3-2
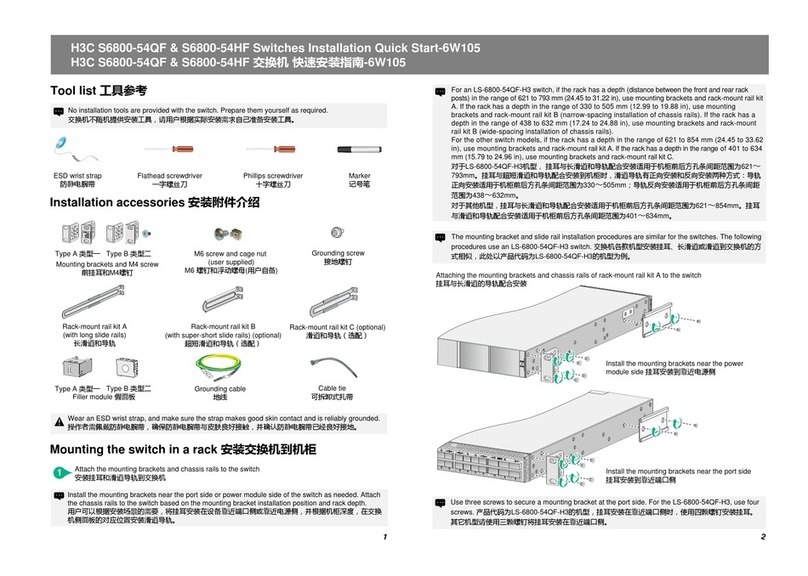
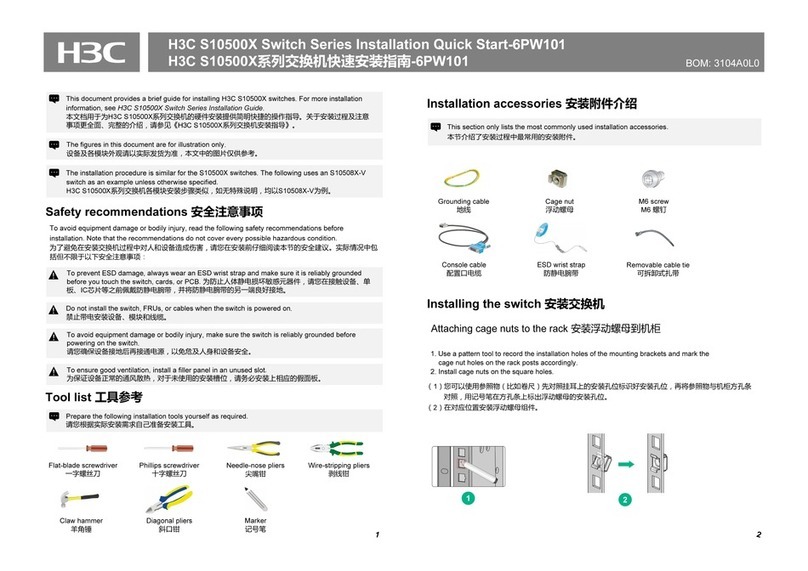
Features Description
DLDP
In the use of fibers, link errors, namely unidirectional links, are likely to
occur. DLDP is designed to detect such errors. This document describes:
zDLDP Introduction
zEnabling DLDP
zSetting DLDP Mode
zSetting the Interval for Sending Advertisement Packets
zSetting the DelayDown Timer
zSetting the Port Shutdown Mode
zConfiguring DLDP Authentication
zResetting DLDP State
LLDP
LLDP enables a device tomaintain and manage its own and its immediate
neighbor’s device information, based on which the network management
system detects and determines the conditions of the communications
links. This document describes:
zIntroduction to LLDP
zPerforming Basic LLDP Configuration
zConfiguring LLDP Trapping
MSTP
MSTP is used to eliminate loops in a LAN. It is compatible with STP and
RSTP. This document describes:
zIntroduction to MSTP
zConfiguring the Root Bridge
zConfiguring Leaf Nodes
zPerforming mCheck
zConfiguring the VLAN Ignore Feature
zConfiguring Digest Snooping
zConfiguring No Agreement Check
zConfiguring Protection Functions
Smart Link
Smart Link is a solution for active-standby link redundancy backup and
rapid transition in dual-uplink networking. This document describes:
zSmart Link Overview
zConfiguring a Smart Link Device
zConfiguring an Associated Device
Monitor Link
Monitor link is a port collaboration function used to enable a device to be
aware of the up/down state change of the ports on an indirectly connected
link. This document describes:
zMonitor Link Overview
zConfiguring Monitor Link
VLAN
Using the VLAN technology, you can partition a LAN into multiple logical
LANs. This document describes:
zIntroduction to VLAN
zTypes of VLAN
zIsolate-user-vlan configuration
zIntroduction and Configuration of Voice VLAN
GVRP
GVRP is a GARP application. This document describes:
zGARP overview
zGVRP configuration
zGARP Timers configuration