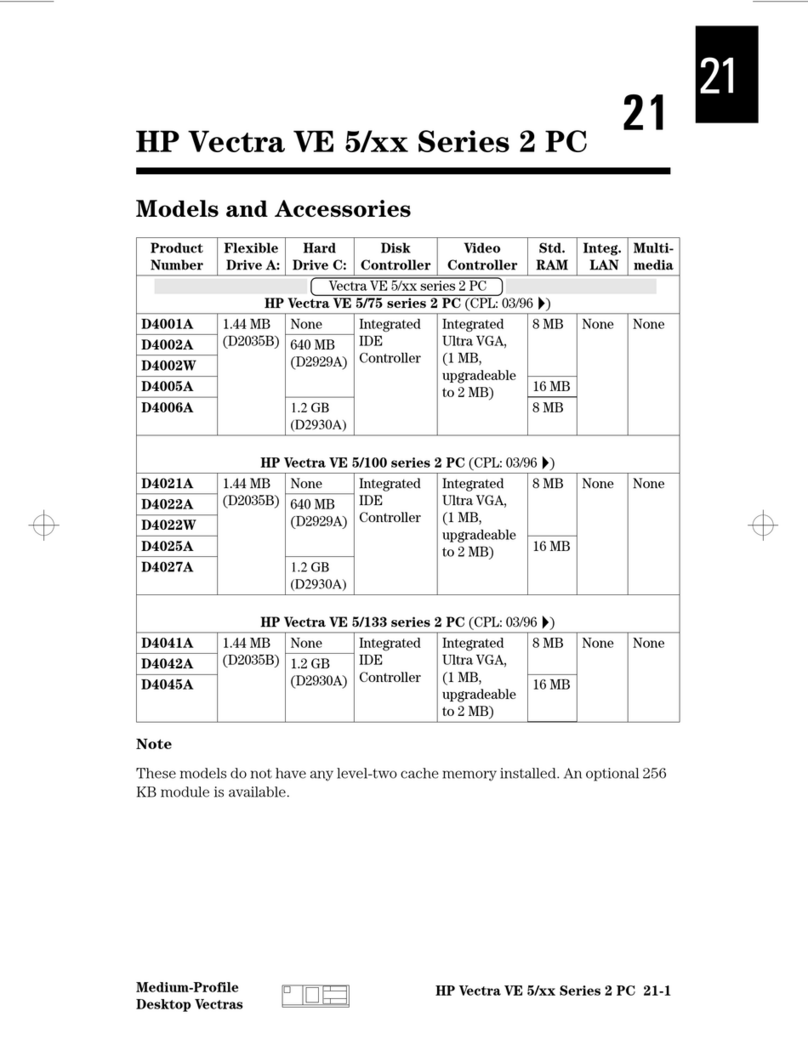
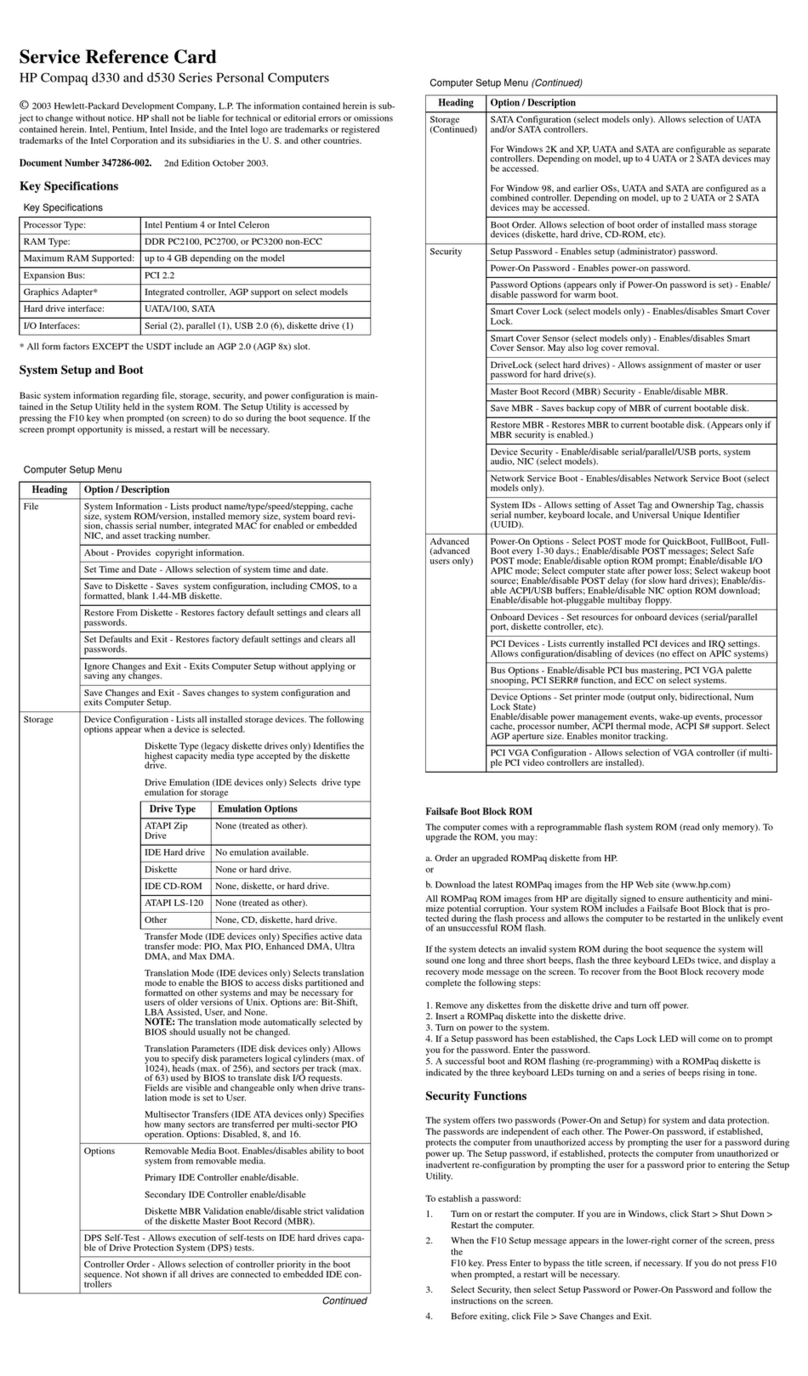
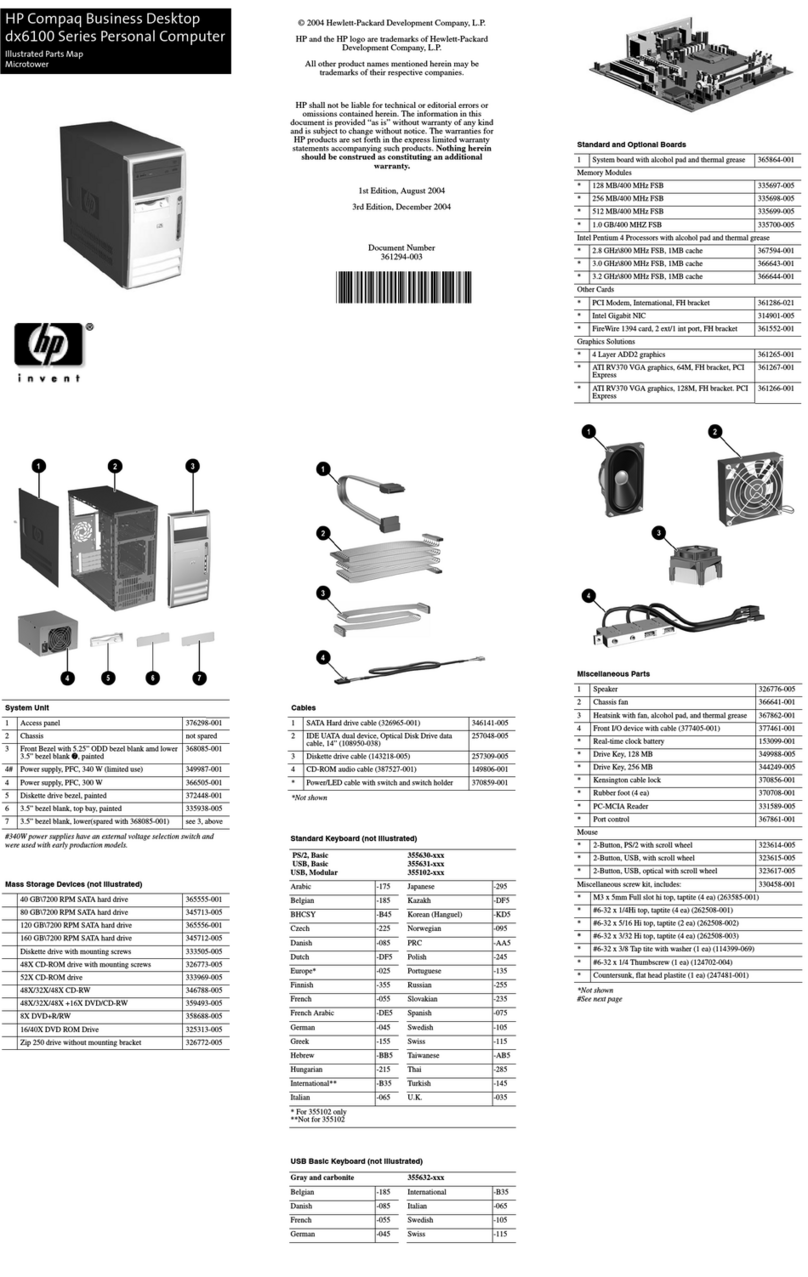
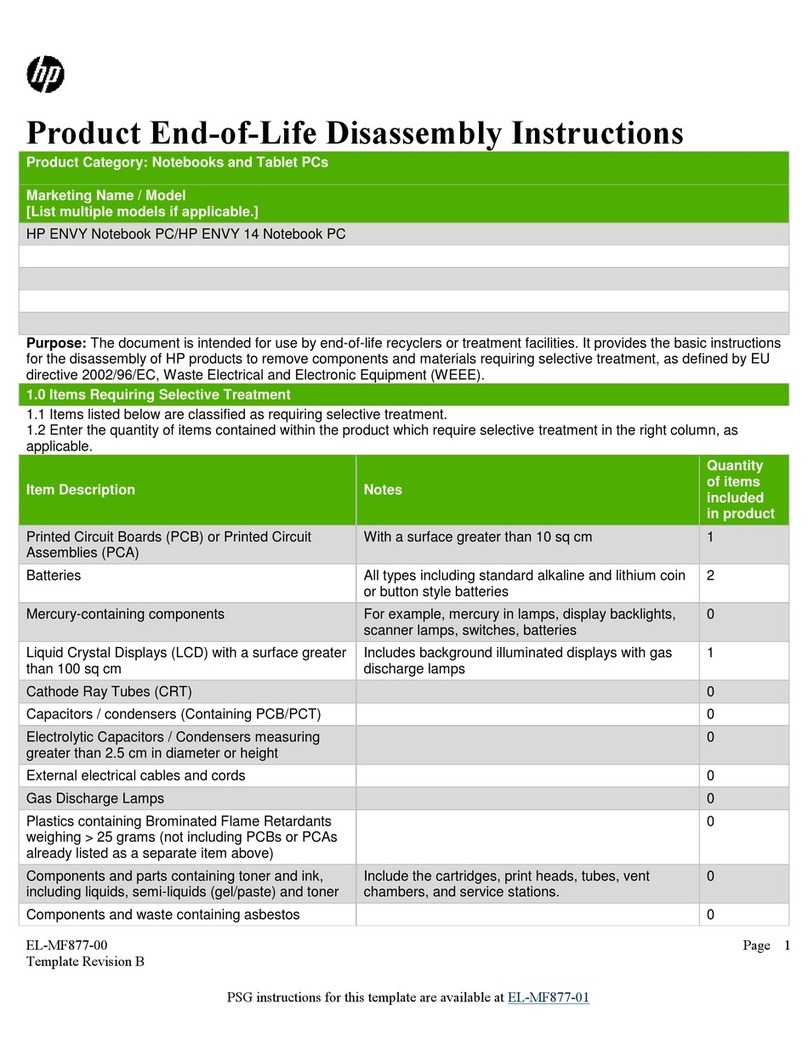
Audio
All HP Workstations come with built-in audio hardware. The audio hardware is supported by Advanced
Linux Sound Architecture (ALSA) sound drivers included with all modern Linux distributions.
The audio hardware provides basic playback and recording features. The ability to simultaneously play
audio from multiple sources, such as applications and CDROM, is provided by software mixing
functionality in the ALSA driver. The performance of software audio mixing and playback functionality
is greatly improved in ALSA version 1.0.13 and later drivers.
Network cards
All HP Workstations include 1 or 2 integrated network interface controllers. Specific network interface
controller cards are also supported as optional devices. Please refer to the Hardware Support Matrix
for HP Linux Workstations at http://www.hp.com/support/linux_hardware_matrix for details on which
cards are supported.
Hyper-threading
The 400, 600, and 800 Workstations support Intel Hyper-Threading Technology. This technology
can provide performance benefits in certain situations.
Hyper-Threading is enabled in the system BIOS. As the system is booting, press F10 to enter the BIOS
Setup Utility. Select Advanced > Processors. Use the arrow keys to set Hyper-Threading to Enable,
and then press F10 to exit the menu. Select the File > Save Changes and Exit. Hyper-Threading is
enabled when the system is restarted.
On most recent Linux distributions including RHEL 5.3, SLED/SLES 10 SP2, and SLED/SLES 11, the
kernel will automatically detect that Hyper-Threading is enabled and work correctly. Certain older Linux
distributions such as RHEL 4.7 require the use of the largesmp kernel for Hyper-Threading support on
dual-socket quad core 600 and 800 configurations.
NUMA
Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) is available on the 600, 800, and xw9400 Workstations.
NUMA offers the potential to improve memory bandwidth and latency for multi-process or multi-threaded
applications or workloads. Observed performance improvements depend on the operating system,
customer workload, system configuration, and the degree to which the applications used are designed
to be NUMA-aware/efficient.
NUMA requires that both processor sockets be populated, and installed memory should be balanced
between both processors for maximum performance.
NUMA is enabled if Memory Node Interleave is disabled in the system BIOS. As the system is booting,
press F10 to enter the BIOS Setup Utility. Select Advanced > Chipset/Memory. Use the arrow keys
to set Memory Node Interleave to Disable. Press F10 to exit the menu. Select File > Save Changes
and Exit. NUMA is enabled when the system is restarted.
The 600 and 800 BIOS also provide a NUMA Split Mode option, which must be set to Disable when
running Linux.
On most recent 64-bit Linux distributions, including RHEL 5.3, SLED/SLES 10 SP2, and SLED/SLES
11, the kernel automatically detects that NUMA is enabled. Certain older 64-bit Linux distributions such
as RHEL 4.7 require the use of the numa=acpi kernel parameter on the 600 and 800 Workstations.
ENWW Audio 3