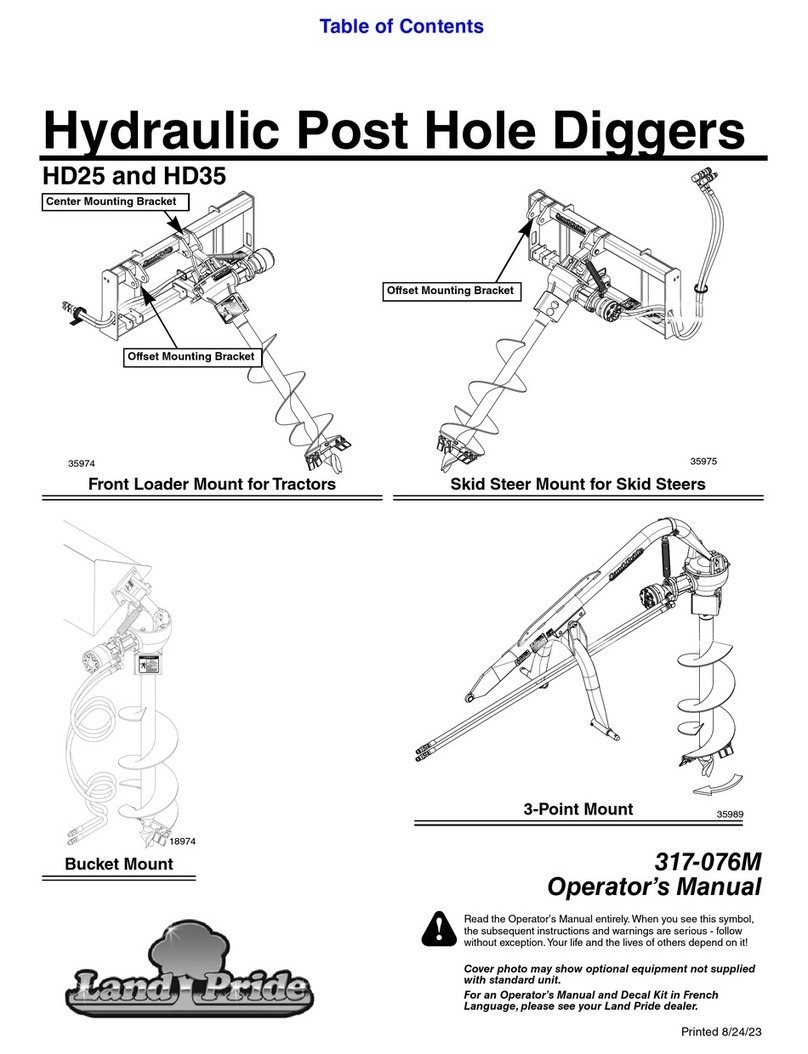
Mosquito Repellent
Model GSK-918
This circuit generates a frequency 10-30 kHz that creates a
sonic zone disturbing to mosquitoes. A piezo board creates the
frequency equal to the frequency generated by the mosquito
during flight causing the mosquito to believe he/she is flying
into a trap.
Technical Specifications
nPower ource: 3 VDC
nPower consumption: 20 mA max.
nPCB dimensions: 1.60 x 1.39 inches
Operating Principles
Transistor 1 and 2 control low frequency 10 kHz, while
transistors 3 and 4 control high frequency 30 kHz. This
circuit is designed to alternate the frequency and transmit
the sound through the piezo board.
PCB Assembl
Please refer to Figures 1, 2, and 3 for aid in component
placement. It is recommended to start with lower components
i.e. diodes, resisters, electrolyte capacitors, and transistors.
Be careful to check polarity with Figure 3 before soldering.
Take extra precaution to ensure electrolytic capacitors are
inserted correctly. If a problem is detected it is best too use a
desoldering pump or desoldering braids to remove component.
This will minimize potential damage to the printed circuit board.
Testing
Connect the piezo board at “PZ” point on PCB. Apply power
source and turn potentiometer “VR1,” a sharp sound should
be omitted from the piezo board.
Troubleshooting
The main cause of problems will come from misplaced
components or faulty soldering. Utilize figure 2 and 3 to
ensure proper placement, polarity and then check solder
points for connectivity.
Accessories
Use G B-03 (sold separately) to house the PCB and batteries.
Electronic Kit Set for Hobb & Education
Figure 1 Installing components
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176
TestEquipmentDepot.com