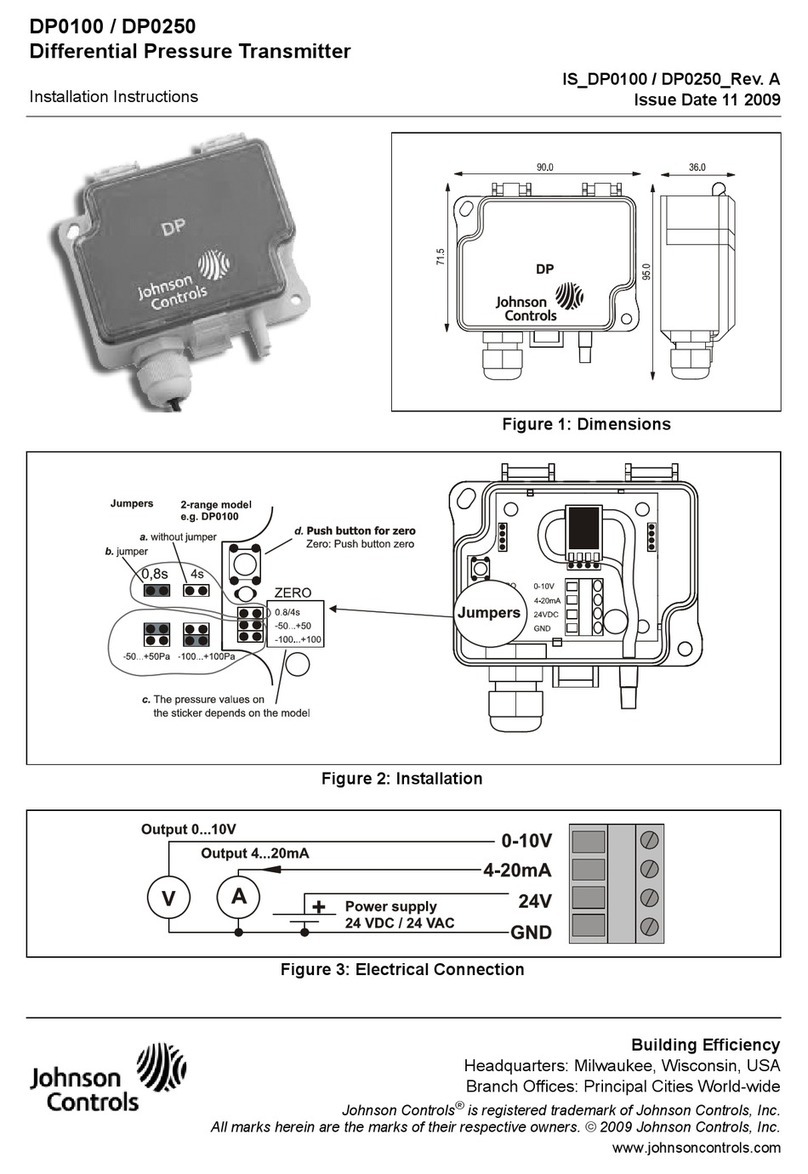
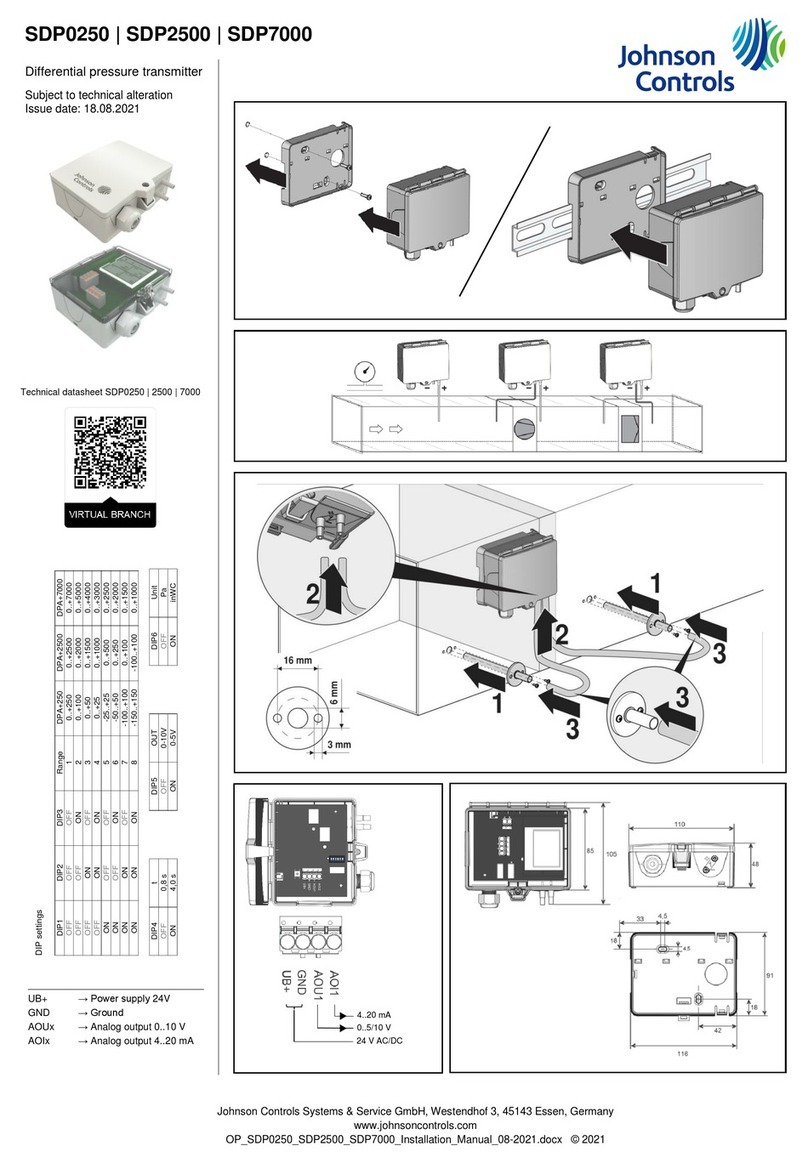
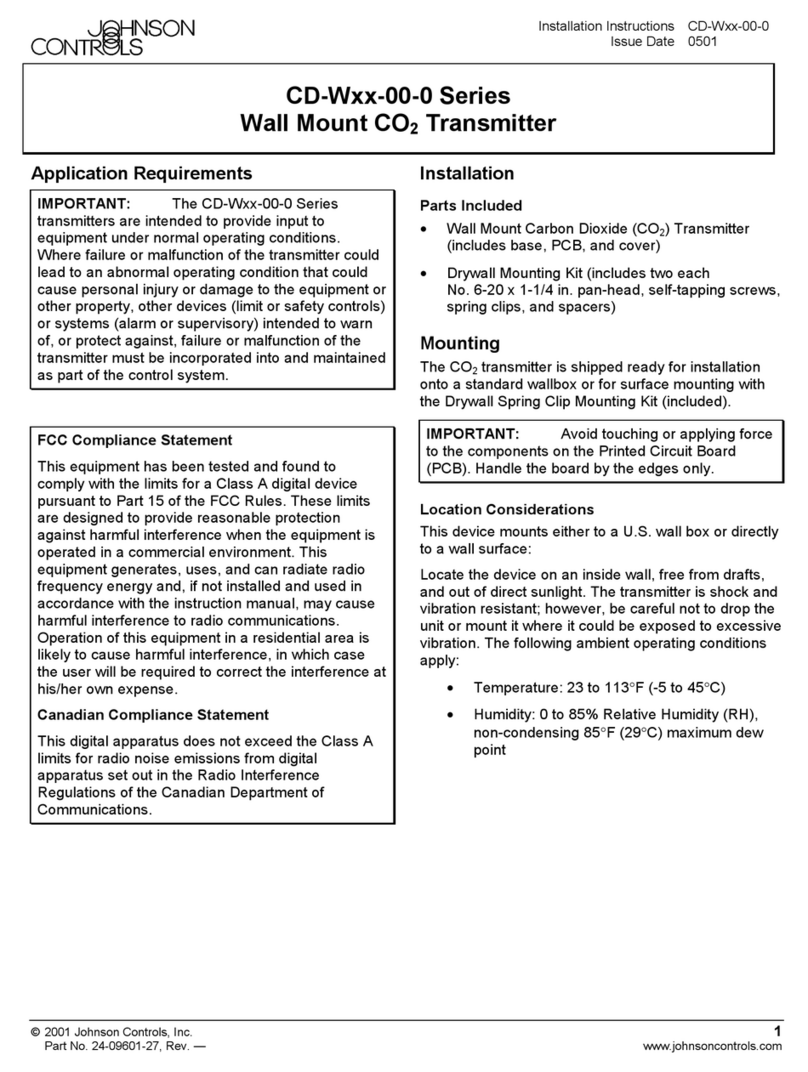
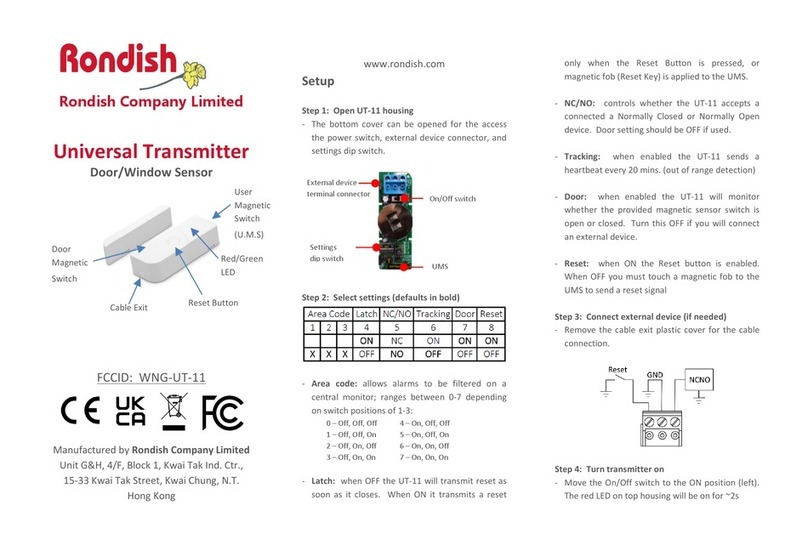
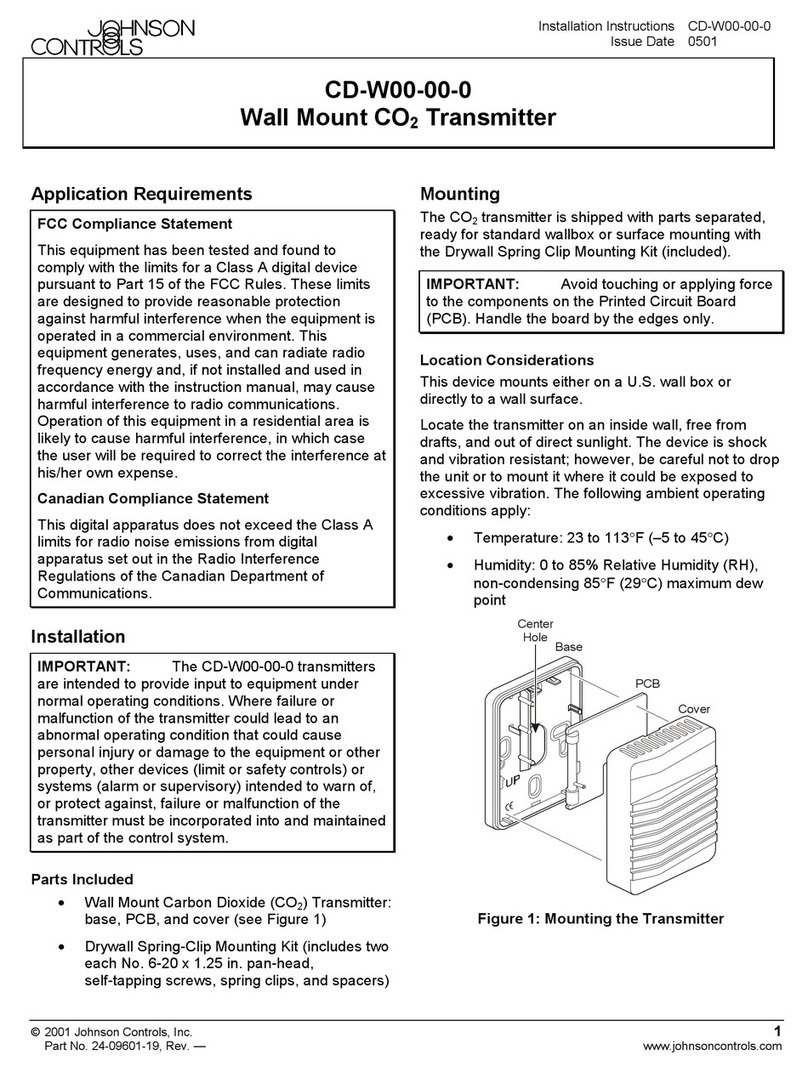
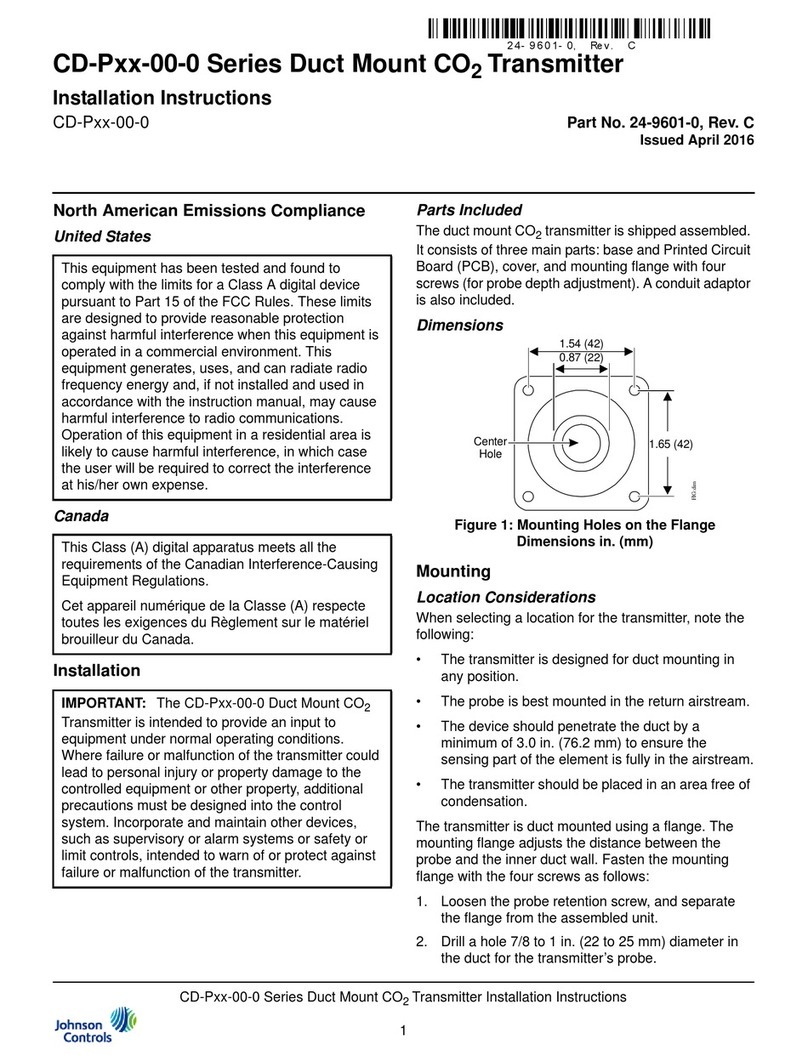
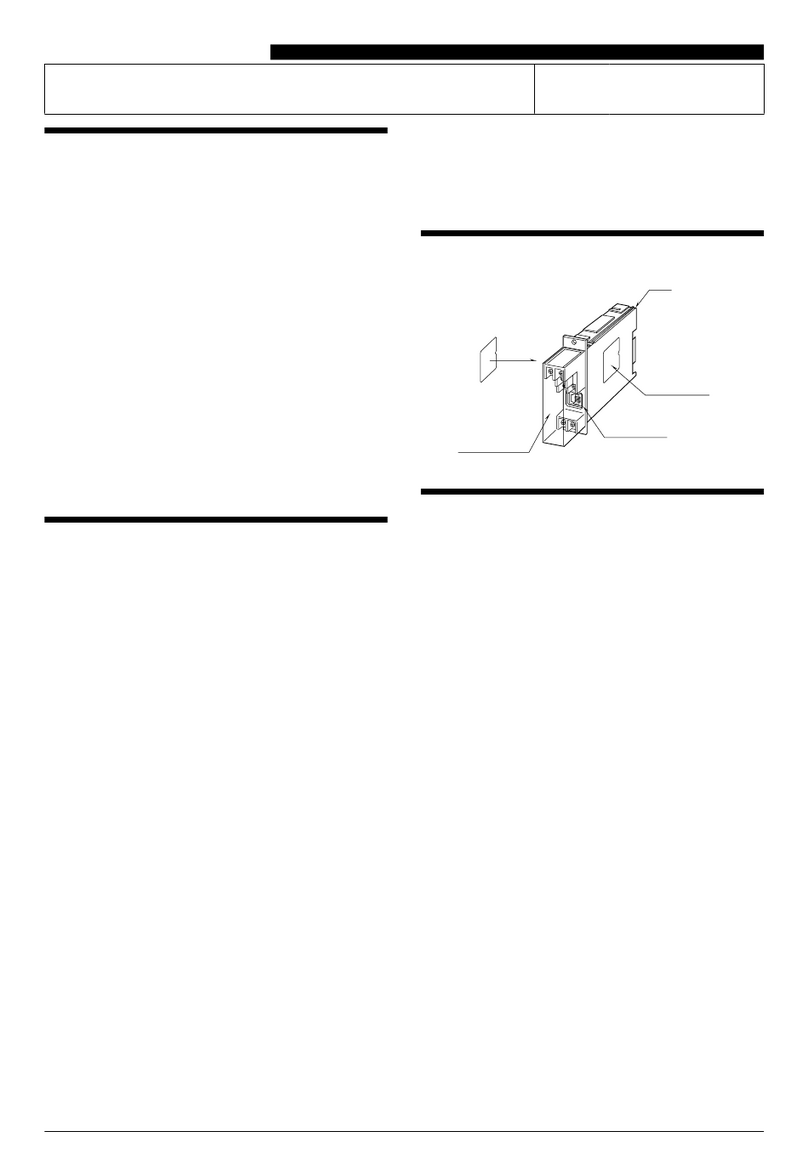
Figure 5: Reinstalling the cover
4. Reinstall the cover and tighten the screws with a
Phillips screwdriver. See Figure 5.
Wiring
About this task:
This device has a half-wave type power supply so use
caution when you wire multiple devices. Ensure that the
circuit ground point is the same on all devices and on the
controller. This device is reverse voltage-protected and will
not operate if you connect the power supply backwards.
Important: Use 22 AWG shielded wire for all
connections and do not locate the device wires in the
same conduit as wires that supply inductive loads
such as motors. Disconnect the power supply before
you make any connections to prevent electrical shock
or equipment damage. Make all connections in
accordance with national and local codes.
Note: If you install the device at either end of the
network, install an end-of-line (EOL) termination
resistor (121 ohm) in parallel to the A (-) and B (+)
terminals. This device includes a network termination
jumper that connects the resistor correctly on the
Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Simply move the PCB
jumper to the EOL position and you do not require
an external resistor. Connect the ground wire of
the shielded pair to earth ground at the end of the
network, the master wire is not grounded. Do not
run bus wiring in the same conduit as line voltage
wiring.
Note: A network segment is a single-shielded wire
loop run between several devices (nodes) in a daisy
chain configuration. The total segment length should
be less than 4000 ft (1220 m) and the maximum
number of nodes on one segment is 255 for Modbus.
Nodes are any device that you connect to the loop
and include controllers, repeaters, and sensors
such as the CO sensor but does not include the EOL
terminators.
To wire the transmitter, complete the following
steps:
1. Connect the RS-485 network with a twisted shielded
pair to the terminals marked A-, B+, and SHIELD.
The positive wire connects to B (+), the negative
wire connects to A (-), and you must connect the
cable shield to the SHIELD terminal on each device.
See Figure 6.
Figure 6: Wiring connections
Figure 7: Daisy chain configuration
2. To install more devices, or to increase the network
length, requires the use of repeaters for correct
communication. The maximum daisy chain
length (segment) depends on transmission speed
(baud rate), wire size, and number of nodes. If
communication is slow or unreliable, it may be
necessary to wire two daisy chains to the controller
with a repeater for each segment. See Figure 7.
Network communication
Each device must have a unique Modbus address for
start-up and you must set the Modbus address before
connection to the network. Use the local DIP switch to
set the Modbus device address from 1 to 255. The factory
default baud rate is 9600. Other Modbus parameter
settings can be found in Modbus protocol. The CO sensor
operates as a subordinate and will not communicate
unless a master connects to the network. When the
master sends a request for information, the subordinate
answers the request.
If the device does not communicate correctly, first check
that you did not reverse the communication wires.
Then check that the subordinate address, baud rate,
transmission mode, parity bit, stop bit, and RTU mode
CRC polynomial are correct. Set the device address. See
GS3000 Indoor Modbus Carbon Monoxide Transmitter Installation Guide2