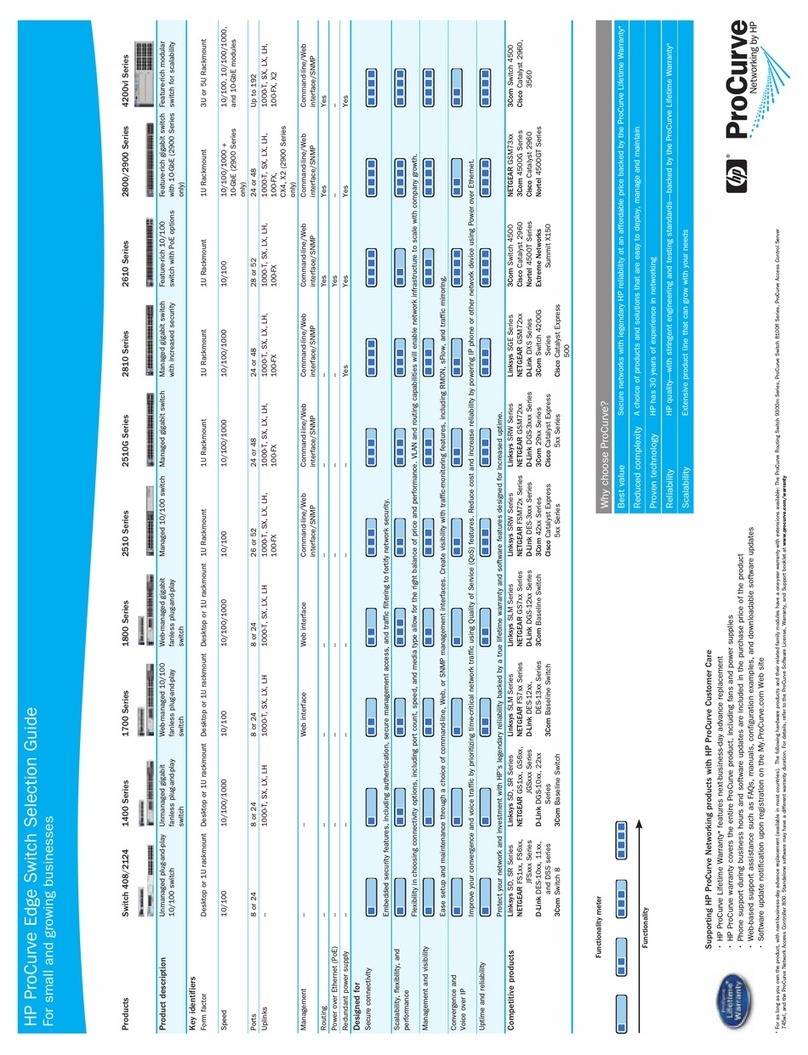
2
Features and benefits
Management
•Remote configuration and management: is
available through a secure Web browser or a
command-line interface (CLI)
•IEEE 802.1ab LLDP discovery: advertises and
receives management information from adjacent
devices on a network
•USB support:
–File copy: allows users to copy switch files to
and from a USB flash drive
•DHCP options: client allows automatic setting of
IP address
•SNMPv1, v2c, and v3: facilitate centralized
discovery, monitoring, and secure management of
networking devices
•NEW Network Time Protocol (NTP):
synchronizes timekeeping among distributed time
servers and clients; keeps consistent timekeeping
among all clock-dependent devices within the
network so that the devices can provide diverse
applications based on the consistent time
Connectivity
•Auto-MDIX: automatically adjusts for
straight-through or crossover cables on all 10/100
and 10/100/1000 ports
•Jumbo frames: on Gigabit Ethernet and
10-Gigabit ports, they allow high-performance
remote backup and disaster-recovery services
Performance
•Hardware-based wire-speed access control
lists (ACLs): feature-rich ACL implementation
(TCAM-based) helps ensure high levels of security
and ease of administration without impacting
network performance
Resiliency and high availability
•Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
(VRRP): allows groups of two routers to
dynamically back each other up to create highly
available routed environments
•Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP):
monitors link connectivity and shuts down ports at
both ends if unidirectional traffic is detected,
preventing loops in STP-based networks
•Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP):
allows users to bundle several physical ports
together to form a single logical channel
Manageability
•RMON (remote monitoring): provides
advanced monitoring and reporting capabilities for
statistics, history, alarms, and events
•Web interface: allows configuration of the switch
from any Web browser on the network
•Multiple configuration files: allow multiple
configuration files to be stored to a flash image
•Troubleshooting: ingress and egress port
monitoring enable network problem solving
Layer 2 switching
•16K MAC address table: provides access to
many Layer 2 devices
•4,094 port-based VLANs: provide security
between workgroups
•Gigabit Ethernet port aggregation: allows
grouping of ports to increase overall data
throughput to a remote device
•10 GbE port aggregation: allows grouping of
ports to increase overall data throughput to a remote
device
•Spanning Tree/MSTP, RSTP, and STP Root
Guard: prevent network loops
Layer 3 services
•Address Resolution Protocol (ARP):
determines the MAC address of another IP host in
the same subnet; supports static ARPs; gratuitous
ARP allows detection of duplicate IP addresses
Layer 3 routing
•Layer 3 IP routing:
–Static IP routing: provides basic routing
(supporting up to 1K static routes); allows manual
configuration of routing
Security
•Advanced processor queuing mechanism:
helps prevent denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, while
DHCP snooping helps ensure that devices can only
receive an IP address from a legitimate DHCP server
on the network
•IP Source Guard: helps prevent IP spoofing
attacks
•HTTPS management: provides secure Web
management