© Copyright 2018 ORIFLOW LLC Rev: 03-2018
2
Introduction
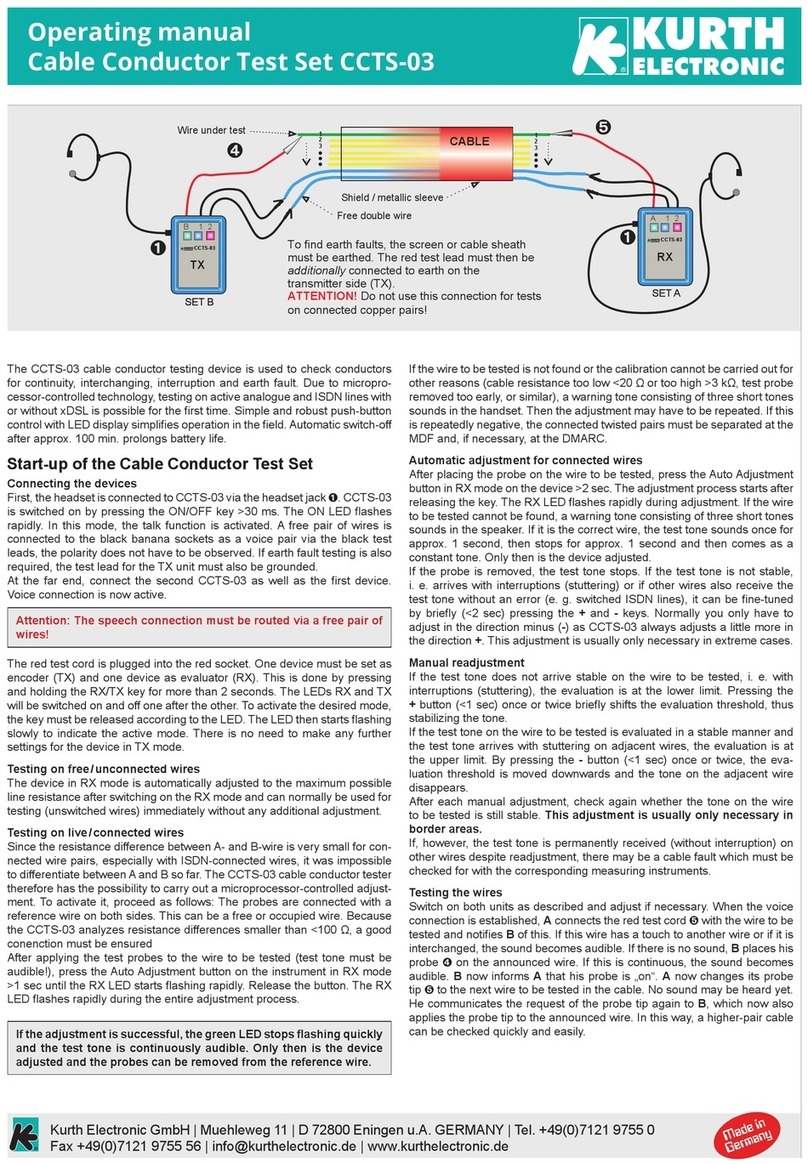
These operating instructions are for ORIFLOW model RHINO air leakage tester.
Take pride in knowing that you have purchased the best air leakage tester on the
market. It is no secret that Oriflow manufactures the highest quality testers, and has
unparalleled customer service and technical support.
The orifice plates available for your duct leakage tester are constructed from laser-
cut 3.2 mm stainless steel and do not require recalibration for 10 years. Note the
authority having jurisdiction may override this requirement, and if so, Oriflow has very
reasonable rates for calibrating orifice plates manufactured by Oriflow.
Safety Precautions
Before operating your tester, read the following safety precautions:
DO NOT operate the tester in the rain,
DO NOT operate the tester while it is near or in water,
DO NOT operate the tester with a damaged electrical cord or plug,
DO NOT remove the inlet safety screen,
DO NOT touch the blower wheel when the unit is plugged in,
DO NOT look into the discharge end of the tester when the unit is plugged in,
DO NOT use the tester as a ladder or step stool,
DO NOT allow children near the tester,
DO use an extension cord of the proper gauge (see Table 2),
DO use the proper voltage and line frequency listed on the motor nameplate,
DO lock the caster when the tester is positioned horizontally,
DO use the tester on level ground,
DO secure the tester when transporting it,
DO wear proper hearing protection, safety glasses and work gloves,
DO seek assistance when lifting the tester (e.g., loading onto truck, going up
or down stairs).