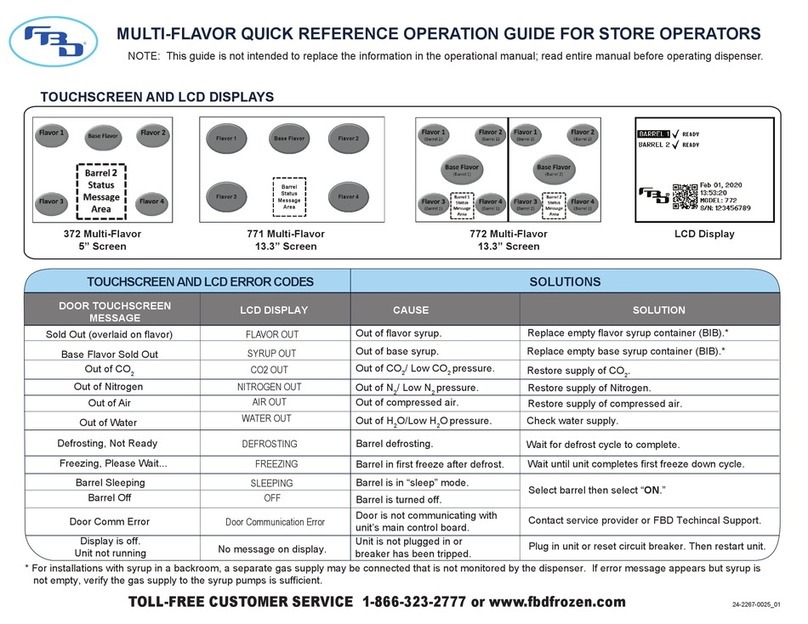
FBD 56 Series Installation guide
Other FBD Dispenser manuals
Popular Dispenser manuals by other brands
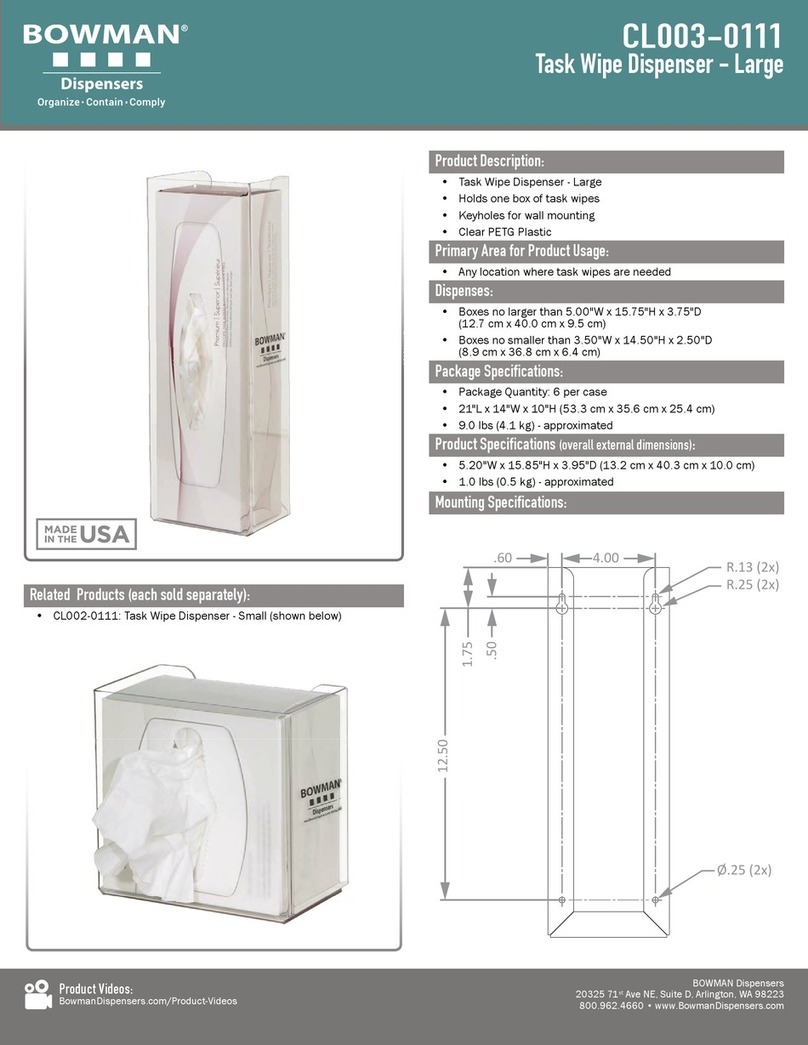
BOWMAN
BOWMAN CL003-0111 manual

SIKA
SIKA Power Cure operating instructions

Silver King
Silver King Majestic SK12MAJ Technical manual and replacement parts list

Franke
Franke F3Dn Twin Service manual

HURAKAN
HURAKAN HKN-MT1 manual

STIEBEL ELTRON
STIEBEL ELTRON UltraHot Plus Operation and installation instructions