Haier RF-8888-39 User manual
Other Haier Refrigerator manuals

Haier
Haier FROST FREE REFRIGERATOR User manual

Haier
Haier HBC-150 User manual

Haier
Haier HYCD-282 User manual

Haier
Haier HB16WMAA User manual

Haier
Haier HRF-183 Instruction Manual

Haier
Haier HRF-800DGS8 User manual

Haier
Haier BC-117SS User manual

Haier
Haier HTD635WISS User manual

Haier
Haier HSP03WNAWW User manual

Haier
Haier HTMR315 User manual

Haier
Haier JR-N40C User manual

Haier
Haier HTR3619FN Series User manual

Haier
Haier REFRIGERATOR / FREEZER COMBO HRF-6631RG User manual

Haier
Haier HBX-IC User manual
Haier
Haier HRF-221FR/A User manual
Haier
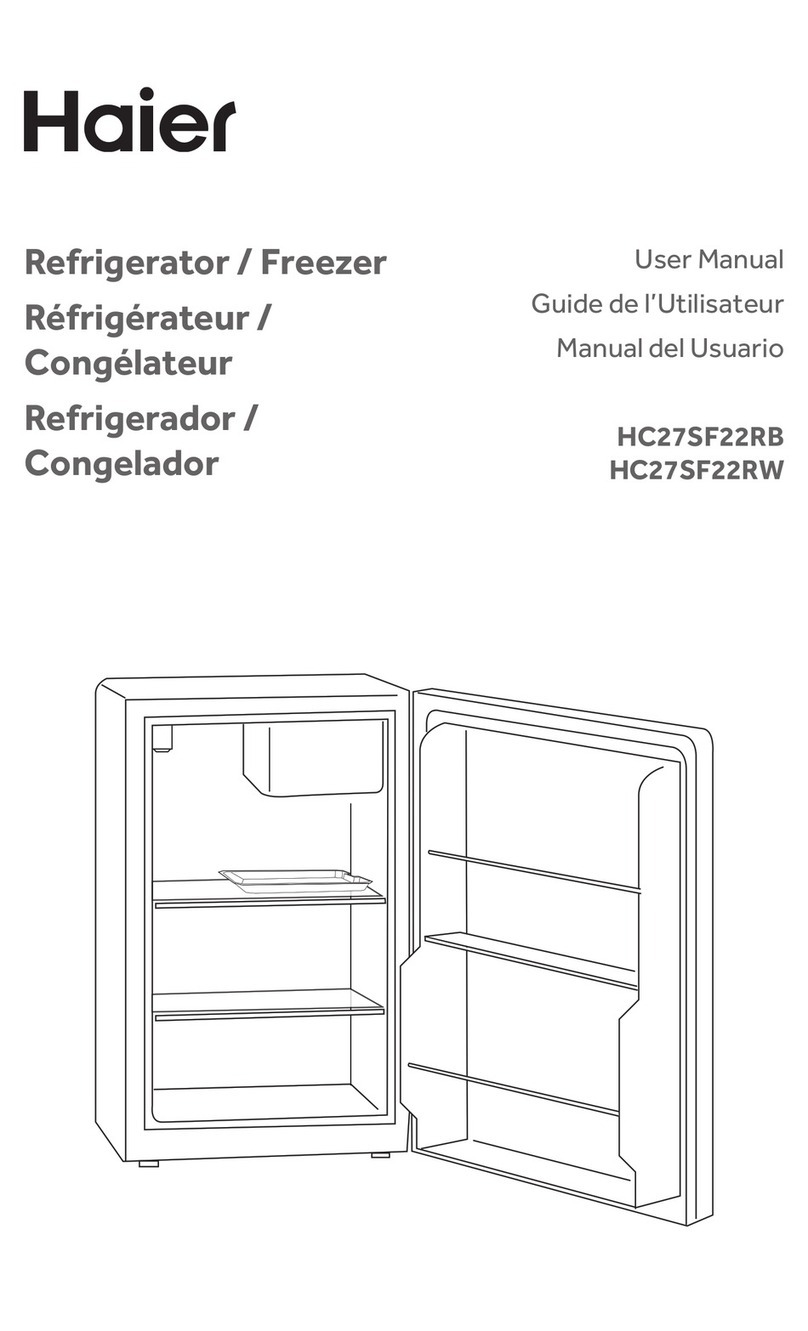
Haier HC27SF22RB User manual

Haier
Haier JR-NF140A User manual

Haier
Haier AFL631CB User manual
Haier
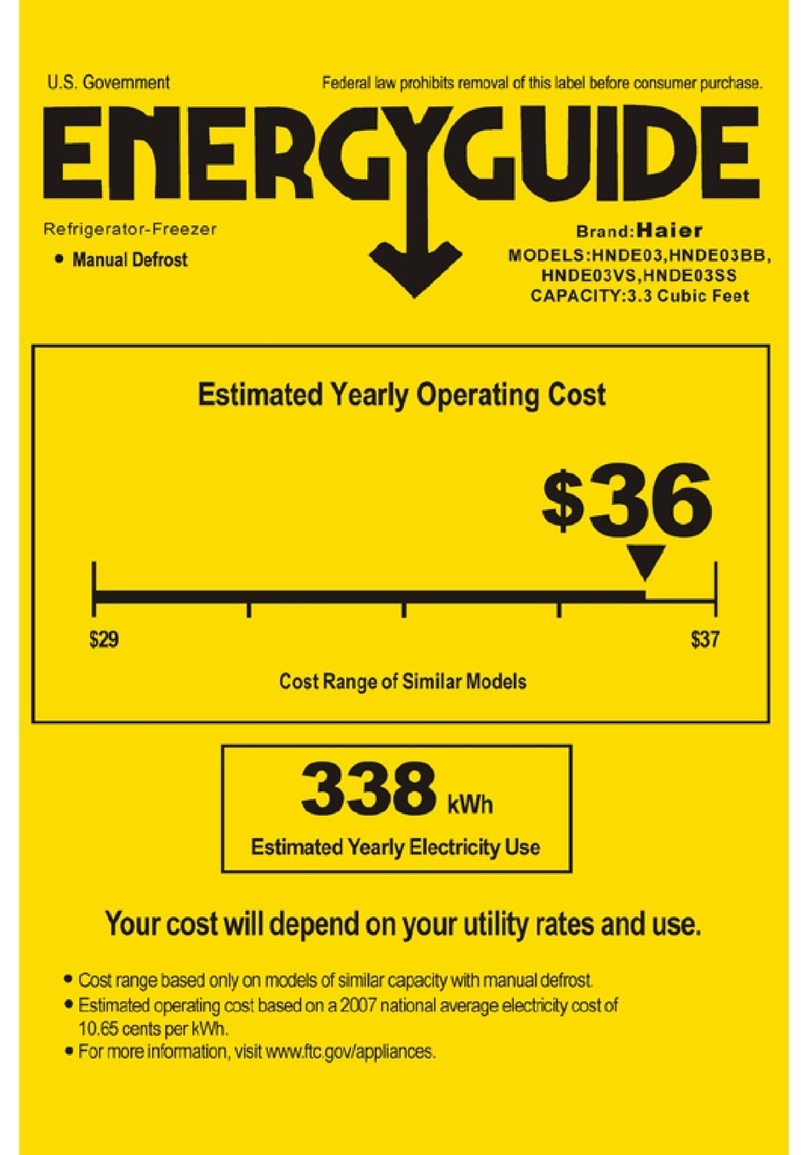
Haier HNDE03 Assembly instructions

Haier
Haier HSBS582AS User manual