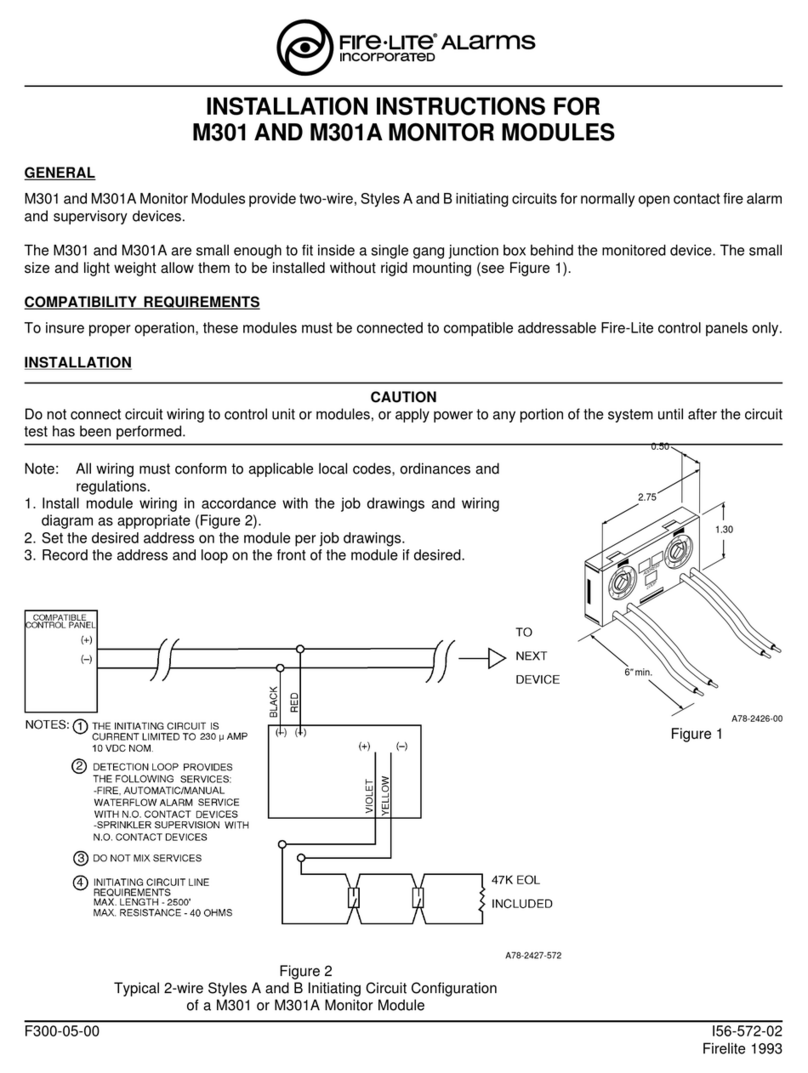
Fire-Lite CMF-300-6 User manual

BEFORE INSTALLING
This information is included as a quick reference installation
guide. Refer to the appropriate Fire•Lite control panel installation
manual for detailed system information. If the modules will be
installed in an existing operational system, inform the operator
and local authority that the system will be temporarily out of ser-
vice. Disconnect the power to the control panel before installing
the modules. This system contains static sensitive components.
Always ground yourself with a proper wrist strap before handling
any circuits so that static charges are removed from the body. The
module housing should also be grounded.
NOTICE: This manual should be left with the owner/user of this equipment.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The CMF-300-6 Six Supervised Control Module is intended for
use in an intelligent alarm system. Each module is intended for
switching applications involving AC or DC which require wiring
supervision. A common SLC input is used for all modules. Each
module has its own address. A pair of rotary code switches is used
to set the address of the first module from 01 to 154. The remain-
ing modules are automatically assigned to the next five higher ad-
dresses. Provisions are included for disabling a maximum of three
unused modules to release the addresses to be used elsewhere.
Each module also has panel controlled green LED indicators. The
panel can cause the LEDs to blink, latch on, or latch off.
In order to synchronize strobes, horn/strobes, and speaker/
strobes, a SYNC-1 accessory card (sold separately) must be used
with the CMF-300-6. See the SYNC-1 installation manual for de-
tails on how to install.
F300-21-00 1 I56-1874-011
Fire•Lite Alarms, Inc. One Fire•Lite Place, Northford, CT 06472 203-484-7161
SPECIFICATIONS
Normal Operating Voltage: 15-32 VDC
Stand-By Current: 2.25 mA
Alarm Current: 35 mA (assumes all six relays have been switched once and all six LEDs solid on)
Temperature Range: 32°F to 120°F (0°C to 49°C)
Humidity: 10 to 93% Non-condensing
Dimensions: 6.8˝H x 5.8˝W x 1.25˝D
Accessories: CH-6 Chassis; BB-6 Cabinet; BB-2 Cabinet
Wire Gauge: 12-18 AWG
Max. NAC Circuit Line Loss: 4 VDC
Power Rating Per Circuit (Speakers): 63 W @ 70.7 VAC; 50 W @ 25 VAC
Maximum NAC Current Ratings: For class B wiring systems, 3A; For class A wiring systems, 2A
CMF-300-6 Six Supervised Control Module
Installation and Maintenance Instructions
Each module has terminals for connection to an external supply
circuit for powering devices on its NAC. Each supply must be
power limited and its voltage/current limits must be at or below
those specified. There is a short circuit protection monitor for
each module. This is provided to protect the external power sup-
ply against short circuit conditions on the NAC.
Included:
Shipped on Board:
(1) Small shunt in Class A/B position
(Shipped in Class B position, remove shunt for Class A)
(6) Large shunts on Enabled Power Supply Monitor
(6) Large shunts on Disable Short Circuit Protection
(3) Large shunts on Sync Generator
(7) 1 × 4
TERMINAL
BLOCKS
(7) 1¼˝ (32mm) STANDOFFS
(15) LARGE
SHUNTS
(4) MACHINE SCREWS
(2) NUTS
(5) SHORT POWER
SUPPLY JUMPERS
(2) SMALL
SHUNTS
(1) LONG POWER SUPPLY JUMPER
(2) EOL RELAY
CONNECTOR
ASSEMBLES
(6) 47K OHM
END OF LINE
RESISTORS
C0202-01
Table 1: Short Circuit Protection - UL 864 9th Edition Requirements
NOTICE TO USERS, INSTALLERS, AUTHORITIES HAVING JURISDICTION, AND OTHER INVOLVED PARTIES
This product incorporates field-programmable software. In order for the product to comply with requirements in the Standard for
Control Units and Accessories for Fire Alarm Systems, UL 864, certain programming features or options must be limited to specific
values or not used at all as indicated below.
Program Feature or Option Permitted in
UL 864 (Y/N) Possible Settings Settings Permitted in UL 864
Disabling short circuit
protection when a single
power supply is shared by
multiple NACs
No Enable or Disable
short circuit
protection
Enable short circuit protection when a single power
supply is shared by multiple NACs. Short circuit
protection can be disabled only when a power supply
is not shared by multiple NACs.
I56-1874-011

with two self-threading screws, which are used to fasten the
chassis to the back wall of the cabinet (see Figure 4).
The BB-2 cabinet comes with the chassis already installed, so
no mounting is necessary.
Figure 3: Typical mounting hole locations
Backbox
Mounting
Holes
C0235-00
Figure 4: Mounting the CH-6 chassis
Mount with self-threading screws
to back of cabinet
C0236-0
3. Module Installation
There are two methods for installing a module in the rear
position of a chassis. Method one is for installation of a rear
module only, when no module will be installed in front of it.
Refer to Figure 5 for instructions. Method two is for installation
of a rear module when another module will be installed in the
chassis position in front of it. Refer to Figures 6a and 6b for
method two. All necessary screws and standoffs are supplied
with the modules.
Figure 5: Installation of rear module only, method one
23
1
C0237-00
Step 1: Insert the bottom of the CMF-300-6 module down into
a rear slot on the chassis.
Step 2: Carefully swing the upper edge of the board back
towards the back of the chassis until it touches
the two standoffs.
Step 3: Align two 4-40 screws with the two standoffs and tighten.
Step 4: Address and wire the modules according to the instruc-
tions in this manual.
COMPATIBILITY REQUIREMENTS
To ensure proper operation, this module shall be connected to a com-
patible Fire•Lite system control panel (list available from Fire•Lite).
COMPONENTS
Following are descriptions of the CMF-300-6 mounting frame-
works. There are two mounting options for CMF-300-6 modules:
• Up to six CMF-300-6 modules can be installed on a CH-6 in
a BB-6 cabinet.
• One or two CMF-300-6 modules can be installed in a BB-2 cabinet.
Chassis
The CH-6 chassis is used to mount CMF-300-6 modules in a BB-6
cabinet. It accommodates up to six CMF-300-6 modules in a single
cabinet row three modules wide and two modules deep.
Figure 1: CH-6 Chassis
C0206-00
The BB-2 cabinet has a built-in chassis that will accommodate
one or two CMF-300-6 modules.
Figure 2: BB-2 Cabinet
0
1
2
3
456789
0
78
6
5
4
3
21
910
11
12
13
14
15
BASE ADDRESS
ADDRESS
DISABLE
NONE
ONE
TWO
THREE
0
1
2
3
456789
0
78
6
5
4
3
21
910
11
12
13
14
15
BASE ADDRESS
ADDRESS
DISABLE
NONE
ONE
TWO
THREE
C0234-00
The front CMF-300-6 module positions of each chassis are offset
below the rear CMF-300-6 module positions so that all of the sta-
tus indicators are visible.
Cabinets
A BB-6 cabinet will house the CH-6 chassis with up to six CMF-
300-6 modules installed on it. Refer to cabinet installation docu-
ments for dimensions and installation instructions.
The BB-2 cabinet houses one or two CMF-300-6 modules on the
internal chassis that is part of the cabinet. Refer to cabinet instal-
lation documents for dimensions and installation instructions.
INSTALLATION STEPS
1. Cabinet Mounting
In a clean, dry area, mount the backbox using the four holes
provided in the back surface of the cabinet (Figure 3).
2. Chassis Installation
The CH-6 chassis is mounted in the BB-6 cabinet. It is shipped
F300-21-00 2 I56-1874-011

and B operation, DO NOT set the lowest address above 154, as the
other modules will be assigned to nonexistent addresses.
NOTE: Some panels support extended addressing. In order to set
the module above address 99 on compatible systems, carefully
remove the stop on the upper rotary switch (see Figure 7). If the
panel does not support extended addressing, do not set the lowest
address above 94.
4. A shunt is provided to disable a maximum of three unused
modules (see Figure 8). Modules are disabled from the highest
address and work downward. If two modules are disabled, the
lowest four addresses will be functional, while the highest two
will be disabled. For example, if the shunt for Address Disable
is placed on “two” and the base address switch is set to 28,
the modules will be assigned to 28, 29, 30 and 31, disabling
the highest two positions.
NOTE: In Class A operation, placing the small shunt on “disable
3˝ will disable all three addresses. Placing the small shunt on “dis-
able 2˝ will disable two out of the three addresses. For example,
if the address switch is set to 28 and the small shunt is placed on
“disable 2˝, addresses 30 and 32 will be disabled while address
28 will be enabled.
5. There is a short circuit protection option for each address. The
board is shipped with short circuit protection disabled for each
address represented by six large shunts on the “Disable Short
Circuit Protection” area. To enable short circuit protection for
an address, remove the corresponding pins from the “Disable
Short Circuit Protection” area. When enabled, the module will
not switch power supply if a short circuit condition exists on a
notification appliance circuit.
NOTE: Power must not be applied to the unit when changing
functionality of the shunts.
NOTE: Place unused shunts on single pin to store on board for
future use.
NOTE: The power supply monitoring
feature is currently not supported.
NOTE: SLC wiring is the top terminal
block, notification appliance/power
supply is the bottom.
NOTE: Whether in Class B or Class
A wiring, power supply monitoring
and short circuit protection must be
enabled on the NAC circuits that are sharing a power supply.
NOTE: Short circuit protection can only be disabled if a power
supply is not being shared by multiple NACs.
Figure 8:
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
SYNC GENERATOR
SIDE VIEW:
TOP VIEW:
SLC WIRING TERMINAL
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE/
POWER SUPPLY TERMINAL
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
A/B SELECT
C0228-01
F300-21-00 3 I56-1874-011
The steps in Figures 6a and 6b describe and illustrate module in-
stallation when the rear chassis position and the position in front
of it will be filled. Front position installation is possible only if the
rear position is filled with a module.
Figure 6a: Installation of CMF-300-6 module in a rear
chassis position, method two
1
C0225-00
Step 1: Insert the bottom edge of the CMF-300-6 module down
into a rear slot of the chassis.
Step 2: Carefully swing the upper edge of the board towards
the back of the chassis until it touches the short stand
off attached to the chassis.
Step 3: Align the long standoff with the short standoff and tighten.
Figure 6b: Installation of CMF-300-6 module in front
chassis position
2
3
1
C0226-00
Step 1: Insert the bottom edge of the CMF-300-6 module down
into a front slot of the chassis.
Step 2: Carefully swing the upper edge of the board towards
the back of the chassis until it touches the 1
1/4˝
(31.75mm) standoffs installed on the rear module.
Step 3: Align two 4-40 screws with the two standoffs and tighten.
Step 4: Address and wire the modules according to the
instructions in this manual.
WIRING
NOTE: All wiring must conform to applicable local codes, ordi-
nances, and regulations.
1. Install module wiring in accordance with the job drawings and
appropriate wiring diagrams.
2. All wiring to the CMF-300-6 is done via terminal blocks. In
order to properly make electrical connections strip approxi-
mately 1/4˝ of insulation from the end of wire, sliding the bare
end of the wire under the clamping plate screw.
3. Set the address on the modules per the job drawing. Use the
rotary code switches to set the address of the first module (be-
tween 01 and 154).
In Class B operation, the remaining modules are automatically
assigned to the next five higher addresses. For example, if the
base address switch is set to 28, the next five modules will be
addressed to 29, 30, 31, 32, and 33.
In Class A operation, a maximum of three Class A circuits are avail-
able. For example, if the base address switch is set to 28, 30 and 32
will be automatically assigned to the modules while 29, 31 and 33
are available to be used for other modules on the SLC. For Class A
TENS
0
78
6
5
4
3
21
910
11
12
13
14
15
Figure 7:
C0227-00

F300-21-00 4 I56-1874-011
All power supplies, external to the cabinet (in which the CMF-
300-6 is housed), should be connected to T0–T5 which are suit-
able connectors for field wiring. The 1 x 4 terminal blocks, shown
on page 1, should be used to make these connections.
All NACs can be wired to be powered by separate external sup-
plies (figures 9 and 11 are typical), or a single supply (figures 10
and 12 are typical) can be shared among multiple NACs. If a sup-
ply is to be shared, between NACs wired to a common PCB, use
the short power supply jumpers shown on page 1. The jumpers
can be used on T11–T15. Refer to Table 4 for jumper functions.
When multiple (2 or more) NAC circuits share a power supply,
the wiring for the power supply must be in conduit and 20 feet
or less from the CMF-300-6 Module.
TABLE 4:
JUMPER LOCATION NAC PAIR SHARING SUPPLY
T11* +0 and +1
T12 +1 and +2
T13* +2 and +3
T14 +3 and +4
T15* +4 and +5
NOTE: Jumpers must be placed on T11, T13 and T15 for all Class
A, Style Z applications.
A supply can be wired to be shared among multiple PCBs in
the same cabinet (figure 13 is typical). To share among multiple
PCBs: use the long power supply jumpers (shown on page 1) to
connect either T10 or T16, of one PCB, to either T10 or T16 of
the other PCB.
An EOL relay must be used for every external power supply (fig-
ures 9–12 are typical). The EOL relay coil should always be con-
nected at the external power supply input of the module which
is connected to the ends of the wires which are farthest from
the power supply. The EOL relay contacts should always be con-
nected in series with the NAC wiring of the same module. The
EOL relay coil should be connected across the PS+ (red wire) and
PS- (black wire) if it is connected at T0 – T5. The EOL relay coil
should be connected across adjacent pins (red – even pin#, black
– odd pin#), of the same connector, if T10 – T16 are used.
All wiring must be in accordance with the NEC, NFPA 72 and
all other applicable codes and standards. All external power sup-
plies must be voltage regulated with battery back-up. All external
power supplies, EOL relays, and notification appliances must be
UL listed for fire protection signaling applications.
WIRING NOTES
• Power-limited circuits must employ type FPL, FPLR, or FPLP
cable as required by Article 760 of the NEC.
• For easier wiring, assign all power-limited wiring to one side
rather than alternating with non power-limited.
PROGRAMMING
The CMF-300-6 module operates with the following Fire Alarm
Control Panels: • MS-9200 • MS-9600 • MS-9050
NAC Wiring and Supervision
For Class B, Style Y applications (figures 9 & 10 are typical): con-
nect the positive terminal of the notification appliance(s) to the
NAC+ terminal and the negative device terminal to the adjacent
NAC- terminal. Connect one (for each NAC) of the supplied EOL
resistors across the NAC+ and NAC- wires, at the ends farthest
away from the NAC terminal of the CMF-300-6.
For Class A, Style Z applications (figures 11 & 12 are typical) wire
the NACs per table 2. The A/B select shunt must be removed
prior to connecting the CMF-300-6 to the SLC. The EOL resistors
should not be used. The CMF-300-6 is capable of supporting 3
Class A, Style Z NACs. The CMF-300-6 will only respond at the
base address, base address +2, and base address +4 (assuming
no addresses have been disabled).
TABLE 2:
NAC# (+) CONNECTIONS (–) CONNECTIONS
+0 +0 NAC+, +1 NAC+,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE+
+0 NAC–, +1 NAC–,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE–
+2 +2 NAC+, +3 NAC+,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE+
+2 NAC–, +3 NAC–,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE–
+4 +4 NAC+, +5 NAC+,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE+
+4 NAC–, +5 NAC–,
NOTIFICATION APPLIANCE–
Power Supply Wiring and Supervision
Table 3 gives an overview of how the power connectors, T0–T5
and T10–T15, are interconnected by the circuit board (PCB). The
external supply connection points, at T0–T5, are marked by PS–
and PS+ on the PCB legend. Pin 1 is indicated by a dot next to
T10–T16. The odd pins, on T10–T16, always connect to PS– pins
(e.g. PS–, of the +0 NAC, is connected to T10–1 and T11–1). The
even pins always connect to PS+ pins (e.g. PS+, of the +5 NAC,
is connected to T15-4 and T16-2).
TABLE 3:
PS OR NAC NUMBER (TERMINAL / PINS) TERMINAL / PINS
+0 (T0 – BOTTOM / PS- & PS+)* T10 / 1 & 2, T11 / 1 & 2
+1 (T1 / PS- & PS+) T11 / 3 & 4, T12 / 1 & 2
+2 (T2 / PS- & PS+) T12 / 3 & 4, T13 / 1 & 2
+3 (T3 / PS- & PS+) T13 / 3 & 4, T14 / 1 & 2
+4 (T4 / PS- & PS+) T14 / 3 & 4, T15 / 1 & 2
+5 (T5 / PS- & PS+) T15 / 3 & 4, T16 / 1 & 2
NOTE: T0–TOP is reserved for SLC connections only (see Figure 8).

F300-21-00 5 I56-1874-011
Figure 9: Example of Class B, Style Y NAC configuration with a single supply dedicated to a single NAC
BASE ADDRESS
STATUS
INDICATORS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
4
5 6 7 8 9
0
7 8
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
TO NEXT
DEVICE
–
+
–
+
FROM PANEL OR
PREVIOUS DEVICE
–
+
–
+
SIGNAL LINE CIRCUIT (SLC) 32 VDC MAX.
SEE PANEL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR WIRE REQUIREMENTS.
(–)
(+)
POWER-LIMITED
AND SUPERVISED
TOP OF T0
EOLR-1
A2143-10
RED
VIO VIO
RED
BLK
BLK
(–)
(+)
+
–
47K
NOTE: EOL RELAY COIL CONNECTIONS MUST BE MADE USING
EOL RELAY CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES ON T10-T16 IN EVENT
THAT ALL NACS ON THE PCB HAVE DEDICATED SUPPLIES.
Figure 10: Example of Class B, Style Y NAC configuration with a single supply shared by 2 NACs
BASE ADDRESS
STATUS
INDICATORS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
4
5 6 7 8 9
0
7 8
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
TO NEXT
DEVICE
–
+
–
+
FROM PANEL OR
PREVIOUS DEVICE
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
SIGNAL LINE CIRCUIT (SLC) 32 VDC MAX.
SEE PANEL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR WIRE REQUIREMENTS.
POWER-LIMITED
AND SUPERVISED
TOP OF T0
+
–
(–)
(+)
VIO VIO
RED
BLK
(–)
(+)
(–)
(+)
(–)
(+)
A2143-10
EOLR-1
A2143-10
47K
47K
C0816-02
C0817-02

F300-21-00 6 I56-1874-011
Figure 11: Example of Class A, Style Z NAC configuration with a single supply dedicated to a single NAC
BASE ADDRESS
STATUS
INDICATORS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
4
5 6 7 8 9
0
7 8
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
REMOVE SHUNT FOR CLASS A.
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
TO NEXT
DEVICE
–
+
–
+
FROM PANEL OR
PREVIOUS DEVICE
–
+
–
+
–
+
SIGNAL LINE CIRCUIT (SLC) 32 VDC MAX.
SEE PANEL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR WIRE REQUIREMENTS.
(–)
(+)
POWER-LIMITED
AND SUPERVISED
TOP OF T0
EOLR-1
(TYP) RED
VIO VIO
RED
BLK
BLK
(–)
(+)
+
–
Figure 12: Example of Class A, Style Z NAC configuration with a single supply shared by 2 NACs
BASE ADDRESS
STATUS
INDICATORS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
4
5 6 7 8 9
0
7 8
6
5
4
3
2
1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
REMOVE SHUNT FOR CLASS A.
TO NEXT
DEVICE
–
+
–
+
FROM PANEL OR
PREVIOUS DEVICE
–
+
–
+
SIGNAL LINE CIRCUIT (SLC) 32 VDC MAX.
SEE PANEL INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR WIRE REQUIREMENTS.
(–)
(+)
POWER-LIMITED
AND SUPERVISED
TOP OF T0
EOLR-1
(TYP) RED
VIO VIO
RED
BLK
BLK
(–)
(+)
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
+
–
(–)
(+)
(–)
(+)
C0818-02
C0819-02

F300-21-00 7 I56-1874-011
©2007 Fire•Lite
Figure 13: Example of multiple boards sharing same external supply. Supply is shared by NACs +0 and +1 (on PCB 1) as
well as +3, +4, and +5 (on PCB 2). Refer to figures 9–12 for typical NAC wiring. Make certain lip on long power supply
jumper engages retaining tab on T10 or T16 as shown in View A-A.
BASE ADDRESS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
A
A
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
456789
0
78
6
5
4
3
21
910
11
12
13
14
15
BASE ADDRESS
NAC
PS
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
PS
—
+
+
—
NAC
TOP
BOT
– +
+ NAC –
– +
– PS +
SLC
PS
—
+
+
—
+1 +2 +3 +4 +5
T11
T10
T0
+0
T12
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
T13 T14 T15
T16
ENABLE POWER SUPPLY MONITOR
DISABLE SHORT CIRCUIT PROTECTION
—
+
+
—
A/B SELECT
DISABLE 1
DISABLE 2
DISABLE 3
0
1
2
3
456789
0
78
6
5
4
3
21
910
11
12
13
14
15
EXTERNAL
POWER
SUPPLY
+–
PCB 1 PCB 2
VIEW A-A
C0233-00
FCC Statement
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Table of contents
Other Fire-Lite Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Digi
Digi XBee ZigBee S2C user guide
Honeywell
Honeywell VQ400 Series Product handbook

Trane
Trane UNT-SVU011C Series Technical guide

Hypermax
Hypermax Mach 7 CXT installation instructions

Quantum
Quantum MKZ2 Instructions for use

Whelen Engineering Company
Whelen Engineering Company CanTrol Installation & operating guide