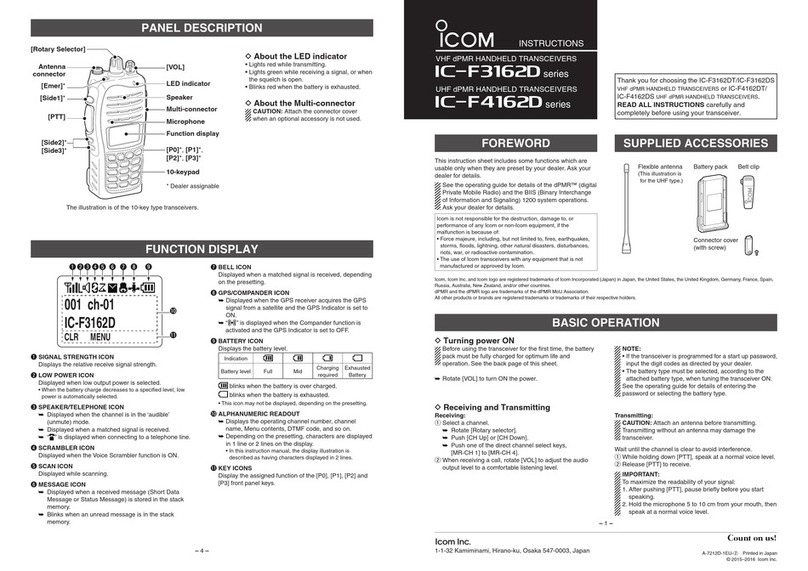
5 - 2
The AF signals from the analog switch (IC3, pin 11) are
applied to the volume buffer amplifier (IC6, pin 9). The buffer-
amplified AF signals are adjusted its level (= audio level)
by volume control pot (R315), then applied to the AF power
amplifier (IC15, pin 4) and amplified to the 0.5 W of audio
output power (max., at 8 Ωload).
The power-amplified AF signals are output from pin 10, then
applied to the internal speaker (CHASSIS; SP1) or an external
speaker via [SP] jack (J2).
5-1-6 SQUELCH CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
5-1-6-1 NOISE SQUELCH
The squelch mutes the AF output signals when no RF signal
is received. By detecting noise components (around 30 kHz
signals) in the demodulated AF signals, the squelch circuit
toggles the mute switch and AF power amplifier ON and OFF.
A portion of the demodulated AF signals from the FM IF IC
(IC9, pin 9) is applied to the D/A converter (IC12, pin 24) for
level (= squelch threshold) adjustment. The level-adjusted
AF signals are output from pin 23 and passed through the
noise filter (IC9, pins 8, 7, R42, R44–R46, R382, C69, C70,
C413, C438). The filtered noise signals are amplified the noise
components only at the noise amplifier.
The amplified noise components are converted into the pulse-
type signal at the noise detector section, and output from pin
13 as the “NOIS” signal. The converted signal is applied to the
CPU (IC22, pin 75). Then the “RMUTE” signal from the CPU
(IC22, pin 96) to the RX mute switch (Q32) and analog switch
(IC3, pins 12, 13) becomes “Low” according to the “NOIS”
signal level to cut off the AF line.
At the same time, the “AFON” signal from the CPU (IC22,
pin 70) to the AF amplifier controller (Q41, Q42, D21, D23)
becomes “Low” and the controller turns the AF power amplifier
(IC15) OFF.
5-1-6-2 TONE SQUELCH
• CTCSS/DTCS
The tone squelch circuit detects tone signals and opens the
squelch only when receiving a signal containing a matched
sub audible tone. When the tone squelch is in use, and a
signal with a mismatched or no sub audible tone is received,
the tone squelch circuit mutes the AF signals even when the
noise squelch is open.
A portion of the demodulated AF signals is passed through the
active LPF (Q39) to filters CTCSS/DTCS signal. The filtered
signal is applied to the CPU (IC22, pin 46). The CPU compares
the applied signal and the set CTCSS/DTCS, then the CPU
controls the status (“Low” or “High”) of “RMUTE” and “AFON”
signals as same as “NOISE SQUELCH”.
• DTMF
DTMF signals in the demodulated AF signals are passed
through the LPF (IC6, pins 5, 7) to remove unwanted
components (voice signals), then applied to the CPU (IC22,
pin 45) and decoded.
5-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
5-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The AF signals from the microphone (MIC signals) are filtered
and level-adjusted at microphone amplifier circuits.
• MIC SIGNALS
MIC signals from the microphone are applied to the A/D switch
(IC25, pins 7, 1), then applied to the D/A converter (IC12, pin
1).
The level-adjusted MIC signals are output from pin 2, and
passed through the MIC mute switch (Q31), HPF (IC5, pins
13, 14) and pre-emphasis circuit (R137, R138, C260), then
applied to the MIC amplifier (IC5, pin 9). The amplified MIC
signals are output from pin 8, and passed through the analog
switch (IC3, pins 4, 3), AF mixer (IC5, pins 6, 7) where the MIC
signals and tone signals are mixed with.
• TONE SIGNALS
The CTCSS/DTCS signals are generated by the CPU (IC22)
and output from pins 19–21. The output signals are passed
through the 3 resistors (R222–R224) to change its waveform.
The waveform changed CTCSS/DTCS signals are passed
through the LPF (IC7, pins 10, 8), tone filter switch (Q40) and
D/A converter (IC12, pins 12, 11) for level adjustment. The
level adjusted CTCSS/DTCS signals are then applied to the
AF mixer (IC5, pin 6).
DTMF signals are generated by the CPU (IC22) and output
from pin 43. The output DTMF signals are passed through two
LPFs (IC6, pins 3, 1 and pins 12, 14), then applied to the AF
mixer (IC5, pin 6).
The mixed AF signals are output from pin 7 of the AF mixer
(IC5) and passed through the analog switch (IC3, pins 9, 8),
then applied to the AF amplifier (IC7, pin 6). The amplified AF
signals are output from pin 7, and applied to the D/A converter
(IC12, pin 9) to be adjusted its level (= deviation). The level-
adjusted MIC signals are then applied to the modulation
circuits as the modulation signals.
5-2-2 MODULATION CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The modulation circuits modulate the VCO oscillating signal
using the modulation signals.
The modulation signals from the D/A converter (IC12, pin 10)
are applied to the D12 at the TX VCO (Q16, D10, D13) to
modulate the VCO oscillating signal by changing the reactance
of D12.
The modulation signals are also applied to the reference
frequency oscillator (X2) via D/A converter (IC12, pins 16, 15)
and the buffer (IC7, pins 12, 14), to ensure the modulation of
lower frequency components of the modulation signals.
The modulated VCO output is buffer-amplified by Q15 and
Q29, then applied to the transmit amplifiers as the transmit
signal via TX/RX switches (D16 is ON, D17 is OFF).