6
INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA
(OBSŁUGI)
SZLIFIERKA KĄTOWA
59G110
UWAGA: PRZED PRZYSTĄPIENIEM DO UŻYTKOWANIA
ELEKTRONARZĘDZIA NALEŻY UWAŻNIE PRZECZYTAĆ NINIEJSZĄ
INSTRUKCJĘ I ZACHOWAĆ JĄ DO DALSZEGO WYKORZYSTANIA.
SZCZEGÓŁOWE PRZEPISY BEZPIECZEŃSTWA
SZLIFIERKA KĄTOWA, OSTRZEŻENIA DOTYCZĄCE BEZPIE
CZEŃSTWA
Wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące szlifowania, szlifowania
papierem ściernym, pracy z użyciem szczotek drucianych i
przecinania ściernicą.
• Niniejsze elektronarzędzie może być stosowane jako
szlierka zwykła, szlierka do szlifowania papierem
ściernym, do szlifowania szczotkami drucianymi i jako
urządzenie do przecinania ściernicowego. Należy stosować
się do wszystkich wskazówek bezpieczeństwa, instrukcji,
opisów i danych, dostarczonych wraz z elektronarzędziem.
Niestosowanie się do poniższych zaleceń może stwarzać
niebezpieczeństwo porażenia prądem, pożaru i/lub ciężkich obrażeń
ciała.
• Niniejsze elektronarzędzie nie może być wykorzystywane do
polerowania. Zastosowanie elektronarzędzia do innej, niż przewidziana
czynności roboczej, może stać się przyczyną zagrożeń i obrażeń.
• Nie należy używać osprzętu, który nie jest przewidziany i
polecany przez producenta specjalnie do tego urządzenia.
Fakt, że osprzęt daje się zamontować do elektronarzędzia, nie jest
gwarantem bezpiecznego użycia.
• Dopuszczalna prędkość obrotowa stosowanego narzędzia
roboczego nie może być mniejsza niż podana na
elektronarzędziu maksymalna prędkość obrotowa.
Narzędzie robocze, obracające się z szybszą niż dopuszczalna
prędkością, może się złamać, a jego części odprysnąć.
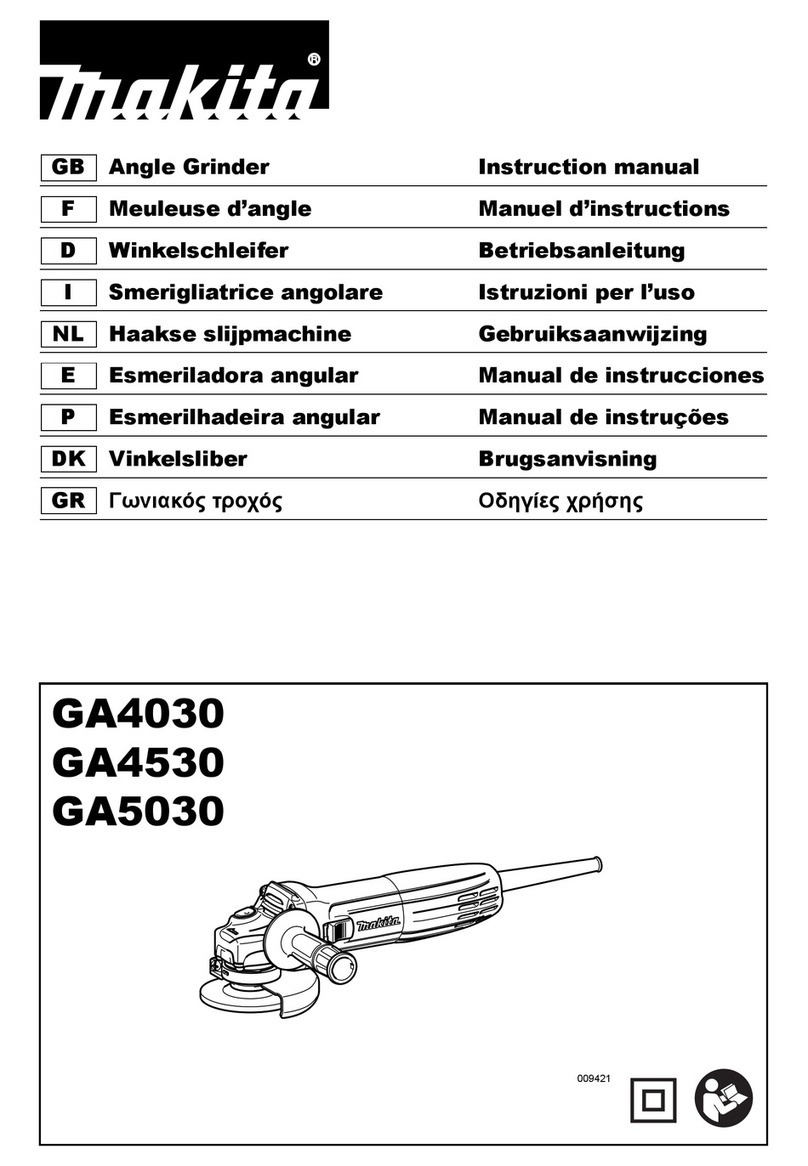
• Średnica zewnętrzna i grubość narzędzia roboczego muszą
odpowiadać wymiarom elektronarzędzia. Narzędzia robocze o
niewłaściwych wymiarach nie mogą być wystarczająco osłonięte lub
kontrolowane.
• Narzędzia robocze z wkładką gwintowaną muszą dokładnie
pasować na gwint na wrzecionie. W przypadku narzędzi
roboczych, mocowanych przy użyciu kołnierza średnica
otworu narzędzia roboczego musi być dopasowana
do średnicy kołnierza. Narzędzia robocze, które nie mogą
być dokładnie osadzone na elektronarzędziu, obracają się
nierównomiernie, bardzo mocno wibrują i mogą spowodować utratę
kontroli nad elektronarzędziem.
• Wżadnymwypadkunienależyużywaćuszkodzonychnarzędzi
roboczych. Przed każdym użyciem należy skontrolować
oprzyrządowanie, np. ściernice pod kątem odprysków i
pęknięć, talerze szlierskie pod kątem pęknięć, starcia
lub silnego zużycia, szczotki druciane pod kątem luźnych
lub złamanych drutów. W razie upadku elektronarzędzia
lub narzędzia roboczego, należy sprawdzić, czy nie uległo
ono uszkodzeniu, lub użyć innego, nieuszkodzonego
narzędzia. Jeśli narzędzie zostało sprawdzone i umocowane,
elektronarzędzie należy włączyć na minutę na najwyższe
obroty, zwracając przy tym uwagę, by osoba obsługująca i
osoby postronne znajdujące się w pobliżu, znalazły się poza
strefą obracającego się narzędzia. Uszkodzone narzędzia łamią
się najczęściej w tym czasie próbnym.
• Należy nosić osobiste wyposażenie ochronne. W zależności od
rodzaju pracy, należy nosić maskę ochronną pokrywającą całą
twarz, ochronę oczu lub okulary ochronne. W razie potrzeby
należy użyć maski przeciwpyłowej, ochrony słuchu, rękawic
ochronnych lub specjalnego fartucha, chroniącego przed małymi
cząstkami ścieranego i obrabianego materiału. Należy chronić oczy
przed unoszącymi się w powietrzu ciałami obcymi, powstałymi w czasie
pracy. Maska przeciwpyłowa i ochronna dróg oddechowych muszą
ltrować powstający podczas pracy pył. Oddziaływanie hałasu przez
dłuższy okres, może doprowadzić do utraty słuchu.
• Należy uważać, by osoby postronne znajdowały się w
bezpiecznej odległości od strefy zasięgu elektronarzędzia.
Każdy, kto znajduje się w pobliżu pracującego
elektronarzędzia, musi używać osobistego wyposażenia
ochronnego. Odłamki obrabianego przedmiotu lub pęknięte
narzędzia robocze mogą odpryskiwać i spowodować
obrażenia również poza bezpośrednią strefą zasięgu.
• Podczas wykonywania prac, przy których narzędzie
mogłoby natrać na ukryte przewody elektryczne
lub na własny przewód zasilający, należy je trzymać
wyłącznie za izolowane powierzchnie rękojeści.
Kontakt z przewodem sieci zasilającej może spowodować
przekazanie napięcia na części metalowe elektronarzędzia, co
mogłoby spowodować porażenie prądem elektrycznym.
• Przewód sieciowy należy trzymać z dala od obracających się
narzędzi roboczych. W przypadku utraty kontroli nad narzędziem,
przewód sieciowy może zostać przecięty lub wciągnięty, a dłoń lub
cała ręka mogą dostać się w obracające się narzędzie robocze.
• Nigdy nie wolno odkładać elektronarzędzia przed całkowitym
zatrzymaniem się narzędzia roboczego. Obracające się
narzędzie może wejść w kontakt z powierzchnią, na którą jest
odłożone, przez co można stracić kontrolę nad elektronarzędziem.
• Nie wolno przenosić elektronarzędzia, znajdującego się w
ruchu. Przypadkowy kontakt ubrania z obracającym się narzędziem
roboczym może spowodować jego wciągnięcie i wwiercenie się
narzędzia roboczego w ciało osoby obsługującej.
• Należy regularnie czyścić szczeliny wentylacyjne
elektronarzędzia. Dmuchawa silnika wciąga kurz do obudowy, a
duże nagromadzenie pyłu metalowego może spowodować zagrożenie
elektryczne.
• Nie należy używać elektronarzędzia w pobliżu materiałów
łatwopalnych. Iskry mogą spowodować ich zapłon.
• Nie należy używać narzędzi, które wymagają płynnych
środków chłodzących. Użycie wody lub innych płynnych środków
chłodzących może doprowadzić do porażenia prądem
Odrzut i odpowiednie wskazówki bezpieczeństwa
•Odrzut jest nagłą reakcją elektronarzędzia na zablokowanie lub
zawadzanie obracającego się narzędzia, takiego jak ściernica,
talerz szlifierski, szczotka druciana itd. Zaczepienie się lub
zablokowanie prowadzi do nagłego zatrzymania się obracającego
narzędzia roboczego. Niekontrolowane elektronarzędzie zostanie
przez to szarpnięte w kierunku przeciwnym do kierunku obrotu
narzędzia roboczego. Gdy, np. ściernica zatnie się lub zakleszczy
w obrabianym przedmiocie, zanurzona w materiale krawędź
ściernicy, może się zablokować i spowodować jej wypadnięcie lub
odrzut. Ruch ściernicy (w kierunku osoby obsługującej lub od niej)
uzależniony jest wtedy od kierunku ruchu ściernicy w miejscu
zablokowania. Oprócz tego ściernice mogą się również złamać.
Odrzut jest następstwem niewłaściwego lub błędnego użycia
elektronarzędzia. Można go uniknąć przez zachowanie opisanych
poniżej odpowiednich środków ostrożności.
• Elektronarzędzie należy mocno trzymać, a ciało i ręce ustawić
w pozycji, umożliwiającej złagodzenie odrzutu. Jeżeli w skład
wyposażenia standardowego wchodzi uchwyt dodatkowy,
należy go zawsze używać, żeby mieć jak największą kontrolę
nad siłami odrzutu lub momentem odwodzącym podczas
rozruchu. Osoba obsługująca urządzenie może opanować
szarpnięcia i zjawisko odrzutu poprzez zachowanie odpowiednich
środków ostrożności.
• Nie należy nigdy trzymać rąk w pobliżu obracających się
narzędzi roboczych. Narzędzie robocze może wskutek odrzutu
zranić rękę.
• Należy trzymać się z dala od strefy zasięgu, w której poruszy
się elektronarzędzie podczas odrzutu. Na skutek odrzutu,
elektronarzędzie przemieszcza się w kierunku przeciwnym do ruchu
ściernicy w miejscu zablokowania.