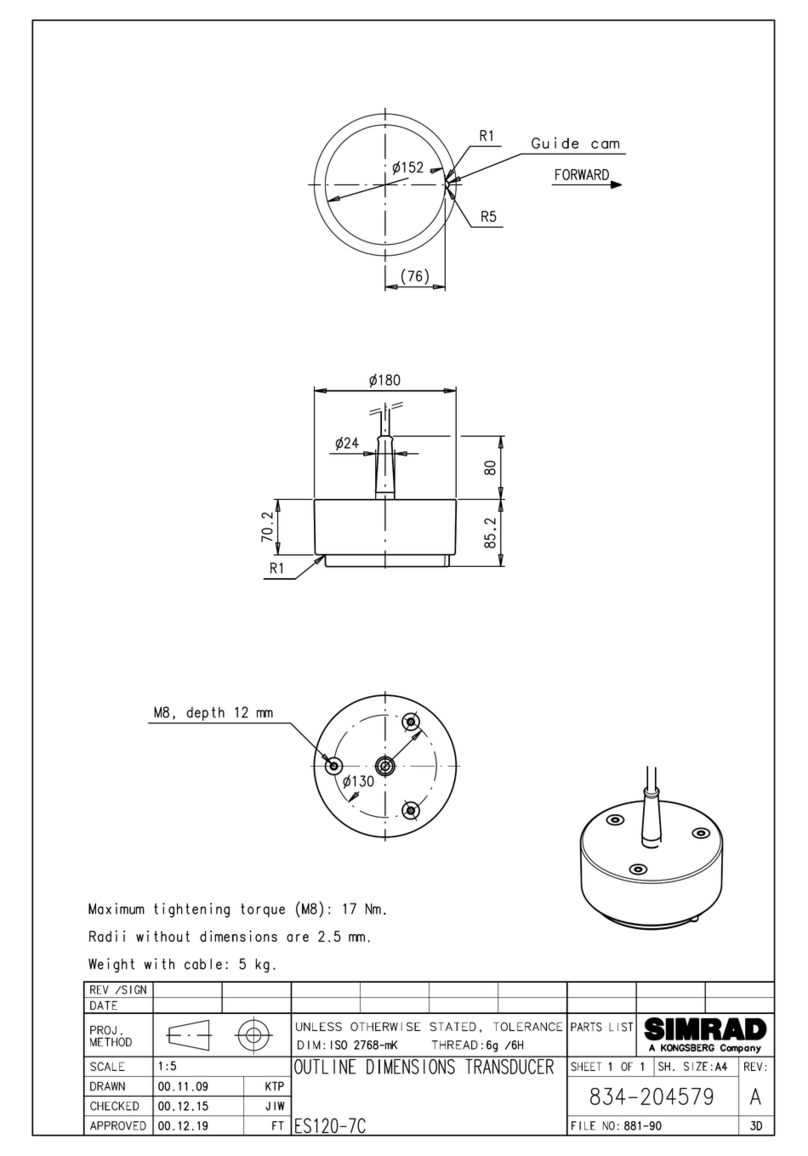
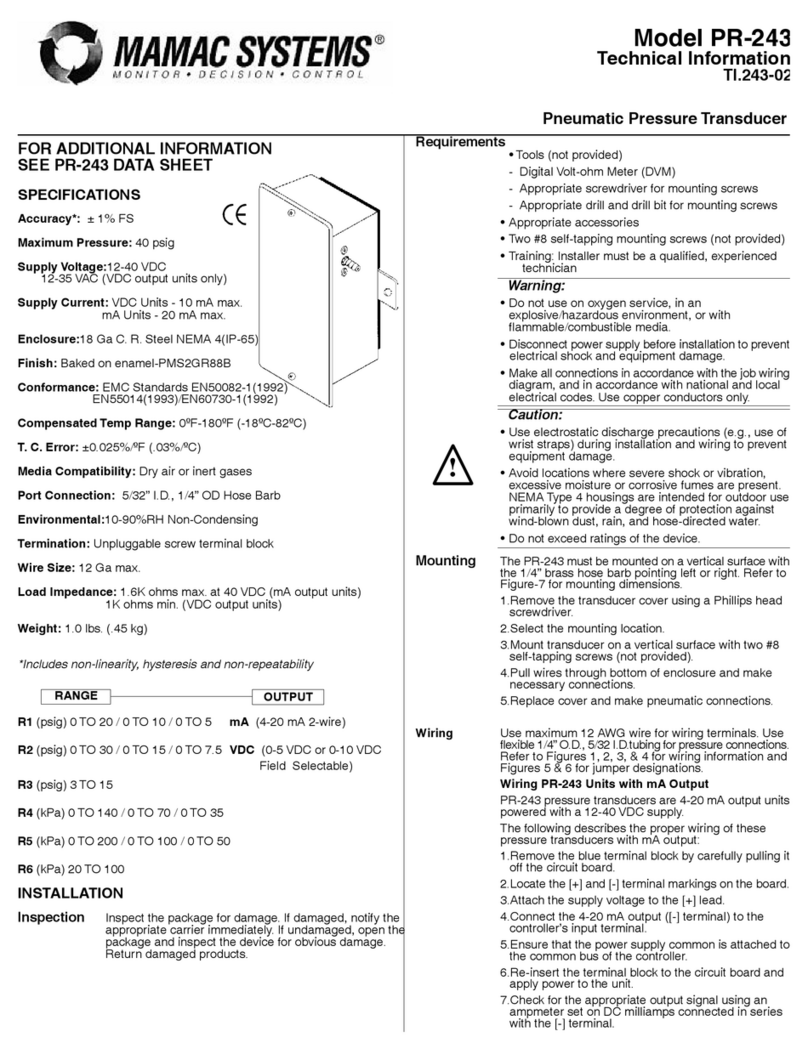
Model T17 Installation Guide vii
Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.2 Transducer Construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.3 Certification and Safety Statements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Chapter 2. Installing Pipe Nozzles
2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.2 Diametrical Path Nozzle Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.2.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components, Diametrical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2.2 Selecting and Marking the First Nozzle Location, Diametrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location, Diametrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2.4 Installing the First Welding Boss, Diametrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2.5 Installing the First Nozzle, Diametrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
2.2.6 Installing the Second Welding Boss and Nozzle, Diametrical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.2.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.3 Non-Diametrical Mid Radius Path Nozzle Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.3.1 Identifying and Checking the Nozzle Installation Kit Components, Non-Diametrical, Mid-Radius . . . . . . . . . . .17
2.3.2 Selecting and Marking the First Nozzle Location, Non-Diametrical, Mid-Radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.3.3 Determining and Marking the Second Nozzle Location, Non-Diametrical, Mid-Radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.3.4 Installing the First Welding Boss, Non-Diametrical, Mid-Radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.3.5 Installing the First Nozzle, Non-Diametrical Mid Radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.3.6 Installing the Second Welding Boss and Nozzle, Non-Diametrical Mid Radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
2.3.7 Hot Tapping the Pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.3.8 Cold Tapping the Pipe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Chapter 3. Installing an Isolation Valve
3.1 Diametrical or Non-Diametrical Nozzle, Valve Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.1.1 For 3 inch Flanges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Chapter 4. Inserting T17 Transducers into the Pipe
4.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
4.2 Inserting Transducers Using the Insertion Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.2.1 Preparing for Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
4.2.2 Mounting the Insertion Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
4.2.3 Aligning the Downstream Transducer for Extended Range Installations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
4.3 Connecting an XAMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Chapter 5. Maintaining the T17 Transducers
5.1 Removing Transducers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5.1.1 Using the Insertion Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Chapter 6. Specifications
6.1 T17 Transducer Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
6.2 T17 Transducer Certifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57