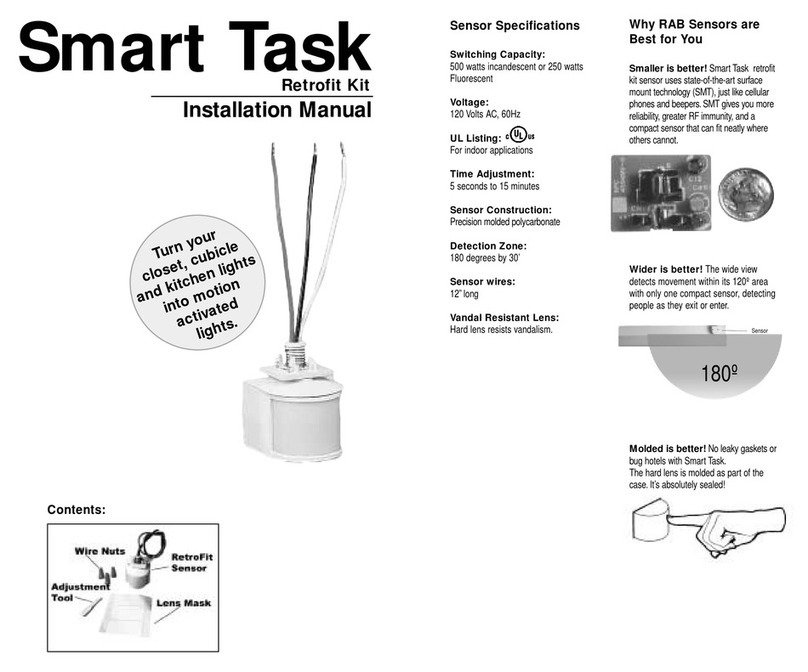
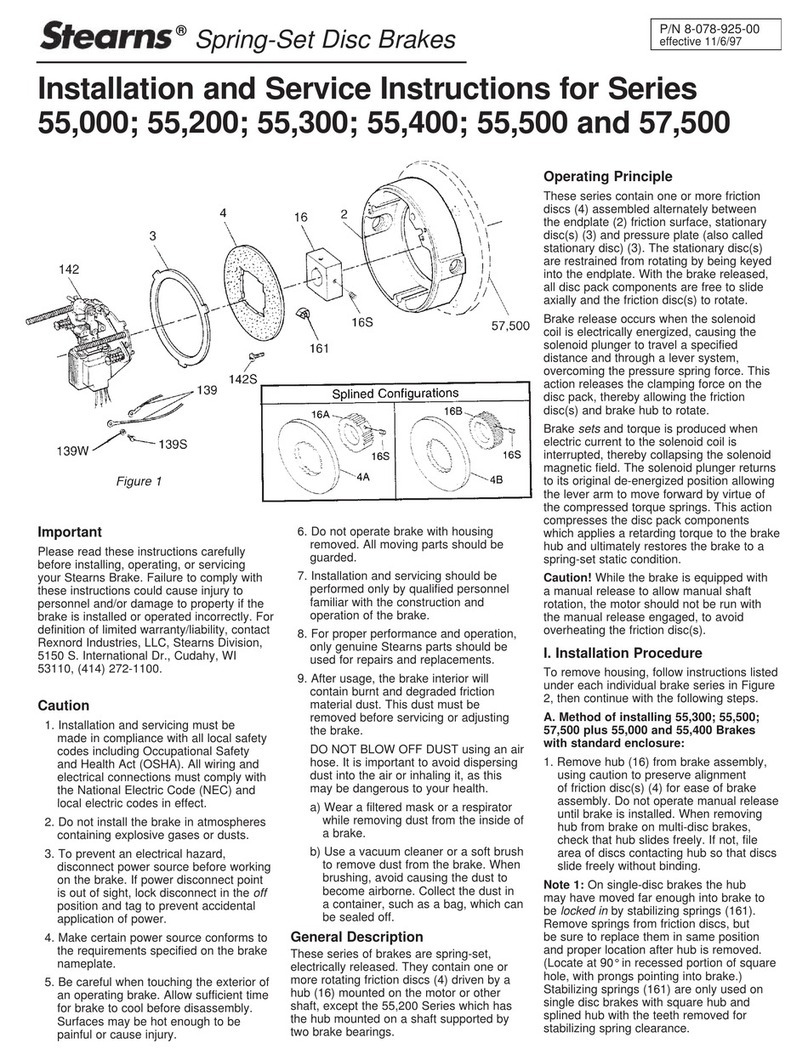
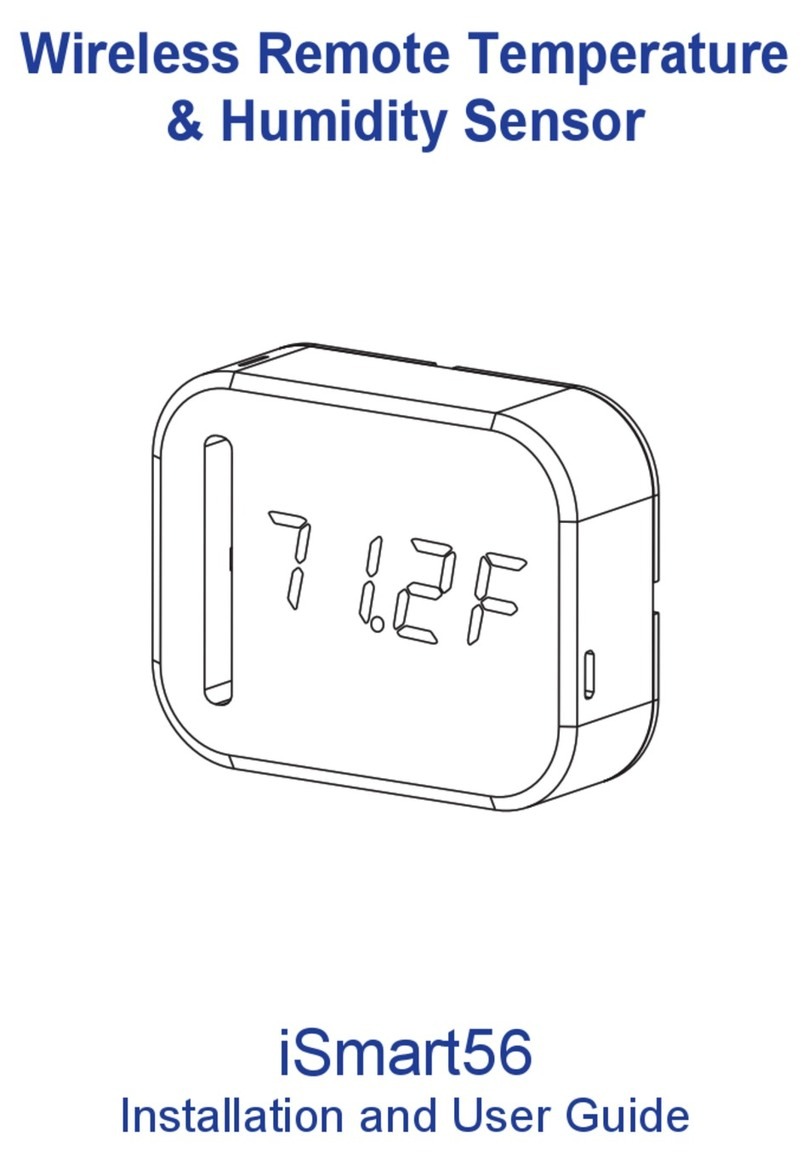
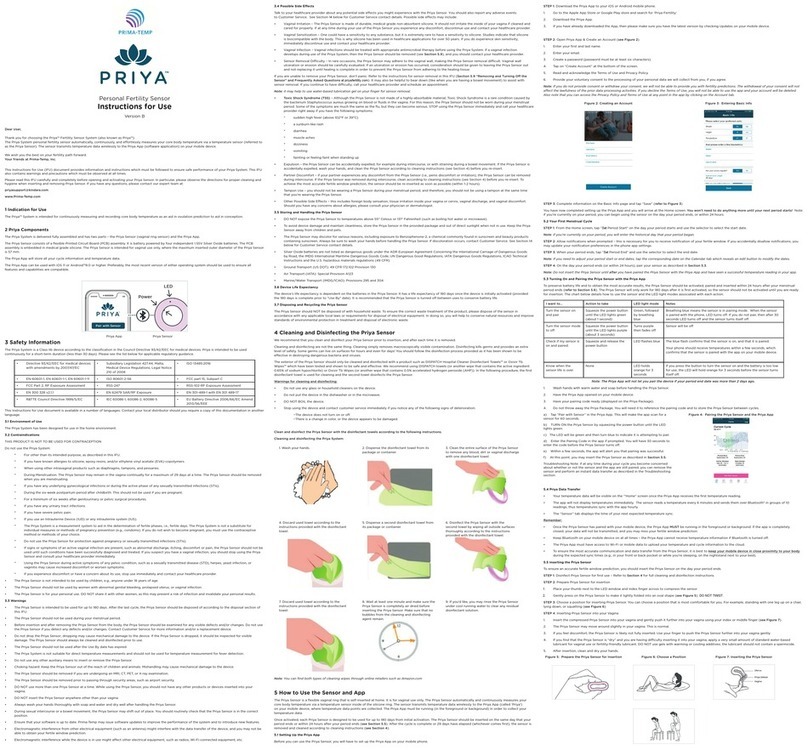
020C-9800 REV A Page 5
3.0 OPERATIONAL CHECK-OUT
3.1 020C Wind Direction Sensor Check-Out (standard 360qoperation)
A. With the sensor connected to the input, upon movement of the sensor’s vane in a
clockwise direction (as seen from above), the module’s output will move up-
scale. Movement of the module’s output will progress up-scale until the 360q(full
scale) mark has been reached; then output will drop to 0q. When the notches on
the rotating hub and the column of the sensor are exactly aligned, the output
signal will correspond to 180q.
3.2 020C Wind Direction Sensor Check-Out (with 540qconversion electronics)
A. With the sensor connected to the input, upon movement of the sensor’s vane in a
clockwise direction (as seen from above), the module’s output will move up-
scale. Movement of the module’s output will progress up-scale until the 540q(full
scale) mark has been reached, and then the output will drop to 180q. Continued
clockwise rotation will again bring the module’s output up-scale to 540qand the
action is repeated. When the notches on the rotating hub and the column of the
sensor are exactly aligned, the output signal will correspond to 180q(or 540qon
the expanded scale.
3.3 If the sensor heater is used, then check internal heater operation by sliding sensor
cover down and touching the housing behind the printed circuit board. The housing
should feet warmer than the adjoining metal parts. The sensor has a built-in heater
that is designed to provide a raise in the internal temperature, providing a small
positive pressure. This heater requires an external 12V (@ 350 ma) power supply.
4.0 MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING
4.1 General Maintenance Schedule
6-12 Month Intervals:
A. Inspect Sensor for proper operation per Section 3.1 or 3.2.
B. Calibration as required per Section 4.4.
12-24 Month Intervals:
A. Replacement of sensor bearings as per Section 4.5.
B. Replacement of potentiometer as per Section 4.6
Table 4-1
020C Wind Direction Sensor Troubleshooting