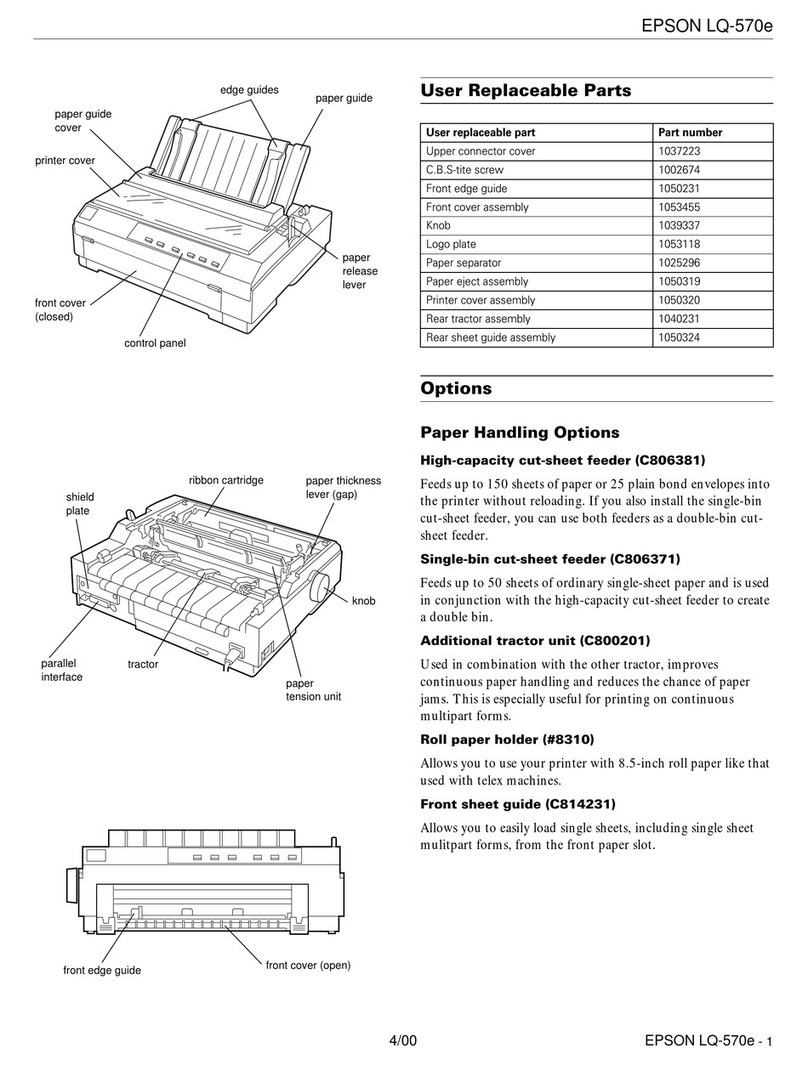
Epson LQ-570e Installation and operation manual

Epson
Epson PictureMate Show - PM 300 - PictureMate Show Digital... Instruction Manual

Epson
Epson AccuSuite 11880 Series User manual

Epson
Epson EPL-N2550 User manual
Epson
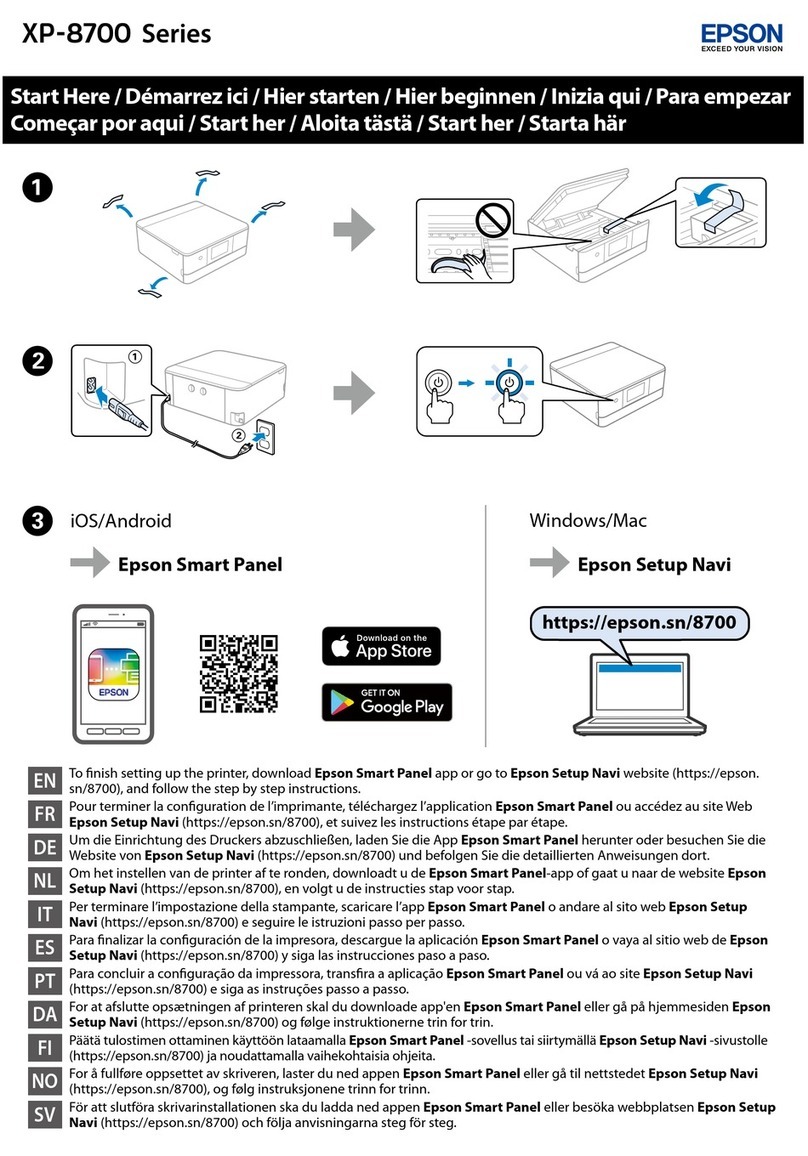
Epson XP-8700 Series Instruction Manual

Epson
Epson Stylus Photo Printer PX800FW Assembly instructions