Specifications subject to change
© Ozone Pollution Technology 2001
Data
Table
Water Purifier Code →WP1 WP1-750
WT1
Ozone Pollution Technology,
Sydney Head Office, 212 Silverwater Road,
Silverwater NSW 2128, Australia.
Phone 02-9748 7748
Fax 02-9748 7749
Web Site http://www.ozonetec.com
Application
Outlets supplied as standard - Nozzle
Oxidant output, maximum (dryer chamber fitted) (mg/hour)
Check valve
5.0
Tap connector
tap faucet
Connect to
- Valve
Oxidant concentration, maximum (ppm)
Air/gas flow rate, maximum (litres/minute)
30
1. For the very best results with the WT1, run the treated water from the tap
into a glass or bottle or vessel. Then leave for 4 minutes prior to drinking.
2. Replace filters and check valves periodically.
3. For best results with the WP1 and WP1-750, run water through pipes to
clean pipes, prior to drinking. Regularly check microbe levels in tank,
ozone levels, and adjust disinfectant levels as required.
4. Water Purifiers are not suitable for water which is biologically unsafe.
5. Read Instruction Manual before use.
Application notes
Useful Conversions
1m = 1000 mm = 3.38 feet
1kg = 1000 g = 2.20 pounds
1Pa = 0.102 mm water = 0.004 inches water
1 l/s = 3.60 m3/hr = 2.12 cfm
1kW = 1000 W = 1.34 hp
Ozone: 1 ppm (by volume) = 2 mg/m3= 2000 µg/m3
(at 1 atmosphere and 25˚C).
K 4 BOAHW014
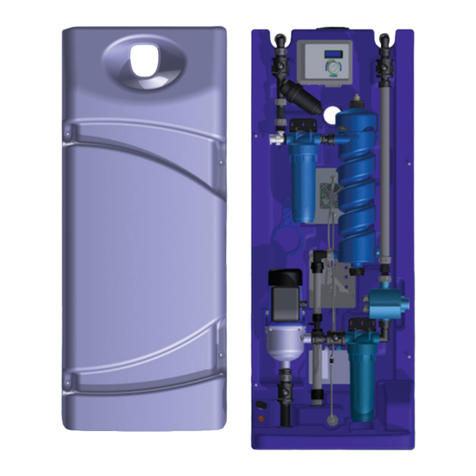
Drinking Water Purifiers
- Hose
170
140
Weight, nominal (kg)
- Length L (mm)
Rated power, nominal (watts)
Dimensions, as standard - Width W (mm)
- Height H (mm)
Water flow rate, design level (litres/minute)
Filter life, recommendation to change (operating hours)
Height of tank or vessel, maximum (m)
Features - plasma ozone emitter, tubular
- air pump
- plastic body
- certified: no electromagnetic interference
- Dryer Chamber accessory can be fitted
- cyclical timer
- automatic on/off, via flow switch and venturi
- on/off switch and safety micro switch
1m hose
200
1,500
0.5
2
1,500
380
–
✔
✔
✔
–
–
–
✔
–
4.0
Porous ball
into vessel
30
330
140
3m hose
200
1,500
0.5
–
–
170
1
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
–
✔
–
Drop ball
Check valve
8.0
Porous ball
into tank
120
550
140
6m hose
750
2,000
1.0
–
–
170
4
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
–
Drop ball
Accessories
Filter Cartridge for
WT1. Code 3848UV.
Check Valve for all
models. Code3847UV.
Replacement Filters & Check Valves Dryer Chamber CD1
For drying feedstock air, to maximise ozone
output and product life, for model WP1 and
WP1-750
"Ozone In Water" Tester EW0Spare Hose
Innovative Electronics
Ozone science (for microbe + colour control)
The air contains pure oxygen
molecules.
Ozone is formed by the Plasma
emitters and then dissolved into
the water.
The third oxygen atom attaches to
a pollutant to oxidise it to a
harmless molecule.
Leaving pure oxygen again.
Simple device for indicating ozone in water
levels, using the DPD method. Comprises a
set of tablets. Fits in your shirt pocket.
Purifier Hose (Type) Hose Code
WT1 10mm x 1m HS10
WP1 6mm x 5m HS6
WP1-750 6mm x 5m HS6
1.
2
3.
4.
✔
The problems with drinking chlorinated water:
- Chlorine and organic matter create THMs (tri-halomethanes) which are
carcinogens.
- Chlorine struggles to kill protozoa such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
- Chlorine can create odours and discoloration.
- Chlorine leaves a chemical residue.
- Chlorine is a relatively weak oxidant (50% weaker than ozone).
- Chlorineis a relatively slow acting oxidant (killscellular microbes 3,000 times
slower than ozone).
The problem with particulate filters:
When used alone they do not remove the following:
- bacteria and viruses - organic contaminants
- chlorine, fluoride - minerals
and they must be replaced regularly, e.g. 6 monthly.
The problem with carbon filters:
When used alone they do not remove the following:
- bacteria and viruses - fluoride
- dissolved ions - minerals
and they are easily colonised by bacteria. They must be replaced regularly or
pollutants just pass straight through them.
Particulate Filters + Carbon + Ozone can solve these problems.
The problems with ultraviolet products (radiation type):
When used correctly they can kill microbes, but they have no effect on other
pollutants such as:
- organic contaminants - off-tastes
- minerals - off-colours
- chlorine - salts and scale.
Their ability to kill microbes reduces dramatically:
- if there is organic load or sediment in the water, which shields the
microbes from UV rays
- if the UV tubes are not regularly cleaned
- if the water flow rate is too high.
The UV tubes break easily.
The UV radiation is carcinogenic if it escapes from the chamber.
Filter life, at 5% utilisation (years) 3.5 3.5 3.5