© 2023 Kohler Uninterruptible Power 12/9/23 5
2: General Description
Inverter (6)
The inverter converts the DC voltage produced by the rectifier (or the battery via the booster/charger) into a sinusoidal AC
output voltage suitable to connect to the load. In addition to providing output voltage regulation, the inverter control logic
also provides various levels of overload protection, frequency regulation and synchronisation, and output voltage error
detection.
Static switch (7)
The static switch provides a means of connecting the UPS output to the inverter or static bypass line. The static switch
control logic transfers the UPS output from the inverter to the static bypass line without a load-break in the event of an
output overload or UPS (inverter) malfunction.
Parallel isolator, IA2 (8)
IA2 is a manually-operated switch that is connected between the static switch and the UPS output supply terminals. In a
single-module installation IA2 can be used to isolate the UPS power electronics to enable repair/replacement procedures
to be carried out while the load is connected to the maintenance bypass line, via IA1. In a ‘redundant’ parallel system IA2
can be similarly used to isolate a UPS module from the parallel system while the remaining modules continue normal
operation.
Battery (9)
The UPS batteries are either installed in a dedicated battery cabinet or on a purpose-designed battery rack. The battery
installation is bespoke but it must include a fuse located near the battery source to enable the batteries to be disconnected
from the UPS. A range of external battery cabinets is available from Kohler Uninterruptible Power on request.
2.3.2 UPS internal operating modes
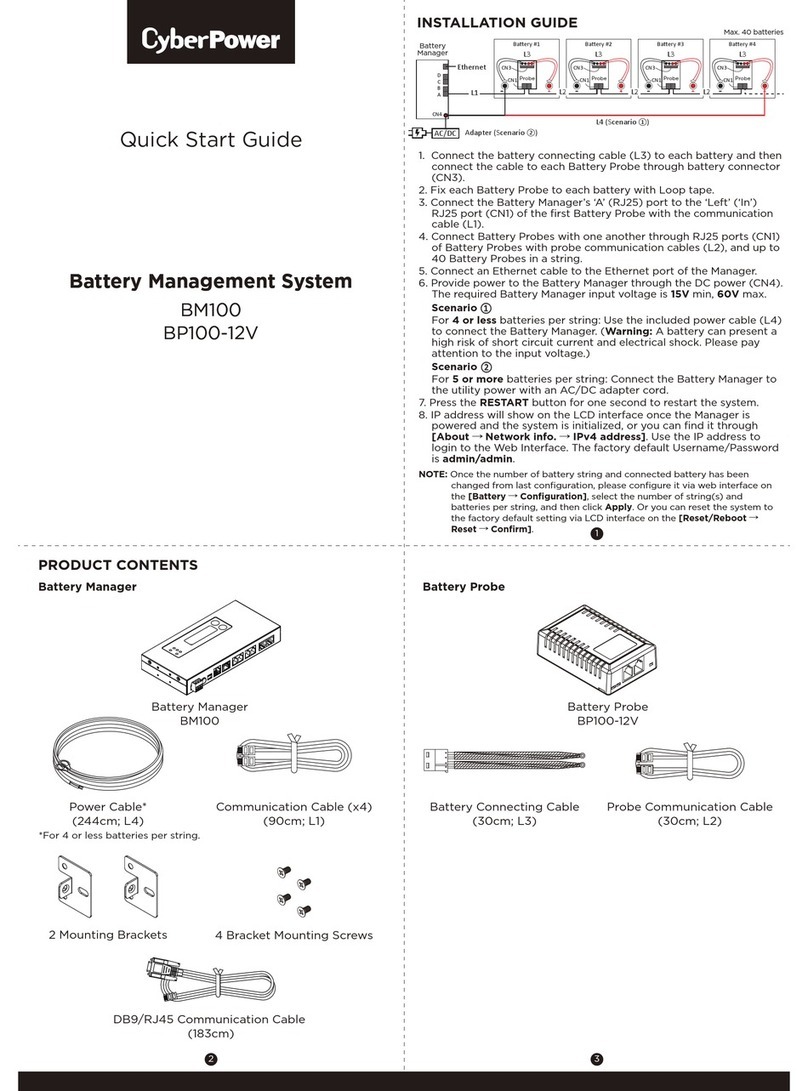
The following simplified block diagrams illustrate various UPS operating modes.
Load on Inverter
ON INVERTER is the normal UPS
operating mode and is the only one
that provides the load with
continuously processed and
backed-up power.
In this mode, the power rectifier
converts the AC input mains supply
to DC which provides the operating
power for the inverter and charges
the battery via the charger/booster.
The inverter then converts its DC
input to a controlled AC output that
is suitable to supply the load.
The ‘inverter side’ of the static
switch is closed and connects the
inverter AC output to the output
supply terminals via the closed parallel isolator switch (IA2).
When operating in the ON INVERTER mode, the inverter output frequency is synchronised to the bypass supply provided
the bypass supply frequency remains within preset limits (normally ±1 Hz). If the bypass supply fails altogether, the
inverter frequency is controlled by a free-running oscillator that will maintain the output frequency at a constant 50/60Hz.
Figure 2.3 Load on inverter