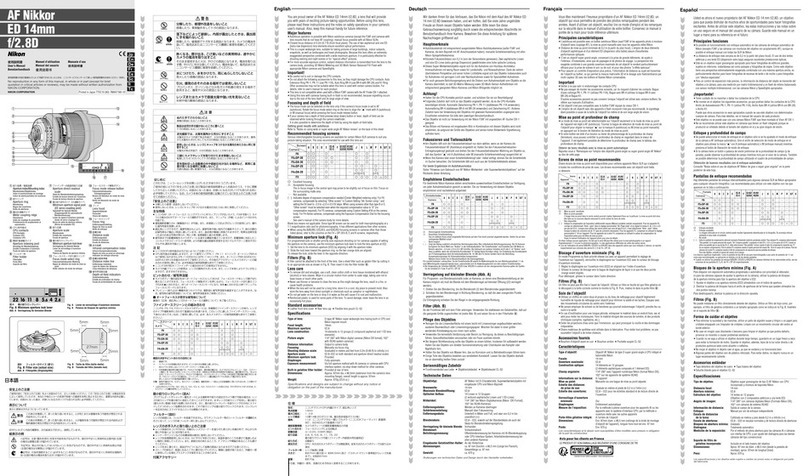
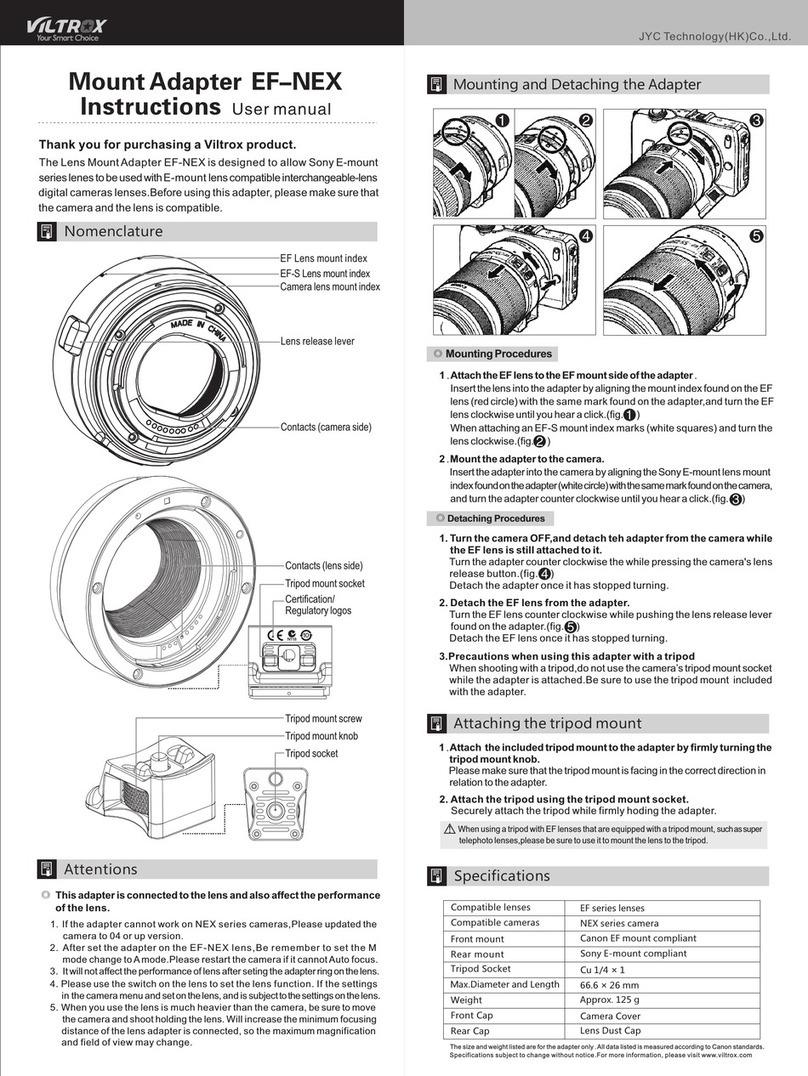
Principles of Modulation Contrast
Since human eyes, cameras, and films capture objects by perceiving differences in light intensity and/or color, they cannot see
(or sense) the colorless, transparent cells or bacteria. These colorless transparent objects are called “phase objects” since they
only change the phase of the light when the light passes through them.
The phase objects can be made visible by dyes, but their life will be deprived. In order to observe the living phase objects,
differential interference contrast and phase contrast microscopy are invented, and modulation contrast microscopy likewise. The
modulation contrast microscopy adopts the same optical system as the ordinary microscopes, but with some additional parts
that convert the transparent specimen into the variation of light intensity. These additional parts modulate the amplitude of the
light that passed through the specimen, thus changing the intensity of the light making up the visible image. (In differential
interference contrast and phase contrast microscopy, the phase objects are converted into the variations of light intensity by the
phase change that occurs when the light passes through the specimen.)
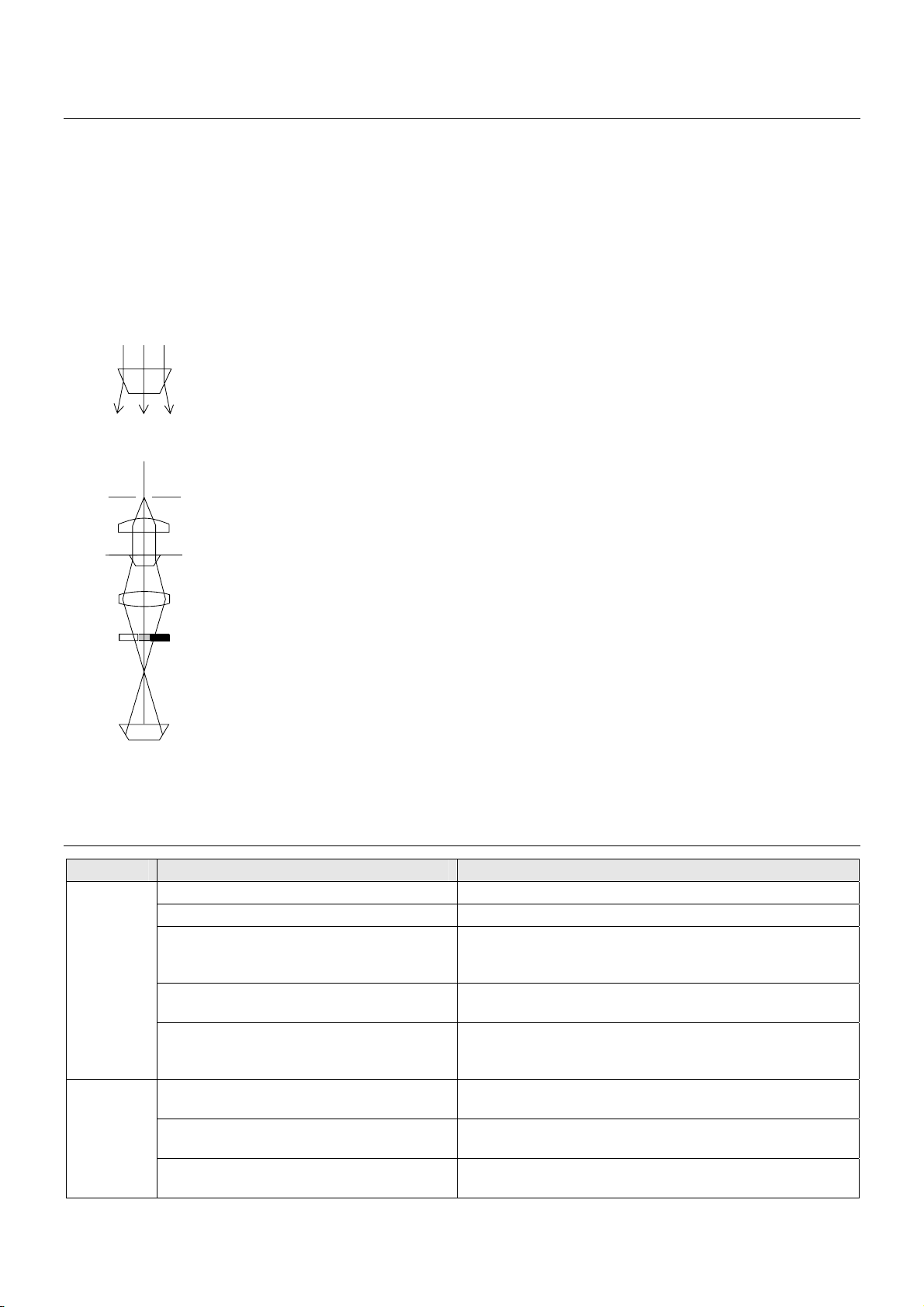
Let’s now think of a light that passes through a specimen. Since a phase object
has the different refractive index than that of its surroundings, the light will be
refracted at its border. (See Figure 7 showing refracted light on trapezoidal phase
object.) The same thing happens to every specimen.
See Figure 8 for the principle of the modulation contrast.
There is a slit diaphragm on the condenser aperture, and modulator inside the
NAMC objective. (The modulator is a density filter placed at the exit pupil of the
NAMC objective. It divides the exit pupil into three regions, dark, half-dark and
transparent.)
If there is nothing on the specimen surface, the light passes through the half-dark
region of the modulator and appears half-dark. If the light is refracted by the phase
object, it passes either the dark or the bright region according to the difference in
the refracted angle. The light then appears dark or bright according to the region
the light passed through. In this way, the phase object is made visible.
In modulation contrast microscopy, the image appears in relief just like the
differential interference contrast microscopy, though its resolution may be a little
inferior. The notable point is that there is no influence of double refraction, thus
enabling you to observe the specimen without double refraction.
Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Countermeasure
No polarizing filter attached. Screw in the polarizing filter to the condenser mount.
No NAMC objectives in the optical path. Use objectives that have “NAMC” indication on its body.
NAMC codes on the NAMC objective and the
NAMC module in the optical path are not the
same.
The NAMC objective and the NAMC module in the optical
path must have the same NAMC code.
Slit aperture image is not correctly aligned to
the gray region on the modulator.
Readjust as described in “Microscopy.”
Poor or dull
contrast
Incorrect condenser position. Set the system condenser firmly on the condenser mount.
Focus the aperture image on the specimen surface and center
it in the viewfield.
Unnecessary filters in the optical path. Remove unwanted filters (ND filters, etc.) from the optical
path.
The DIC analyzer is in the optical path (when
using the DIC attachment at the same time).
Remove the analyzer from the optical path.
Dark Image
Low illumination voltage. Adjust the light intensity control dial to raise the illumination
voltage.
Refer to the instruction manual supplied with the microscope for other troubles than mentioned above.
Figure 7
Figure 8
Phase object
Slit aperture diaphragm
Condenser lens
Specimen
Objective
Modulator
Image
Dark Bright