RAD-Star User’s Guide
1© 2015-2016 Intrepid Control Systems, Inc.Version 1.2 - June 1, 2016
1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing a RAD-Star BroadR-Reach (100BASE-T1) active tap from Intrepid
Control Systems. The RAD-Star is an inexpensive but powerful tool that facilitates the design,
development, analysis and troubleshooting of Automotive Ethernet (AE) networks.
The RAD-Star is primarily used as an active tap inserted between a pair of AE devices. The
RAD-Star’s hardware passes all trafc between these devices with virtually no added latency,
while sending a timestamped copy of each message to a standard Ethernet device (such as
a laptop PC) for monitoring. The RAD-Star can also be used as a media converter, allowing
an ECU to be interfaced directly to a PC or other conventional Ethernet device. In both
applications, it is also possible to send messages from the PC to the ECU(s) using a tool like
Intrepid’s Vehicle Spy software, allowing those devices to be directly controlled.
2 Package Contents
Your RAD-Star package includes the following:
• The RAD-Star device.
• A pair of standard 4-wire Ethernet cables.
• A pair of BroadR-Reach cables terminated with Molex Mini50 connectors.
If anything is missing, please contact Intrepid for prompt assistance, using the information at
the end of this guide. More information about cabling can be found in Section 6 of the guide.
3 Overview of Operation and Features
We’ll now briey outline the RAD-Star’s construction, operation and features. This overview will
help you better understand the design of the device and get the most of its capabilities.
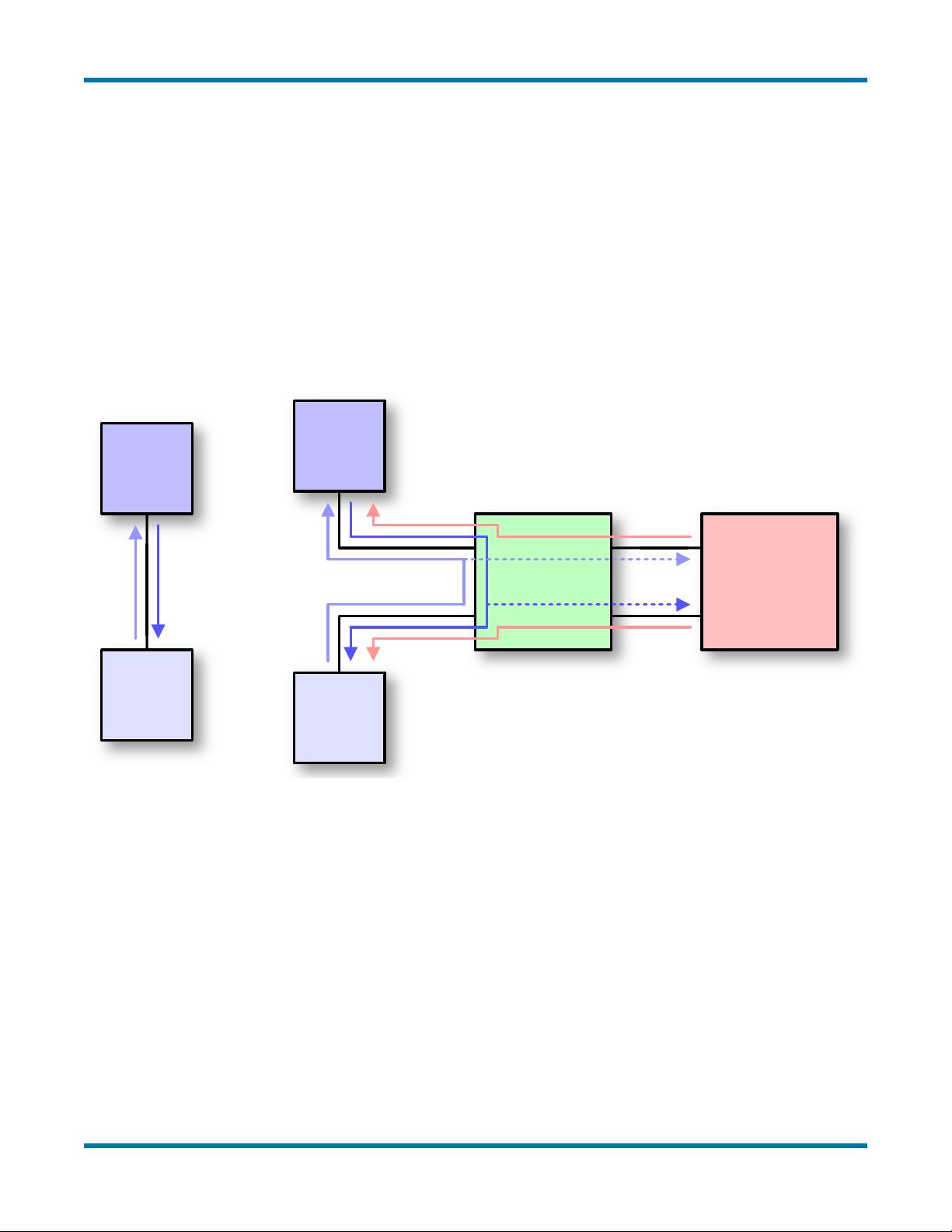
Operation as an Active Tap
Due to the high performance and complexity of BroadR-Reach—now also known by its formal
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet name, 100BASE-T1—typical approaches for interfacing to a network
(such as attaching a probe to the bus) do not work. This problem is resolved by interposing the
RAD-Star between two Automotive Ethernet devices, typically an ECU and a switch. Instead
of connecting the ECU and switch directly, both are attached to the BroadR-Reach ports of the
RAD-Star. The 10/100 Ethernet links of the RAD-Star are then connected to a laptop PC or
similar conventional Ethernet device.
The RAD-Star is now set up as a “middle man” in the connection, managed by a custom-
designed XMOS active tap chip. When a message is sent by the ECU to the switch, the
RAD-Star receives it and immediately retransmits it over its other BroadR-Reach port so the