HELI G3 Series Installation and operating instructions







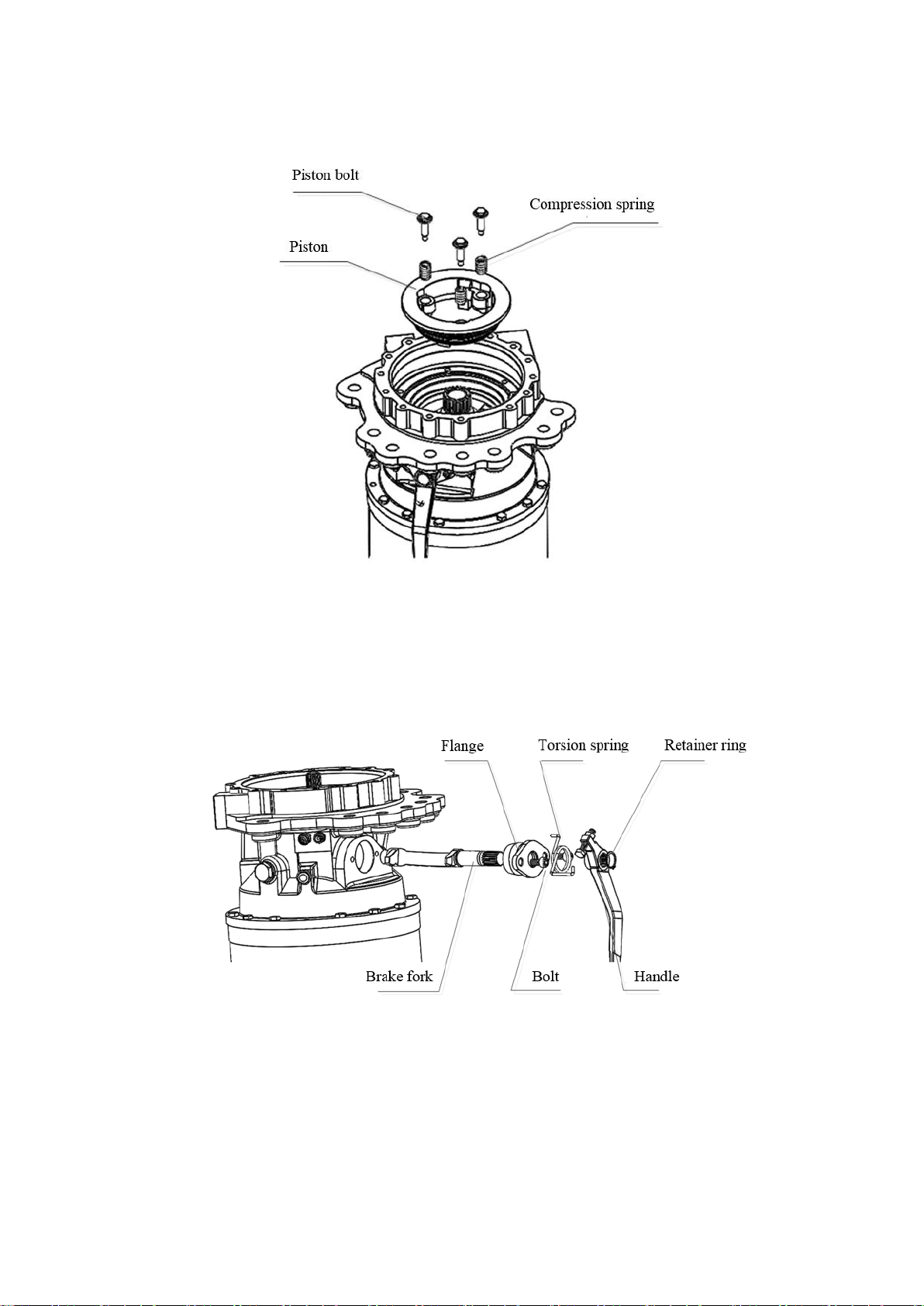
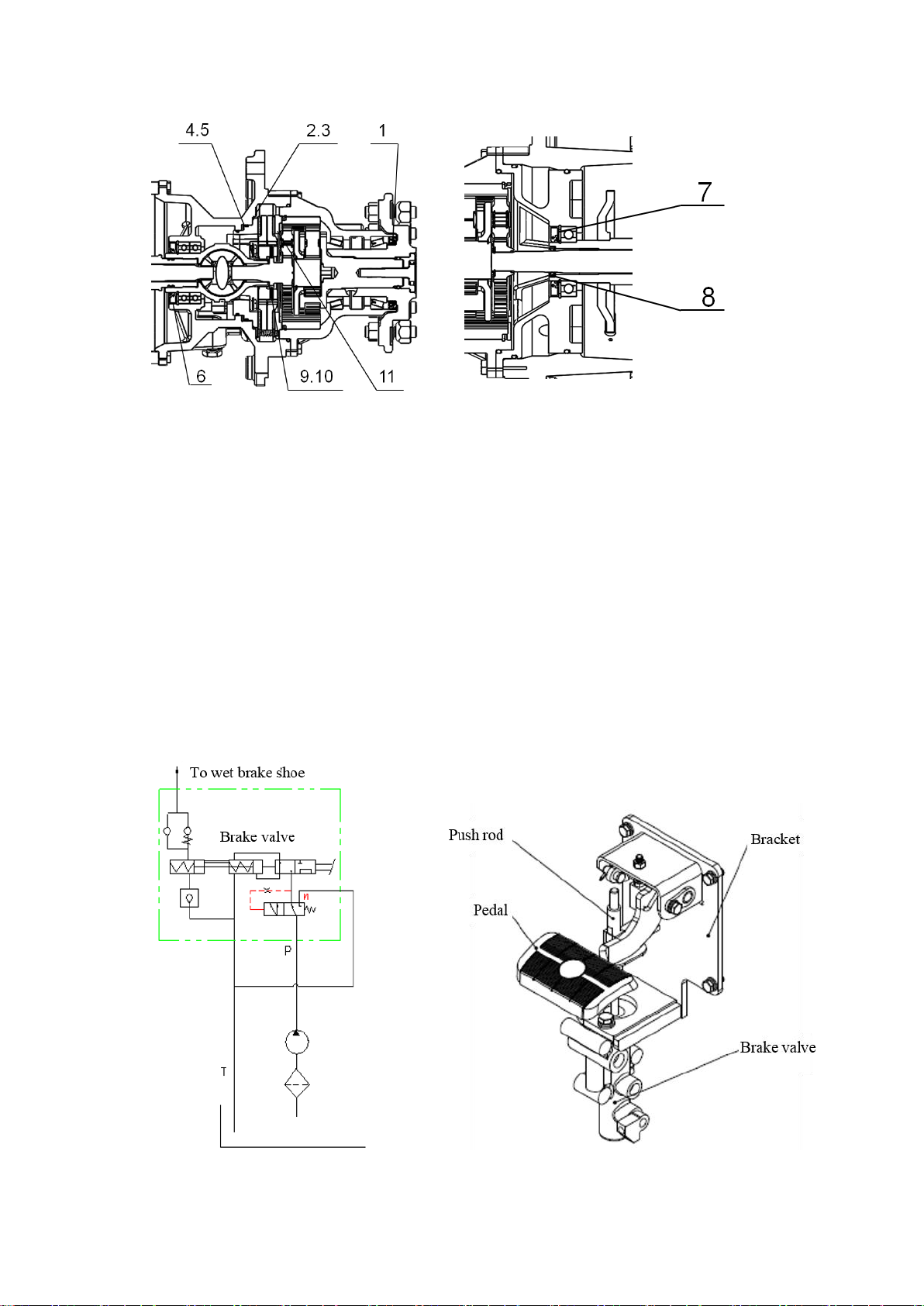
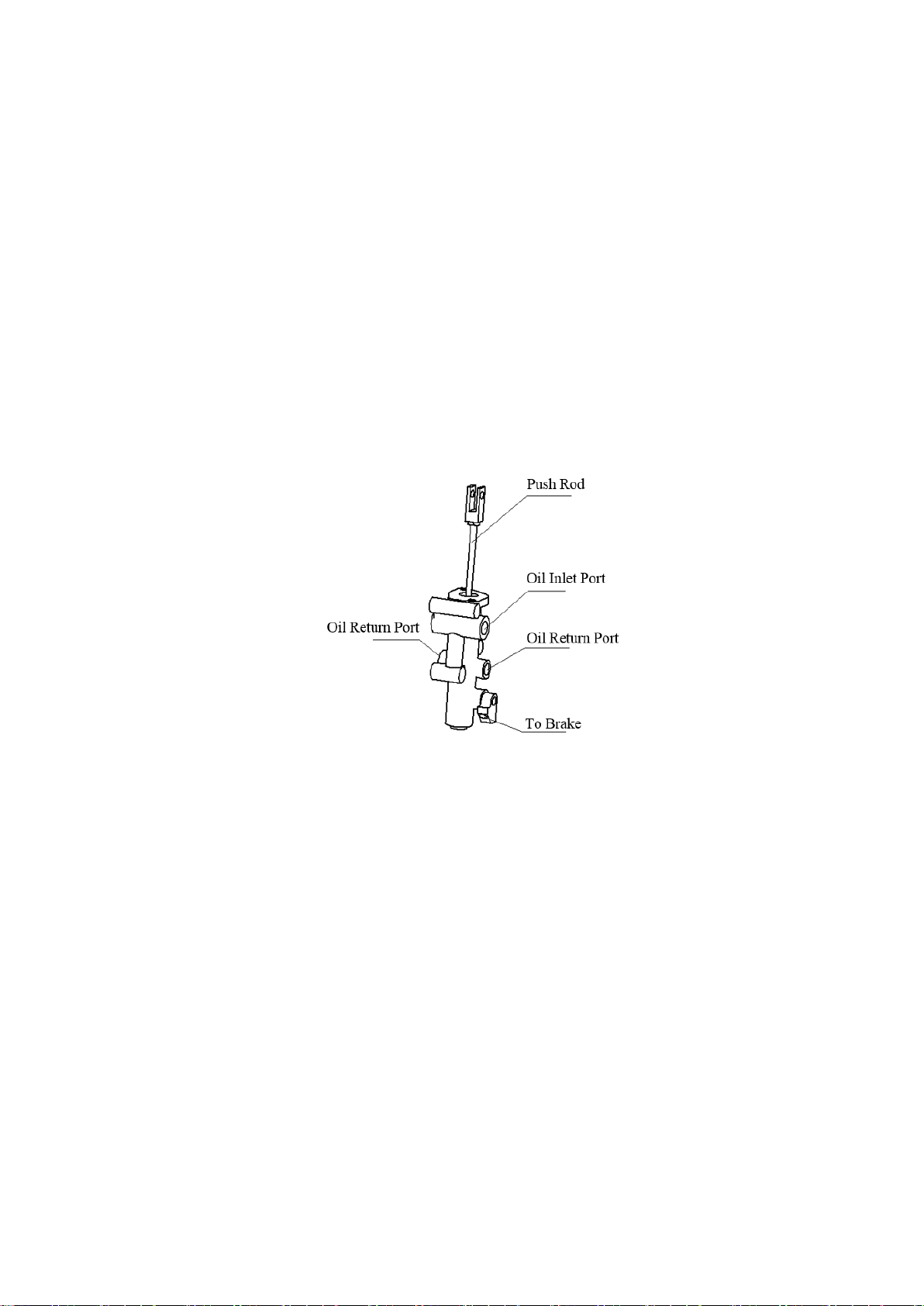



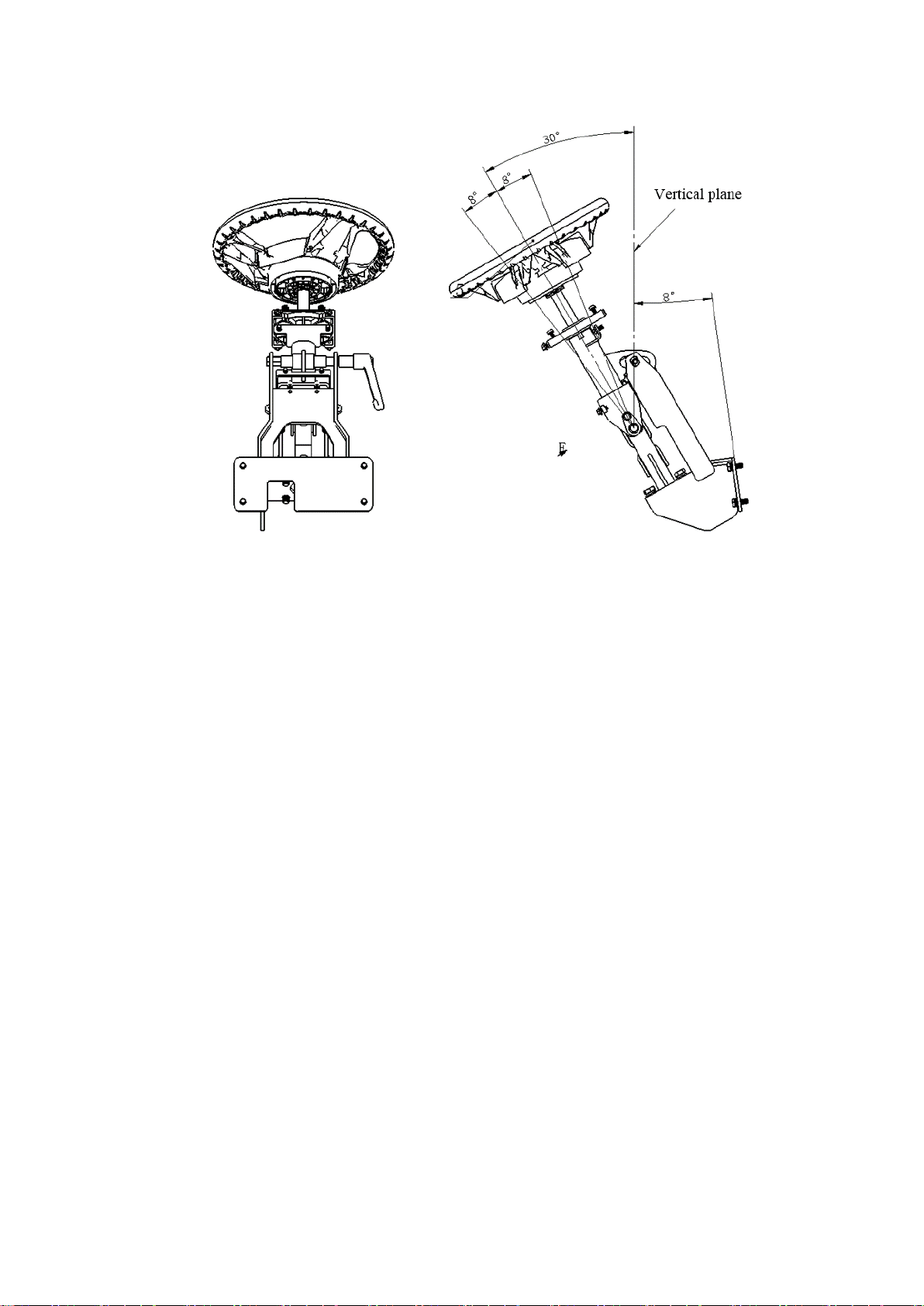
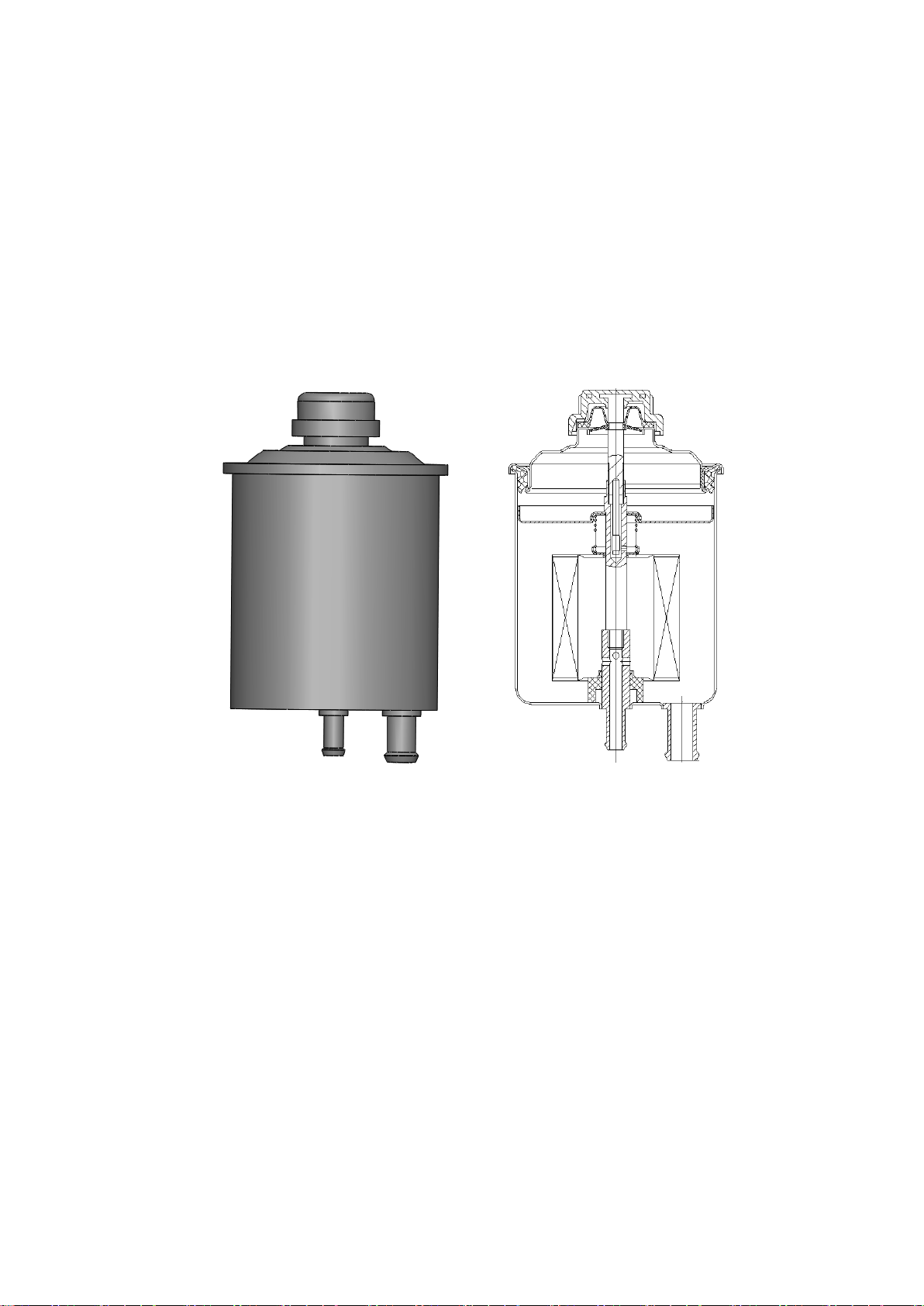

Table of contents
Other HELI Truck manuals

HELI
HELI CPD15 Installation and operating instructions

HELI
HELI CBD15J-Li2 Series User manual

HELI
HELI G Series Installation and operating instructions

HELI
HELI gieen Series Installation and operating instructions

HELI
HELI green Series User manual

HELI
HELI CQDH13 User manual

HELI
HELI CBD35-530 User manual
Popular Truck manuals by other brands

HARBEN
HARBEN 4018 Operation & maintenance manual

Chevrolet
Chevrolet 30 Series 1967 Service manual

Chevrolet
Chevrolet LIGHT DUTY TRUCK 1975 Service manual

Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz Unimog 416 1976 instruction manual

Iveco
Iveco DAILY 4x4 2020 Body builder instructions

Lift-Rite
Lift-Rite LCR55 Owner's Manual, Operating Instructions Manual, and Replacement Parts Manual

Komatsu
Komatsu HD1500-5 Operation & maintenance manual

swaploader
swaploader SL-2418 Parts and operation manual

MERLO
MERLO PANORAMIC User and maintenance manual

Taylor-Dunn
Taylor-Dunn ET 1-50 Operation and maintenance manual

U-Line
U-Line H-9379 manual

freightliner
freightliner BUSINESS CLASS M2 Driver manual