GENETIX > CLONESELECT IMAGER DESCRIPTION OF THE AUTOMATION API
Page 3of 8
Theory of Operation
Manual Mode
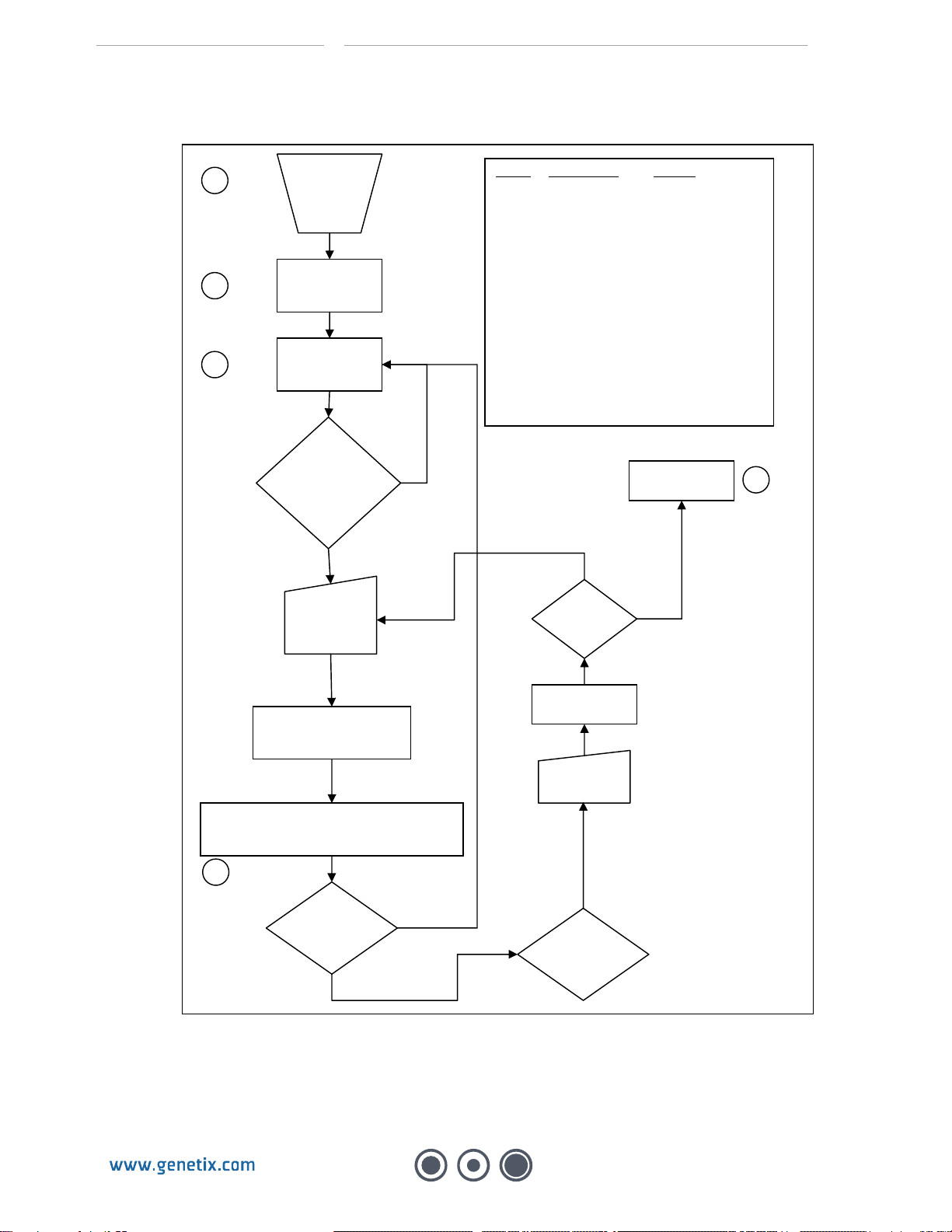
The CloneSelect Imager takes images of cell culture microplates and generates confluence data
for each well. When the instrument is used by a human operator in manual mode, they operate
the instrument by running processes in the software. There are two processes available that
image a well plate. One is named “Image Plate”, the other is named “Microscope mode”.
Microscope mode is a point-and-click way for the user to look at a well plate without saving the
result, so will not be discussed further.
Image Plate mode prompts the user for the well plate type and then asks them for the wells they
want to image. It next allows the user to adjust the focus, brightness and alignment of the
images. Finally, the wells are imaged and the results displayed.
Whilst it is possible for the user to save the process configuration to a file so that they can load it
later, in practice this is not used on the CloneSelect Imager. The saved processes do not contain
brightness, focus and alignment settings.
Automated Mode
To run the instrument from external software, it is first necessary to start the CloneSelect Imager
software as normal, then start the “Automation Process” from the start screen. When this
process runs, it opens the automation server and waits for an automation client to connect. It is
not possible for the user to operate the software whilst it is in this state. The automation client
can use the functions in the automation interface to control the instrument. When the automation
client has completed its task, it disconnects from the automation server. At this point, the user is
able to close the automation process in the CloneSelect Imager software and begin using
manual processes again.
Communication with the automation sever is via a SOAP protocol. Details of the automation API
and a sample application that illustrates its use are available once an order has been placed.
Please note that the Automation Process is an optional extra and is not included in the standard
CloneSelect Imager package.
Remote Results Viewing
An optional component of the CloneSelect Imager system is the Remote Data Viewer. This is a
software program that can be installed on any PC, and used to view the results of plates
scanned on the CloneSelect Imager. The results can be on the CloneSelect Imager PC and
shared using Windows® network folder sharing, on a Network server, on a CD or DVD, or
copied to the local PC and viewed from there.
The Remote Data Viewer is especially useful when used in conjunction with the CloneSelect
Imager that is fed by an automatic arm, since then it can be used on a remote PC to view recent
results whilst the CloneSelect Imager itself is in use.