Symptom
Unit fails to start
The sensor may not be connected or it is defective.
With the probe disconnected, use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance
between the probe wires. It should match the chart in Appendix B (see below).
If you read an OPEN or SHORT, replace the sensor. If a pressure sensor is used,
measure the DC voltage between GND and the sensor output at BWG and compare
your reading to the expected pressure in Appendix A.
Check the Line 1 power on the is being supplied by the same leg of
power which is also supplying the run capacitor common.
Fan overheats, over
amps or runs very
rough
Check with the motor manufacturer to see if the motor is able to be speed
controlled by reducing the input voltage. Verify the motor is a single phase PSC
motor.
The fan cycles from
full ON to full OFF
with little or no
modulation
Check the Hard start setting in the App. Too much hard start can drop pressure
Should the fan cycling persist, move the probe up several bends into the
condenser to increase the sensitivity to the condensing temperature.
placement on the condenser.
The fan does not
come on at all
Using an AC voltmeter, measure the voltage between the 24 VAC terminals. It
should read approximately 24 volts.
present. Check Line 1 of the
of power as the common of the Run capacitor.
Remove the thermistor probe from the terminal block and measure its resistance
at ambient temperature. Compare your reading at the appropriate temperature
in Appendix B to see if the actual resistance approximates the listed value.
a pressure sensor is used, measure the DC voltage between GND and the sensor
output at BWG and compare your reading to the expected pressure in Appendix A.
The high pressure
switch trips o
Move the probe further into the condenser where the temperature is higher. This
will produce a higher fan RPM and will decrease the head pressure.
Fine adjust the cutout and hard start settings in the App.
Green and yellow LEDs
alternate
Using an AC voltage meter, measure the voltage between the control input
terminals. It should read the control voltage you are using (18-240 VAC)
Also verify you have the voltage between Line 1 and LINE 2 terminals.
When a sensor is mounted into the condenser, the control responds more rapidly to
changes in head pressure than when it is mounted on the liquid line. This is espe-
line, the control responds more slowly which could result in a fan that cycles on and
condenser instead of mounting it on the liquid line (see illustration below). A spot
on the condenser that is 100°F when the pressures are correct is ideal.
°C °F )
0°
5° 41° 25.4
10° 50° 19.9
15° 59° 15.7
20° 68° 12.5
25° 77° 10.0
86° 8.1
95° 6.5
40° 104°
45° 4.4
50° 122°
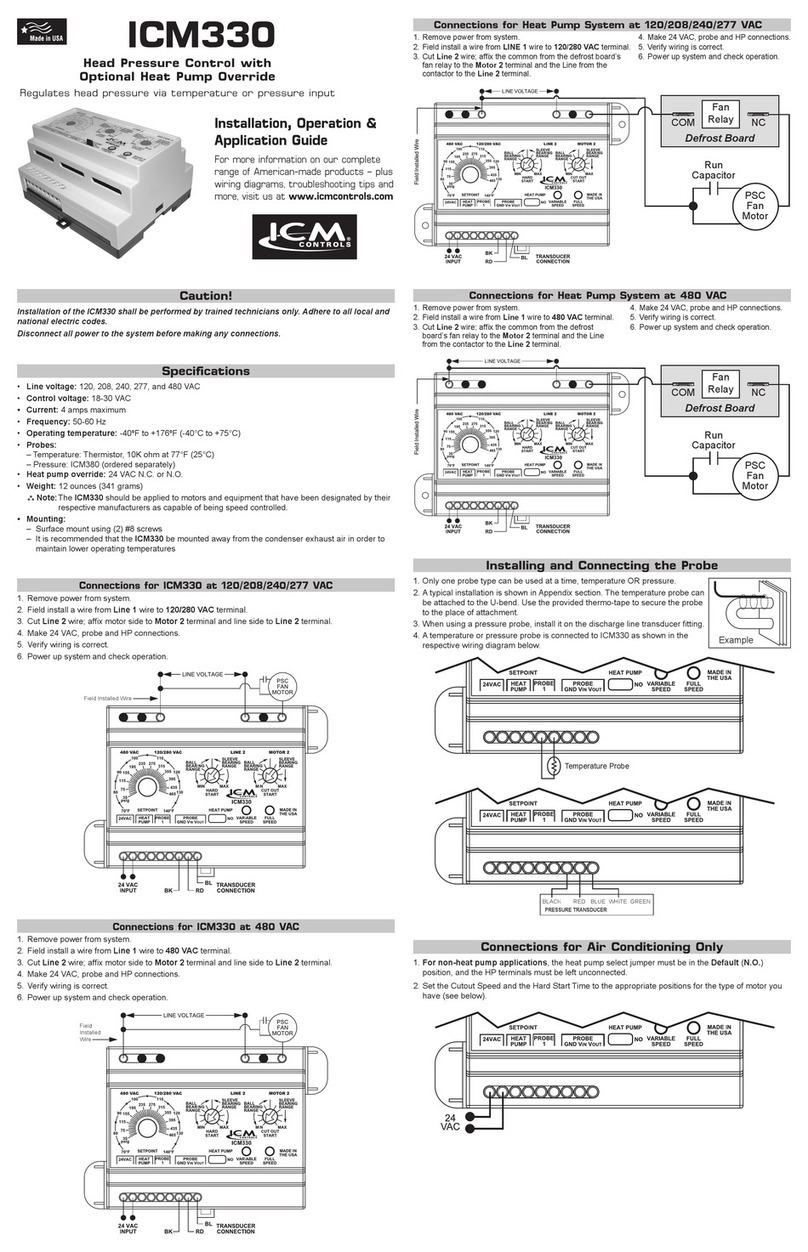
Wiring of the to a heat pump is the same as for air conditioning with the
exception of the Motor 2 output and the reversing valve input. For a heat pump, the
Motor 2 terminal is connected to the outdoor fan relay input power termi-
nal (com) on the defrost board. The condenser fan common remains connected to
the normally closed terminal of the fan relay on the defrost board.
run capacitor.
Heat pump bypass mode runs the fan continuously at full speed when the system is
operating in heat mode to move as much air as possible across the condenser coil
during heating. The HP RV determines which mode the heat pump is in by
detecting voltage on the reversing valve. The is defaulted to cool activecool active
reversing valves and will allow bypass when the reversing valve is de-energized
in heating. If the HP B RVHP B RV jumper is placed, the will be set for heat activeheat active
reversing valves and will go into bypass when the reversing valve is energized in the
heating mode.
Connect the wires from the contactor (load side), run capacitor, and the condenser
fan as shown in diagram above. If control voltage is desired, ensure the jumper is
placed on the control voltage enable input and the proper voltage (24-240 VAC)
is applied to the control voltage input. Place the temperature probe at T1/P1 and
5V and mount the probe on a U-bend in the upper third of the condenser. If two
temperature probes are needed, wire the additional temperature probe to T2/P2 &
5V. If a pressure transducer is used, mount the transducer on the discharge line at
(blue/white/green) wire to T1/P1 input. If two pressure sensors are used, connect
the black and red wires of the additional pressure sensor to the same points as pre-
00.5
50 0.9
100
150 1.7
200 2.1
250 2.5
2.9
400
450 4.1
500 4.5
MOTOR 2
ICM325A
LINE 2
LINE 1 / MOTOR 1
120 - 600 VAC
FULL SPEED
VARIABLE SPEED
CONTROL
INPUT
24-240VAC
HP RV
24-240VAC
GND
+5V
T2/P2
T1/P1
CONTROL INPUT
HP B RV
MADE IN THE USA
SENSOR
ENABLE
Line Voltage
120-600 VAC
Fan
Relay
Single
Phase PSC
Fan Motor
Place jumper to enable
the control voltage input
Place jumper to enable
a heat active reversing
valve at the HP RV input
24-240 VAC Heat Pump cool
active (default) reversing
valve voltage input
24-240 VAC
Control Voltage
Temperature
Sensor
Defrost Board
COMN
Run
Start Common
C
L1
L2
T1
T2
Contactor
Run
Capacitor
To Compressor
Field Installed Wire
Com
Herm
Fan
MOTOR 2
ICM325A
LINE 2
LINE 1 / MOTOR 1
120 - 600 VAC
FULL SPEED
VARIABLE SPEED
CONTROL
INPUT
24-240VAC
HP RV
24-240VAC
GND
+5V
T2/P2
T1/P1
CONTROL INPUT
HP B RV
MADE IN THE USA
SENSOR
ENABLE
Line Voltage
120-600 VAC
Single
Phase PSC
Fan Motor
Place jumper to enable
the control voltage input
24-240 VAC
Control Voltage
Temperature
Sensor
Run
Start Common
L1
L2
T1
T2
Contactor
Run
Capacitor
To Compressor
Field Installed Wire
Com
Herm
Fan
800.365.5525
www.icmcontrols.com