EN
III
Heavy Duty Diagnostic Tool HD I User’s Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Introduction...................................................................................................1
2. General Information......................................................................................1
2.1 On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) II ..................................................................1
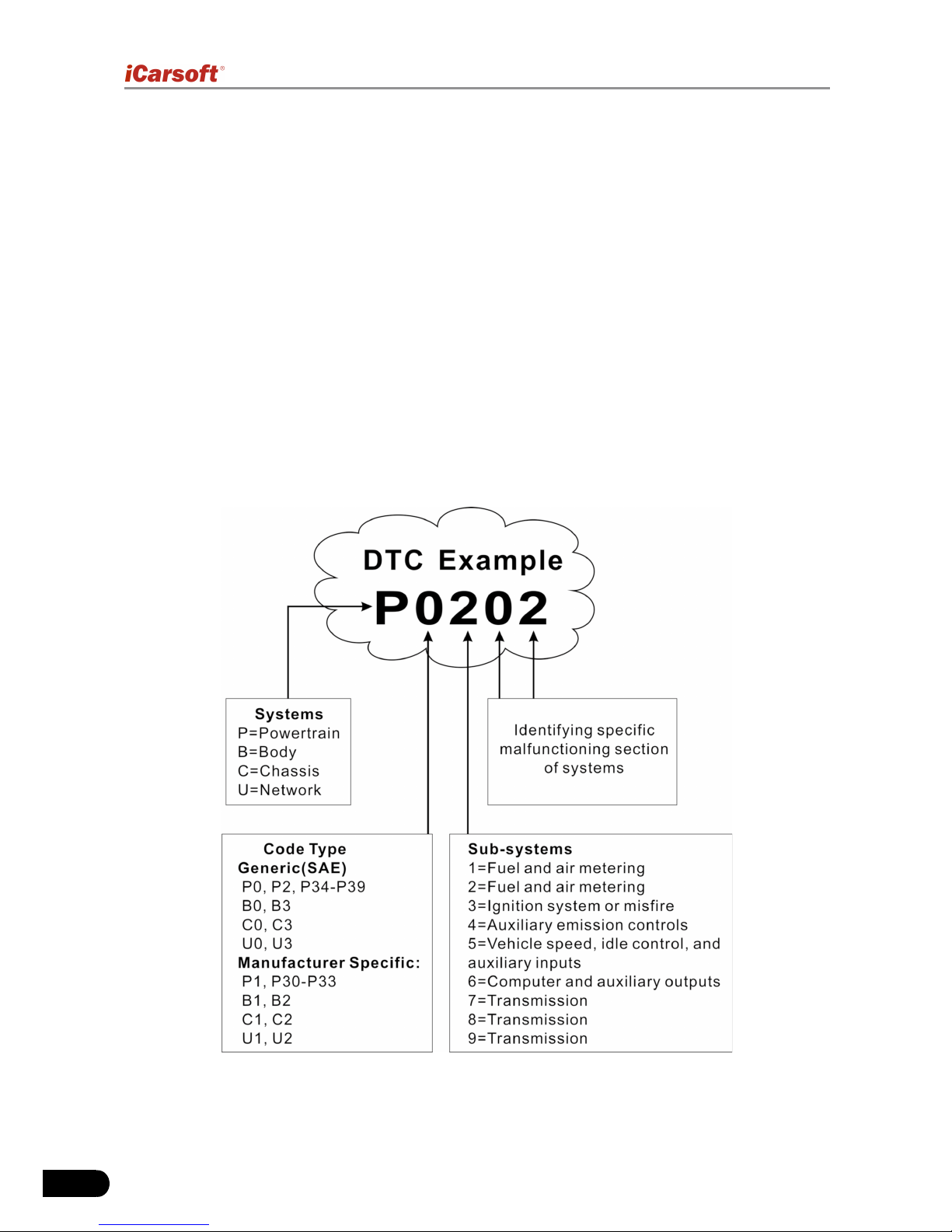
2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)..............................................................2
2.2.1 OBDII DTC..........................................................................................2
2.2.2 DTCs for J1587/J1708 and J1939......................................................3
2.3 J1708/J1587/J1939 ....................................................................................3
2.4 OBD II Denitions.......................................................................................4
3. Product Descriptions ....................................................................................6
3.1 Outline of HD I............................................................................................6
3.2 Specications .............................................................................................7
3.3 Accessories ................................................................................................7
3.4 Power supply..............................................................................................8
4. Connections & General Operations..............................................................9
4.1 Connections................................................................................................9
4.2 On-screen Buttons ...................................................................................10
4.3 Tool Setup.................................................................................................10
5. Diagnose ....................................................................................................11
5.1 HD OBD Diagnosing.................................................................................13
5.1.1 Read DTC.........................................................................................14
5.1.2 Clear DTC.........................................................................................14
5.1.3 Live Data...........................................................................................14
5.2 OBDII Diagnosing.....................................................................................15
5.2.1 Read Codes......................................................................................15
5.2.2 Erase Codes.....................................................................................16
5.2.3 I/M Readiness...................................................................................16
5.2.4 Data Stream......................................................................................17
5.2.5 View Freeze Frame ..........................................................................17
5.2.6 O2 sensor test ..................................................................................17
5.2.7 On-board monitor test.......................................................................17
5.2.8 Evap System.....................................................................................17
5.2.9 Vehicle Infomation ............................................................................17
6. How to Upgrade HD I .................................................................................18
6.1 HD I upgrading owchart..........................................................................18
6.2 User registration .......................................................................................18
6.3 Upgrading.................................................................................................19
7. FAQ ............................................................................................................20