INTORQ BFK468 User manual
Other INTORQ Spring Applied Brake manuals

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK471-25 Quick guide

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK458 User manual

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK470 Series Quick guide

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK458-ATEX Quick guide

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK464-R Series Quick guide

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK455 User manual

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK455-25 Quick guide

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK468 User manual

INTORQ
INTORQ 14.105 Series User manual

INTORQ
INTORQ BFK457 Series User manual
Popular Spring Applied Brake manuals by other brands

Kendrion
Kendrion 76..P..B00 Series operating instructions

Nexen
Nexen AIR CHAMP DBSE user manual

Kendrion
Kendrion EEX Series operating instructions

Leantechnik
Leantechnik SHB Series operating instructions

Kobelt
Kobelt 5022-A Owner's Operation, Installation & Maintenance Manual

Mayr
Mayr ROBA-stop-M 250 Operational instructions

COREMO OCMEA
COREMO OCMEA E4N-ID User and maintenance manual

Nexen
Nexen AIR CHAMP DPB-9T user manual

Mayr
Mayr ROBA-diskstop 894.5 Series Installation and operational instructions

WABCO
WABCO PAN 17 Assembly and maintenance instructions

Kendrion
Kendrion INTORQ BFK458-ATEX Original operating instructions
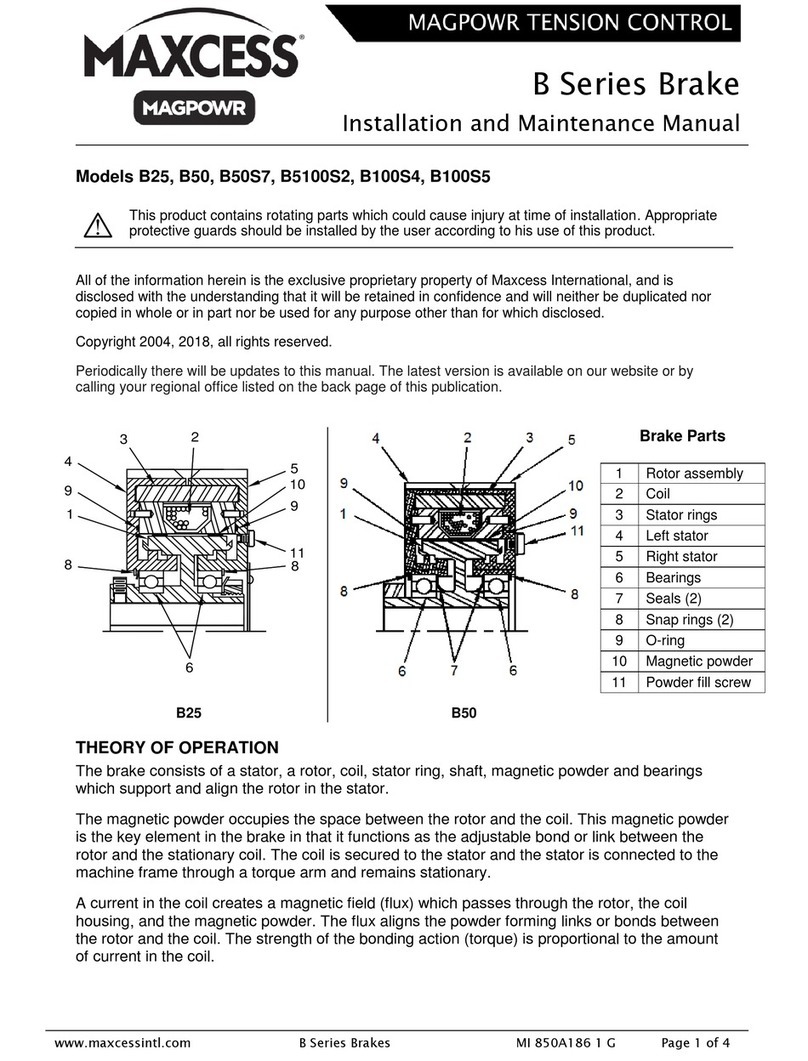
Maxcess
Maxcess MAGPOWR B Series Installation and maintenance manual

Haldex
Haldex Maxibrake 50 Series Service parts

Kendrion
Kendrion INTORQ BFK551 Translation of the original operating instructions
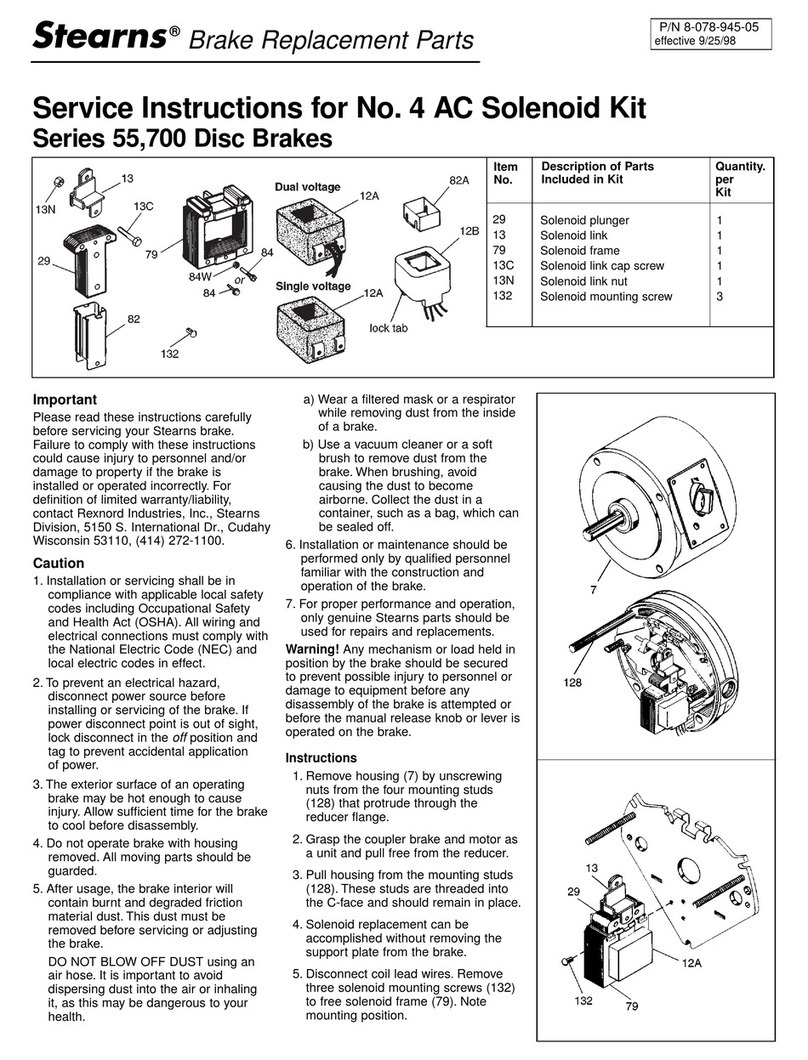
Rexnord Industries
Rexnord Industries Stearns 55,700 Series quick start guide

Rexnord Industries
Rexnord Industries Stearns 57,000 Series Service instructions

Alligator
Alligator Gatorbrake 6 Piston Installation and service manual

COREMO OCMEA
COREMO OCMEA G-M User and maintenance manual