3
ROTATING PARTS MAY BE DANGEOUS:
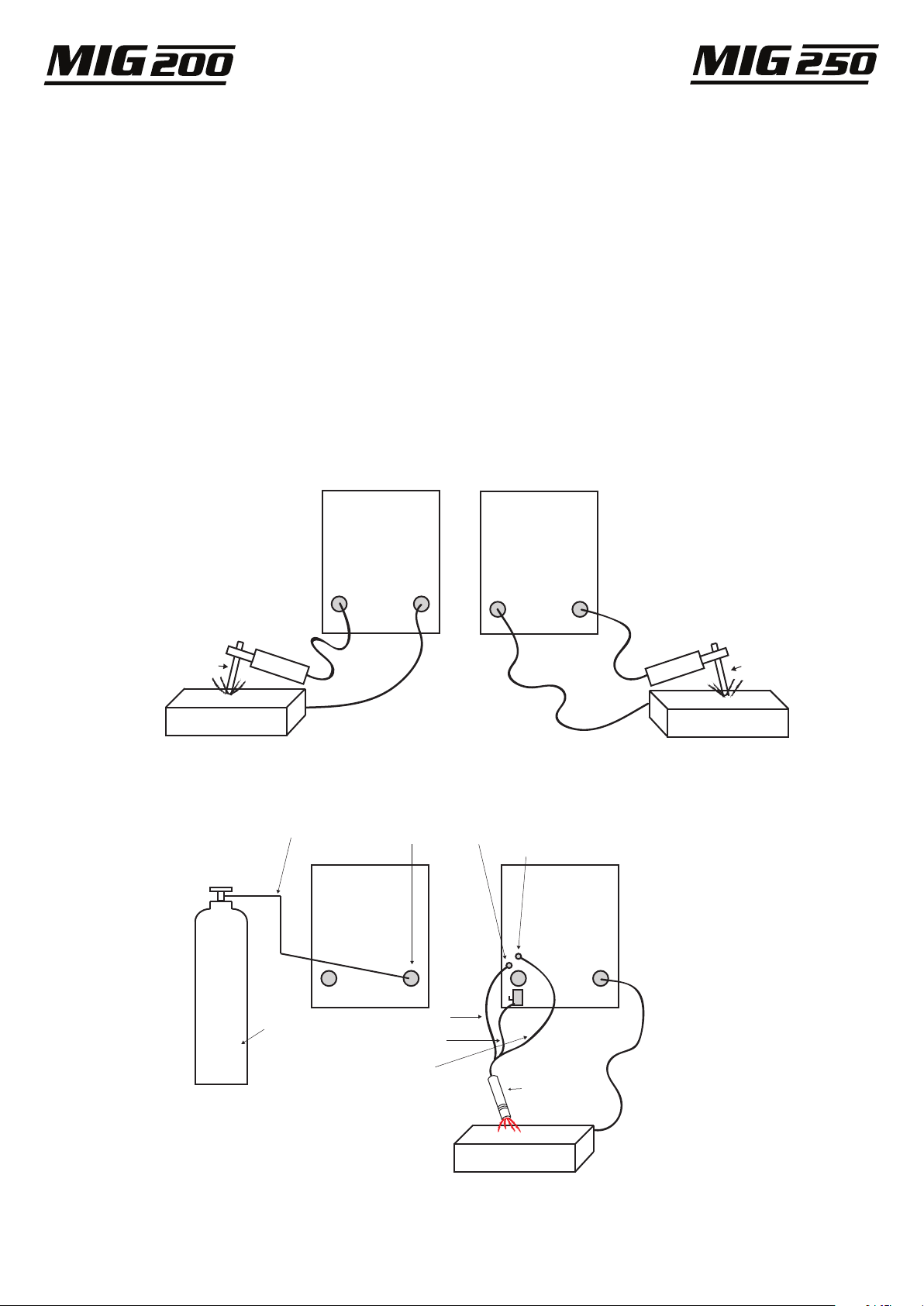
• Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct
shielding gas for the process used and properly operating
regulators designed for the gas and pressure used. All hoses,
fittings, etc. should be suitable for the application and
maintained in good condition.
• Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely
chained to an undercarriage or fixed support.
• Cylinders should be located:
- Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected
to physical damage.
- A safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations
and any other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
• Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other
electrically “hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
• Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve
outlet when opening the cylinder valve.
• Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand
tight except when the cylinder is in use or connected for
use.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS:
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes
localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). The discussion
on the effect of EMF is ongoing all around the world. Until
now, no material evidences show that EMF may have effects
on health. However, the research on damage of EMF is still
ongoing. Before any conclusions are made, we should
minimize exposure to EMF as much as possible.
In order to minimize EMF, we should use the following
procedures:
• Route the electrode and work cables together – Secure
them with tape when possible.
• All cables should be put away and far from the operator.
• Never coil the power cable around your body.
• Make sure the welding machine and power cable are as
far away from the operator as possible.
• Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as
possible to the area being welded.
• People with heart pacemakers should stay away from the
welding area.
The equipment complies with electromagnetic compatibility
on the class A which is intended for users in any locations
other than residential locations where the electrical power is
provided by public low-voltage supply system.
• Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant
material to protect your skin and that of your helpers from
the arc rays.
• Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flam-
mable screening and /or warn them not to watch the arc nor
expose themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.
WELDING SPARKS CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION.
• Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If this is not
possible, cover them to prevent the welding sparks from
starting a fire. Remember that welding sparks and hot
materials from welding can easily go through small cracks
and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near hydrau-
lic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
• Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site,
special precautions should be used to prevent hazardous
situations.
• When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode
circuit is touching the work or ground. Accidental contact
can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
• Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until
the proper steps have been taken to insure that such
procedures will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from
substances inside. They can cause an explosion even though
they have been “cleaned”.
• Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting
or welding. They may explode.
• Connect the work cable to the work as close to the
welding area as practical. Work cables connected to the
building framework or other locations away from the
welding area increase the possibility of the welding current
passing through lifting chains, crane cables or other alter-
nate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting
chains or cables until they fail.