Image Engineering GEOCAL User manual

Image Engineering GmbH & Co. KG · Im Gleisdreieck 5 · 50169 Kerpen · Germany
T +49 2273 99 99 1-0 · F +49 2273 99 99 1-10 · www.image-engineering.com
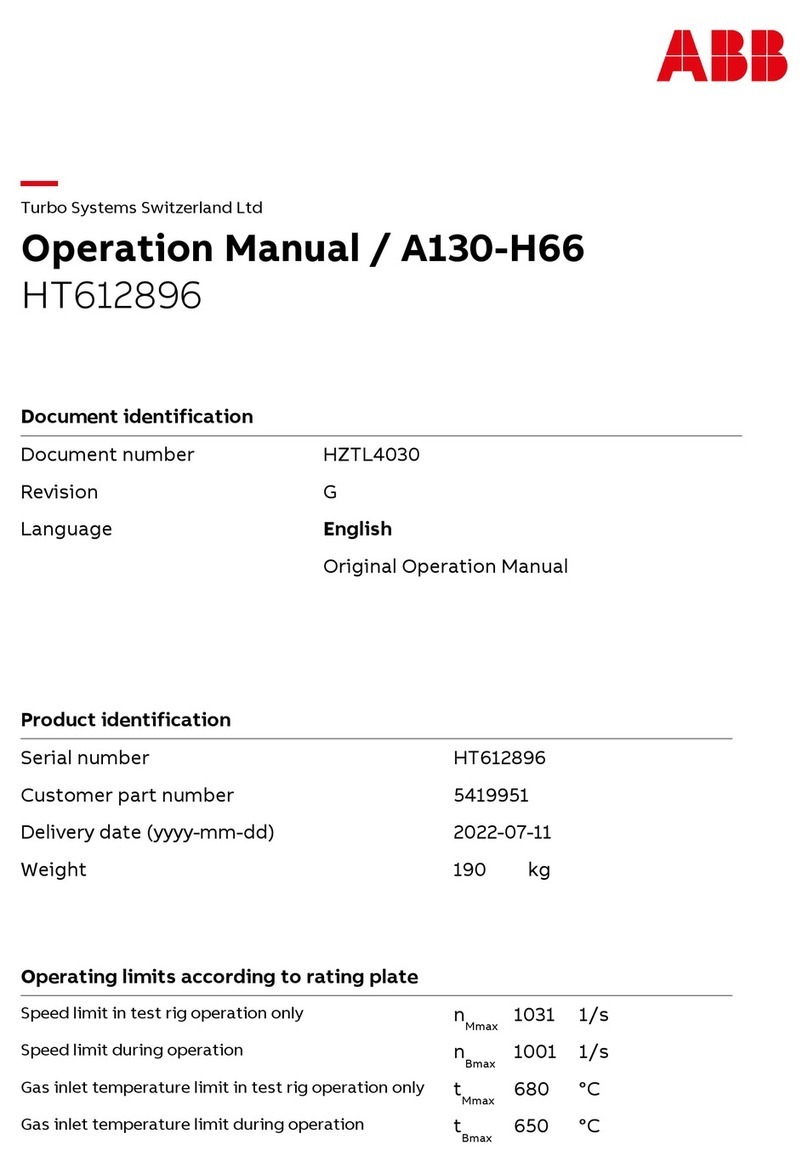
GEOCAL / GEOCAL XL
User Manual
December 22, 2023

Image Engineering
Seite 2von 16
CONTENT
1INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................4
1.1 Conformity..............................................................................................................4
1.2 Intended use...........................................................................................................4
1.3 General safety information......................................................................................4
2GETTING STARTED....................................................................................................5
2.1 Scope of delivery....................................................................................................5
2.2 Commissioning.......................................................................................................5
3OPERATING INSTRUCTIONSHARDWARE................................................................6
3.1 GEOCAL / GEOCAL XL..........................................................................................6
3.2 Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) ...........................................................................6
3.3 Camera settings......................................................................................................6
3.3.1 Camera position and suitable lenses................................................................ 7
3.3.2 Exposure......................................................................................................... 8
4DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GEOCAL AND GEOCAL XL .............................................9
4.1 Why a larger version of the GEOCAL?....................................................................9
5OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS SOFTWARE...............................................................10
5.1 Installing GEOCAL software..................................................................................10
5.2 Configuration file (XML format)..............................................................................10
5.3 Artificial sample images.........................................................................................10
5.4 Loading images for analysis..................................................................................11
5.5 Deleting images....................................................................................................11
5.6 Image analysis......................................................................................................12
5.7 Saving results.......................................................................................................13
5.8 Export Grids..........................................................................................................14
5.9 Plotting.................................................................................................................14
5.9.1 Grid view........................................................................................................ 14
5.9.2 Distortion curve.............................................................................................. 14
5.9.3 Quiver plot..................................................................................................... 14

Image Engineering
Seite 3von 16
5.9.4 2d color scatter.............................................................................................. 14
5.9.5 Histogram...................................................................................................... 14
5.10 Logging................................................................................................................15
5.11 Quit......................................................................................................................15
5.12 TRADEMARK AND COPYRIGHT.........................................................................15
6ADDITIONAL INFORMATION....................................................................................16
6.1 Disposal instructions.............................................................................................16
6.2 Power circuit modification for production line use...................................................16
7TECHNICAL DATA SHEET........................................................................................16

Image Engineering
Seite 4von 16
1 INTRODUCTION
Important information: Read the manual carefully before using the device. Inappropriate utilization may cause
damage to the device, to the DUT (device under test), and/or other components of your setup.
Keep these instructions in a safe place and pass them on to any future user.
1.1 Conformity
We, Image Engineering GmbH & Co. KG, hereby declare that GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL corresponds to the
essential requirements of the following EC directives:
- 2011/65/EU - RoHS 2
- 2014/35/EU - Low Voltage
- 2014/30/EU - Electromagnetic Compatibility
And standards or normative documents:
- EN 61326-1:2013 –Electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use - EMC
requirements - Part 1: General requirements
- EN 61000-3-2:2014 - Electromagnetic compatibility(EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits -Limitsforharmoniccurrent
emissions
- EN 61000-3-3:2013 - Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-3: Limits
- EN 62471-2:2009 - Photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems
- DIN EN 60825-1 - Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
1.2 Intended use
GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL consistsof an illuminating hardware device and software for the geometriccalibration of
camera systems. The GEOCAL software is used for calculating the calibration parameters from a single image
taken with a camera system of the point grid generated by the GEOCAL hardware device.
•Only suitable for indoor use.
•Place the system in a dry and constant tempered environment. Avoid high air humidity.
1.3 General safety information
WARNING! GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL uses a laser diode for illumination.
LASER RADIATION CLASS 1M LASER PRODUCT
•Do not stare into the beam
•Do not view directly with optical instruments
•Do not open the housing of GEOCAL / GEOCAL XL under any circumstances

Image Engineering
Seite 5von 16
2 GETTING STARTED
2.1 Scope of delivery
•GEOCAL or GEOCAL XL hardware device
•The latest software version on the USB storage device
•Power supply + cable
•USB cable (type B to type A)
•Test report
2.2 Commissioning
•Remove the packaging material.
•The power socket and the main power switch are located on the back side of the device next to the
USB type B socket.
Connect GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL to a power outlet and switch it on.
Please note that the blue LED next to the power switch indicates thatthe power line is active and that
GEOCAL is ready for operation.
•Install the latest GEOCAL software (Windows, 64bit)

Image Engineering
Seite 6von 16
3 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS HARDWARE
3.1 GEOCAL / GEOCAL XL
After switching on, GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL is ready for use. No warm-up phase is required.
3.2 Diffractive Optical Element (DOE)
A diffractive optical element (DOE) isusedto split the incoming light beam and generate a calibration grid of
evenly distributed light spots with a wavelength of 633 nm. The DOE is mounted on the front of the
GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL device (visible glass plate mounted in circular cutout, see Figure 2).
3.3 Camera settings
Set the camera to manual exposure mode.If manual mode is notavailable, use the automatic exposure mode.
The image should be saved in a lossless formatfor best results. TIFF format is recommended, and PNG and
JPEG (lossy) are also supported. If you convert RAW image data to another format, ensure the image is
debayered in the process.
The autofocus must be turned off. Since GEOCAL / GEOCAL XL uses a collimated light beam virtually
originatingfrominfinity, the appropriate focus distance will be near infinity. Using manual focus, ensure the
camera is focused on the light points.
Exposure program
Manual
Aperture
No default value
ISO Speed
Lowest value (e.g.,100)
Autofocus
Off
File type
TIFF is recommended. PNG
and JPEG are also supported
DOE
Figure 1: Calibration grid
(the brightest spot marks the center)
Figure 2: Location of the DOE

Image Engineering
Seite 7von 16
3.3.1 Camera position and suitable lenses
Place the camera in front of the diffractive optical element in the circular opening on the front of
GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL.
The camera can be placed directly in front of the DOE; no minimumdistance is needed (view Figure 3 below).
The principal axis of the lens should be aligned approx. perpendicular to the DOE. Achieve this by aligning the
0th diffraction order, the brightest spot in the grid center, with thecenter of theimage.See Figure 4 forreference.
Make sure that the point grid covers the whole image and that the border of the DOE is not visible.
The top side of GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL and the top side of the camera must have the same orientation. A rotation
of the camera around the optical axis of approx. +/- 2° will be tolerable.
No furtheralignmentsteps are necessary. The camera's translation does not influence the mapping of the light
points. The camera rotation to the DOE is part of the calibration and is determined during the process and
reported as part of the result.
The lens's front elementmust notbe larger than 77 mm in diameter for GEOCAL or 155 mm for GEOCAL XL to
capture the point grid in full format.
Figure 3: Setting the distance between the camera and GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL
Figure 4: Good alignment (0th order in the center of image) Bad alignment (0th order far off center)

Image Engineering
Seite 8von 16
Note: Please use caution when positioning the camera. The DOE is made of glass and has a
thickness of only 1.5 mm.
Ensure the calibration is performed in a dark environment to avoid stray light, reflections, or similar
interfering factors.
3.3.2 Exposure
Forbest results, theexposure should beselectedso that the individual light points are not saturated (i.e., no
white pixels or a minimal number of white pixels in the center of each point) with the exception of the 0th
diffraction order. The 0th orderwill always be much brighter than the points surrounding it. See Figure 5 below for
an example.
Depending on your camera, you might encounter different problems:
The exposure time of my camera cannot be set short enough to avoid saturation.
Possible solutions:
- Set the ISO to the lowest native value available (ISO 100 for most cameras)
- Stop down the aperture if possible
- If the image is stilltoo bright, you could use an ND-Filter to reduce the amount of light reaching the
image sensor
The intensity drop-off is too steep towards the edges of the image, and no more points are visible.
This problem may occur for ultra-wide-angle lenses. If the images cannot be adequately analyzed, try the
following.
Generate an HDR image by taking multiple images of the point grid using a range of exposure times (do not
change aperture settings in this case) and combine theminto a high dynamic range image to achieve more or
less uniform exposure across the entire sensor. Do not change the camera's orientation between images
because the points would no longer be aligned to one another through multiple images.
Figure 5: Suitable exposure (dark background, small points) Exposure too bright (red background, larger, saturated points)

Image Engineering
Seite 9von 16
4 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GEOCAL AND GEOCAL XL
The key difference between GEOCAL XL and the standard GEOCAL is the physical size of the diffractive
optical element(DOE) thatgeneratesthe point grid. While the standard GEOCAL has a usable diameter
of 77 mm, the GEOCAL XL provides a functional diameter of 155 mm.
4.1 Why a larger version of the GEOCAL?
A larger DOE is needed when the device under test (DUT) cannotbe placed directly in front of the DOE,
for example, whenacar's windshield isinvolved. As mentioned in chapter 3.3.1, "Camera position and
suitable lenses," the generatedpoint gridneeds to cover the entire camera sensor to provide a reliable
calibration.
Figure 6: Use case for the larger DOE provided in the GEOCAL XL
As illustrated in Figure 6 above, the windscreen angleprevents the standard GEOCAL from being placed
close enough to the camera to provide a full-frame image of the standard DOE. This angle would result in
a less precise and less reliable calibration.

Image Engineering
Seite 10 von 16
5 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS SOFTWARE
The GEOCAL software allows you to calibrate your camera system in a matter of seconds.
The results can be saved as CSV or XML files.
5.1 Installing GEOCAL software
•Execute the GEOCAL installer (GEOCAL_Vx.x.x.exe, 64-bit) and follow the instructions.
•The software is now ready for use.
5.2 Configuration file (XML format)
Four default configuration filesin XML format are provided with the software.If your calibration procedure does
not require special settings, you can use one of the four configuration files for the desired distortion model. You
can modify these files by copying them from the install location in:
C:\Program Files\Image Engineering\GEOCAL 1.x.x\configuration
to some other folder, modify them and then load them with the software for usage.
See document GEOCAL_calibration_models_.pdf for details on the usage of the configuration files.
Loading a config file:
Click File →Load configuration (Ctrl+c)→navigate to the folder containing the file →select the file and click
"open."
5.3 Artificial sample images
There are four sample images available, which can be found in this location:
C:\Program Files\Image Engineering\GEOCAL 1.x.x\samples
These images were synthetically created with the following parameters:
Focal lengths [fx, fy]:
3030
Skew:
0
Tangential coefficients:
0
Principal point [u0, v0]:
[960, 752]
DOE parameters [grating constant, wavelength]:
[43.9, 0.6328]
DOE and camera angles [Alpha, beta, omega, phi, kappa]:
0
Image
Model
Radial coefficients [1 to 6]
simulate_model1.png
CUSTOM_MODEL_1
[1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]
simulate_model2.png
CUSTOM_MODEL_2
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] * 10-6
simulate_modelf.png
FISHEYE_MODEL
[0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
simulate_modele.png
EVEN_BROWN_MODEL
[0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]

Image Engineering
Seite 11 von 16
To familiarize yourself with the variousmodels and the interactionsof the parameters in the configuration files,
you can use the default configurations given for each model and execute the GEOCAL software on the
simulatedimages. You should obtain results that are close to those used to create the simulated images.
5.4 Loading images for analysis
Click File →Load images (ctrl+o) →navigate to the folder containing the images →select one or multiple
images and click "open."
In its current state, the software supports the analysis of 8bit and 16bit images.
The following file types are supported (de-bayered images): .TIFF, .JPG, .PNG
Images for analysis must be taken so that the point grid fills the sensor completely.
5.5 Deleting images
Right-click on the selected image in the list to open a delete option.

Image Engineering
Seite 12 von 16
5.6 Image analysis
•Image selection: Select an image from the list in the "Image data" section (1). The image will then be
displayed in the "Image" section (4) under the "Image" tab. You can zoom in and out of the image using
your mouse wheel; the zoom will be centered around the position of your cursor.
•Point detection: Detect the grid points in the image by clicking the "Detect" button in the "Detection &
analysis" (2) section.
Detection is finished when the progress bar at the bottom of the window (5) reaches 100%. By clicking
"Show Detected Grid" under the image tab, you can display a visualization of the detected points.
If auto-detection fails, you can make a manual ROI selection by setting the checkmark in the "Detection
& analysis" section (2). Five preset ROIs will then appear in the visualized image.
The size and position of these ROIs are adjustable by click ing and dragging.
One ROI must be positioned on the 0th diffraction order (the brightest point in the center of the grid).
Adjust the ROI size so that it contains only one point.
The four remaining ROIs must be positioned on the points closest to the 0th diffraction order, i.e., the one
above, below, and to the left and right. These four ROIs may also only contain one point. Furthermore,
Figure 7: Software user interface overview

Image Engineering
Seite 13 von 16
the individual ROIs should not significantly overlap. See Figure 8 below for reference.
•Analysis: After detection, the actual analysis can be performed. Click on the "Analyze" button in the
"Detection & analysis" section (2) to start the calibration. The progress bar (5) indicates when the
calibration is finished.
Depending on the number of points detected, the time needed for calibration may vary slightly.
•Calibration results: the results will be listed under the "Result table" tab in the "Image" section (4).
Please find an explanation of the values in chapter 4.2 of this manual. The RMSE of the calibration is
also included in the result table. You can clear the result table if needed by clicking "clear table."
Under the tab "Distortion curve," you also get a graphical visualization of the determined distortion of the
camera (Geometric Distortion vs. Field).
•Generate HDR image: Set the exposure times for every HDR image data (6). Choose an algorithm
(Mertens, Debevec or Robertson) for the generation and click the “Generate HDR” button (7). A subfolder
“HDR” is generated in the HDR image data folder, in which all generated images will be saved.
5.7 Saving results
You have the option to either save your results to an XML or CSV-type file. If you have analyzed multiple
images, select one or multiple images you would like to save the results fromthe list in the "Image data"section.
Then click File →Save result →Save XML or Save CSV →navigate to the desired location →click Save
If you selected multiple images, all results would be saved in one CSV or XML file.
Figure 8: Manual point detection

Image Engineering
Seite 14 von 16
5.8 Export Grids
You can export three different grids, which are saved in CSVfiles. For each exported grid, two files are saved,
one for the x and one for the y coordinates.
To export a grid,click File →Save grid →choose the desired grid →navigate to the desired location →click
Save.
Available grids:
- Detected grid: Describes the grid type containing the detected light points.
- Reprojected grid:Describes the grid type that contains the reprojected lightpoints used to determine
the distortion.
- Undistorted reference grid: Describes the grid type, which containsthe points of the reference grid
without lens distortion. This grid includes only distortion given by the DOE physics and the
determined extrinsic and intrinsic parameters.
5.9 Plotting
There are several plots available:
5.9.1 Grid view
After a successful analysis, the detected and reprojected points are displayed on the original image. Zoom into
the image for a clearer view. The points have a size of one pixel.
5.9.2 Distortion curve
The curve is calculated from the distortion coefficients and shows the grid of the analyzed distortion.
5.9.3 Quiver plot
The quiverplot shows the direction of deviation. The respective arrows indicate how the detected points are
located concerning the reprojected points.
5.9.4 2d color scatter
This plot shows a grid of color-coded points, with each point representing the distance ratio between detected
and reprojected points. The scalar on the right side shows the individual color coding.
5.9.5 Histogram
Two differenthistogramsareshown.Thefirsthistogramcontains the successfully detected diffraction points
dependentonthe radius.The values start at zero (principal point) and run along the image diagonalto the image
corner (one).

Image Engineering
Seite 15 von 16
The second histogram contains the successfully detected diffraction points dependent on the angle. The values
start from a straight line definedfrom the principal point to the right edge of the image. The angles increase
counterclockwise.
5.10 Logging
The browser displays logging data for each action in the "Logging" section of the user interface. If errors occur,
this can be helpful. The software also has a status bar at the bottom, where error messages from the API are
displayed directly.
5.11 Quit
Click File (Quit (Ctrl+q) to exit the software or close the window.
5.12 TRADEMARK AND COPYRIGHT
Trademarks
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corp.
Copyright Information
See separate Terms and Conditions document.

Image Engineering
Seite 16 von 16
6 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
6.1 Disposal instructions
After the service life of GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL, it must be disposed of properly.Electricaland electromechanical
components are included in GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL.Observe all national regulations. Ensure that third parties
cannot use GEOCAL/GEOCAL XL after disposing of it.
Contact Image Engineering if assistance for disposal is required.
6.2 Power circuit modification for production line use
If you plan to use yourGEOCAL/GEOCAL XL on a production line, we offer the option of modifying the unit to
eliminate the need to press the switch to turn it on and off.Afterthe modification, moving the switch to the "ON"
position is sufficient. The unit will immediately startoperating when power is supplied withouthaving to press the
switch again.
For more information on this option, please contact Image Engineering.
7 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET
See the website of Image Engineering: https://image-engineering.de/support/downloads.
Other manuals for GEOCAL
2
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Image Engineering Industrial Equipment manuals
Popular Industrial Equipment manuals by other brands

ROCON
ROCON DeltaPoint Jr Installation and operation manual

Neopost
Neopost AS-Orbit Base R2L Mounting instruction

Insta
Insta 414 Operation and maintenance manual

Absolute Process Instruments
Absolute Process Instruments API 4059 G Series quick guide

Tri-sure
Tri-sure Pneumatic Tab-Seal Installation and operating instructions

HBK
HBK CA80 Instructions for use