PRESSCON VERNIT N2 User manual

VERNIT - HORNIT N2(i) expansion
systems
User manual
Type
:
User manual
Date
:
18-09-2019
Version / Revision
:
Version 4.2, Revision 00
Status
:
Approved
Company
:
PRESSCON
Location
:
Honselersdijk

2

3
Table of content
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................................... 5
Important to know ................................................................................................................................................. 7
1.1.1 Working with the safety valve .............................................................................................................. 9
1.2 Description of hazard symbols .......................................................................................................................... 9
2 System components .................................................................................................................................. 11
2.1 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY A ............................................................................................................ 11
2.2 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY B ............................................................................................................ 12
2.3 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY DUO ...................................................................................................... 13
2.4 Vacuum- overpressure safety valve and vacuum safety valve ....................................................................... 15
2.5 Vacuum- overpressure safety valve with tracing band ................................................................................... 16
2.6 Pressure sensor ............................................................................................................................................... 17
2.7 Pressure sensor with tracing ribbon ............................................................................................................... 17
3 General operation ....................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1 Operation of the expansion system ................................................................................................................ 19
3.1.1 Compressed air supply ....................................................................................................................... 19
3.1.2 Nitrogen production ............................................................................................................................ 19
3.1.3 Water monitoring ................................................................................................................................. 19
3.1.4 Systems that also regulate the water level (optional) .................................................................... 20
3.1.5 Protection against overpressure and vacuum with VERNIT systems ......................................... 20
3.1.6 Protection against vacuum with HORNIT systems ........................................................................ 21
3.1.7 Leak detection measurement (SLDM or CLDM) for VERNIT systems (optional) ...................... 22
3.1.8 Heating tape at the pressure sensors and vacuum overpressure relief valve (optional) .......... 22
3.1.9 Manual operation of the return valve (optional) .............................................................................. 23
3.2 Assembly of components on the buffer tank .................................................................................................. 24
3.2.1 Vertical buffer tank .............................................................................................................................. 24
3.2.2 Vertical buffer tank in a DUO setup .................................................................................................. 26
3.2.3 Horizontal buffer tank ......................................................................................................................... 27
3.2.4 Horizontal buffertank in a DUO setup .............................................................................................. 29
3.2.5 DUO system for a High and low temperature networks ................................................................ 29
3.3 Schematic overview of the expansion system ................................................................................................ 30
3.3.1 VERNIT 2.0 -30.0 N2(i) system ........................................................................................................ 30
3.3.2 HORNIT 2.0 -30.0 N2(i) system ........................................................................................................ 31
3.3.3 VERNIT 2.0 -30.0 N2(i) DUO system ............................................................................................... 32
3.3.4 HORNIT 2.0 -30.0 N2(i) DUO system .............................................................................................. 33
4 Touchscreen ............................................................................................................................................... 34
4.1 Main screen of the Touchscreen ..................................................................................................................... 34

4
4.1.1 Main screen lay-out VERNIT ............................................................................................................ 35
4.1.2 Main screen lay-out HORNIT ............................................................................................................ 35
4.2 Icons on the main screen ................................................................................................................................ 36
4.2.1 Compressor ......................................................................................................................................... 36
4.2.2 PSA generator ..................................................................................................................................... 37
4.2.3 Oxygen sensor .................................................................................................................................... 37
4.2.4 Valves ................................................................................................................................................... 37
4.2.5 Overpressure safety relief .................................................................................................................. 38
4.2.6 VERNIT tank malfunction status ....................................................................................................... 38
4.2.7 VERNIT tank water level status ........................................................................................................ 40
4.2.8 HORNIT tank malfunction status ...................................................................................................... 41
4.2.9 HORNIT tank water level status ........................................................................................................ 42
4.2.10 HORNIT pressure tank failure status ............................................................................................... 43
4.2.11 HORNIT druktank waterhoogte status ............................................................................................. 43
4.3 User menu ...................................................................................................................................................... 44
4.3.1 User menu schematic for Touchscreen type (ECONOMY A and ECONOMY DUO) ............... 44
4.4 Service menu ................................................................................................................................................... 45
4.5 Factory menu .................................................................................................................................................. 45
4.6 Standby ........................................................................................................................................................... 45
5. PRESS-display ............................................................................................................................................ 46
5.1 Buttons on the PRESS-display ......................................................................................................................... 46
5.1 Menu structure and access ............................................................................................................................. 47
5.2 User Menu ...................................................................................................................................................... 47
5.3.1 User menu for the VERNIT ECONOMY B systems ....................................................................... 48
5.4 Service Information screen ............................................................................................................................. 49
5.4.1 Service information screen for the VERNIT ECONOMY B ........................................................... 49
5.5 Factory information screen ............................................................................................................................. 50
5.5.1 Factory information screen for the VERNIT ECONOMY B ........................................................... 50
5.6 Service menu ................................................................................................................................................... 51
5.7 Factory menu .................................................................................................................................................. 51
5.8 Standby ........................................................................................................................................................... 51
6 PRESS-control ...................................................................................................................................................... 52
6.1 Types of PRESS-control ................................................................................................................................... 52
7 Alarms and error handling ........................................................................................................................ 53
7.1 Faults and alarms ........................................................................................................................................... 53
7.2 Overriding the boiler alarm relay ................................................................................................................... 54
7.3 Faults and alarm messages ............................................................................................................................. 55

5
7.3.1 Fault and alarm messages for the PressControl (ECONOMY A and ECONOMY DUO) ............................... 55
7.3.2 Fault and alarm messages for the Touchscreen ............................................................................ 57
7.3.3 Fault and alarm messages for the PRESS-Basic control(ECONOMY B) ....................................................... 60
8 Maintenance and service ................................................................................................................................ 63
8.1 Expansion system maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 63
8.2 Compressor maintenance ............................................................................................................................... 63
9 Warranty ....................................................................................................................................................... 63
10 Appendix .................................................................................................................................................. 65
11 Document history ................................................................................................................................... 65
12 To conclude ................................................................................................................................................... 71
Introduction
The VERNIT HORNIT expansion system monitors and controls the pressure that is present in the expansion chamber of
a central heating system. It is applicable for the central heating systems in the horticulture industry. The system is
comprised out of a nitrogen generator with an air compressor, a set of pressure sensors that measure the water level
and pressure in a buffer tank and a control module that controls the nitrogen generator.
The central heating systems that are used in the horticulture industry store their heat in a vertical or horizontal buffer
tank. The buffer tanks are not fully filled with water but have an expansion chamber above the water. When looking at a
vertical buffer tank the expansion chamber is right above the water inside the tank. When looking at a horizontal buffer
tank the expansion chamber is also right above the water inside the tank but it can also be located in a separate
expansion vessel. The expansion chamber is intended for the water in the central heating system to expand and shrink
when the water is heated up or cooled down. During this process the pressure in the expansion chamber also changes.
The VERNIT HORNIT expansion system monitors the pressure in the expansion chamber. When the pressure becomes
too high then an overpressure valve relieves the extra pressure. When the pressure becomes to low then the VERNIT
HORNIT expansion system will produce nitrogen in order to get the expansion chamber pressurized again. The nitrogen
generator of the VERNIT HORNIT expansion system produces an air mixture with a nitrogen concentration of 99,0 vol. %
N2. The system uses nitrogen because it is an inert gas. Inert gasses have the ability to prevent the formation of rust
when it is available in a high concentration. The VERNIT HORNIT expansion system makes sure that there is always a
blanket of nitrogen present in the expansion chamber within the buffer tank and that it is kept at a steady overpressure.
Next to the pressure management of the nitrogen blanket, the VERNIT HORNIT expansion system also acts as a
monitoring device for the water level in the buffer tank. By using pressure sensors the system determines the height of
the water level. Once the water level becomes too high or too low, the VERNIT HORNIT expansion system will generate
the appropriate fault or alarm messages and can also send a stop signal to other relevant devices. The water level
monitoring is important for the conservation of the buffer tank. It prevents the water level from becoming too high and
damaging the roof of the buffer tank.

6
It also prevents the water level from becoming too low, which leads to air in the heat supply spray tube and in the central
heating network.
These are important features for maintaining the buffer tank and preserving the central heating system.

7
Important to know
The expansion systems are produced in 2 different types. Namely, the VERNIT and HORNIT systems. These 2 types
have the following differences.
• VERNIT, the expansion system regulates the pressure of the nitrogen blanket in the vertical heat storage tank.
• HORNIT, the expansion system regulates the total system pressure in a horizontal heat storage tank. This is
done either directly or via an external expansion vessel.
In addition to VERNIT and HORNIT, there are a few additional indications that define the function of the expansion
system. These are:
2.0 – 30.0
The number in the type designation indicates the capacity of the nitrogen generator. This number
represents the flow rate in m³/h that the generator can produce with a purity of 99.0 Vol%N2. The
smallest capacity per generator is 2.0 m³/h and the largest possible capacity is 30.0 m³/h. Larger
capacities are also possible, but several nitrogen generators have to be combined with each other.
H.P.
"High Performance" stands for the design of the PSA tube. Indicates that the PSA applied to the
system was manufactured by PRESSCON. Nitrogen generators from before 2009 do not have this
addition.
ECONOMY
This indicates that the generator is equipped with a valve control system designed for high output
and energy efficiency.
N2i
N2i stands for direct injection of nitrogen. In this case, the expansion system will blow nitrogen
directly into the heat storage tank.
N2
N2 without the "i" stands for an expansion system without direct injection. In this case, the expansion
system uses a separate pressure vessel in which the nitrogen is first stored before it is blown into the
heat storage tank.
A (panel)
The addition "A" indicates that the expansion system is equipped with the A-type control panel which
is the most comprehensive version.
B (panel)
The addition of "B" indicates that the expansion system is equipped with the B-type control panel,
which is a simpler version than the A-type panel.
DUO(panel)
DUO means that the expansion system is suitable for monitoring 2 separate heat storage tanks.
ELC
The expansion system is prepared to operate in an Equal Level Control setup. This function allows
for control of the level difference in two tanks by controlling a pump. For this purpose, the expansion
system will work together with 1 or more expansion systems via CAN-bus.
SLC
The expansion system is prepared to use the Switching Level Control function. This function
generates a switching signal based on the level difference in two tanks. For this purpose, the
expansion system will work together with 1 or more expansion systems via CAN-bus.
SLDM
Leak detection measurement that works on the basis of a 3rd pressure sensor at the bottom of the
vertical buffer tank.
CLDM
Leak detection measurement that works on the basis of information that the system receives from
the horticultural computer. The horticultural computer then indicates the fill level of the vertical buffer
tank.
The type designations described above are compatible with each other according to the matrix below.
VERNIT
HORNIT
N2i
N2
A (panel)
B (panel)
DUO
(panel)
ELC /
SLC
SLDM /
CLDM
VERNIT
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
HORNIT
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
No
No
N2i
Yes
Yes
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
N2
Yes
Yes
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes

8
A (panel)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
B
(panel)
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
No
No
DUO (panel)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
Yes
Yes
ELC / SLC
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
N/A
Yes
SLDM /
CLDM
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
N/A
Touchscreen and PRESS-Display
The touchscreen and the PRESS-display are both control units that can be used for the PRESSCON nitrogen
generators. Originally, the PRESS-display was conceived as a multi-purpose digital display showing the water level,
nitrogen blanket pressure and any alarms. The Touchscreen also performs these functions, but offers a more visual
overview of the system and more intuitive controls. The Touchscreen can also be universally used for multiple types of
nitrogen generators.
• The Touchscreen is used as standard for the types VERNIT - HORNIT ECONOMY A and ECONOMY DUO.
Optionally, this display can also be used with a VERNIT ECONOMY B.
• The PRESS-display is used as standard with the VERNIT ECONOMY B
If 2 or more expansion systems are connected to each other via CAN-bus, it is important that the displays within that
network are all of the same type. Touchscreen and PRESS-display do not work together within a CAN-bus network. This
could occur, for example, in an ELC setup.

9
1.1.1 Working with the safety valve
The safety valve is commonly located on the roof of the buffer tank. When working on the safety valve, the following
hazards should be considered.
Symbol
Description
Applies to
HOT PARTS,
Do not touch parts with bare hands.
Use heat-resistant clothing.
The housing of the safety valve and relieved nitrogen from the
buffer tank. The upper layer of water can heat up the nitrogen in
the safety valve. The housing can then be too hot to touch. The
relieved nitrogen from the vacuum- overpressure safety valve on
top of a vertical buffer tank can also contain steam with a
temperature of 90°C which could cause burn injury. Vacuum safety
valves on the horizontal buffer tanks do not release nitrogen.
ATTENTION! WORKING AT HIGHTS,
Working on the roof of a vertical or horizontal buffer tank is
considered working at heights. Fall protection is recommended
when working on the safety valve.
HIGH PRESSURE, Relief pressure
from components before work is
conducted.
The safety valves on both the vertical and horizontal buffer tanks.
The safety valve on a vertical buffer tank can be depressurized by
hand. The pressure is not higher than 28 mBar. The safety valve
on a horizontal buffer tank can only be depressurized by relieving
water pressure for the buffer tank. The pressure is not higher than
1200 mBar.
1.2 Description of hazard symbols
In addition to the identified risks for the nitrogen generator, compressor and safety valve, the following symbols can also
be applied. When a hazard symbol is encountered, please observe its meaning carefully before further commencing the
work.
Symbol
Description
Symbol
Description
1. OVERPRESSURE VALVE,
Be aware of the sudden relief of
overpressure.
7. HIGH PRESSURE,
Relief pressure from components before work is
conducted.
2. DANGEROUS VOLTAGE,
Forbidden to work on the system if the
power is on.
8. HOT PARTS,
Do not touch parts with bare hands. Use heat-
resistant clothing.
3. DANGEROUS TO INHALE GAS,
Avoid the specified area or wear
appropriate breathing equipment.
9. MOVING PARTS,
Risk of getting stuck or injuries to limbs. Turn the
machine off completely before working on it.

10
4. NOISE,
Wear ear protection to prevent hearing
damage.
10. ROTATING FAN,
Risk of getting stuck or injuries to limbs. Turn the
machine off completely before working on it.
5.MACHINE WITH AUTOMATIC START,
Machine stops and starts automatically when it
is operating normally. Turn off the machine
completely before working on it.
11. ATTENTION,
Special situation occurs, follow additional instructions.
6. READ THE OPERATING AND
MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS,
It is advised that the maintenance instructions
are read before continuing work.

11
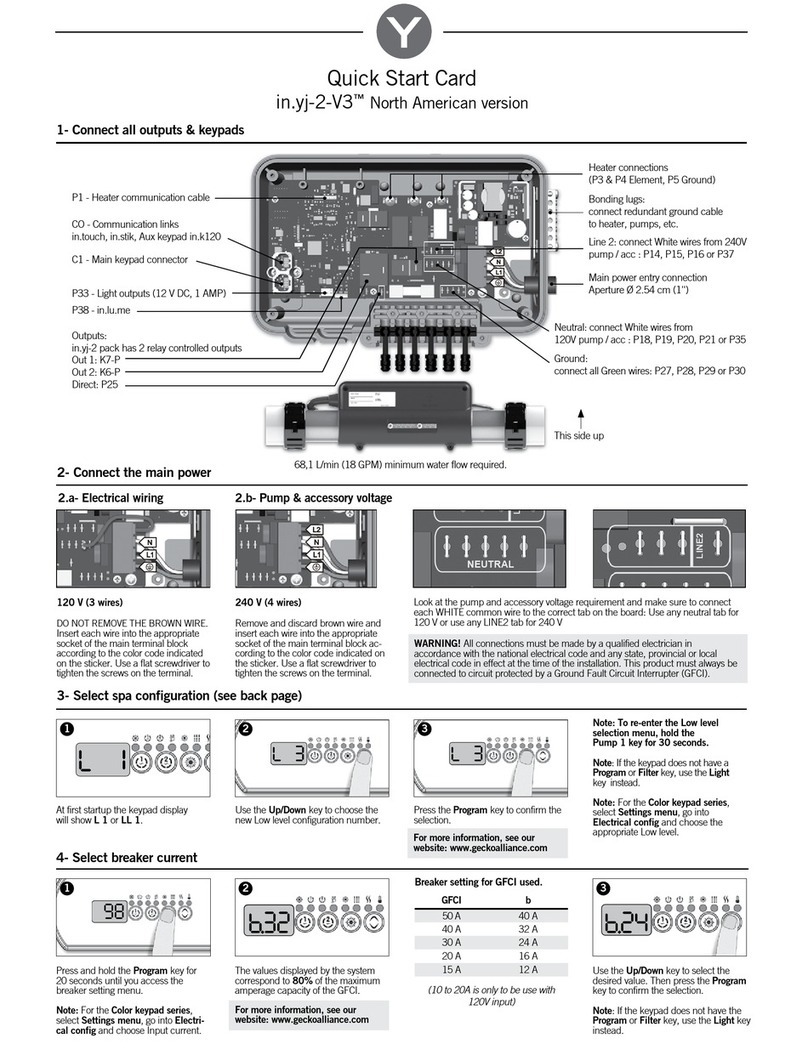
2 System components
The PRESSCON expansion systems consist out of the following components: a nitrogen generator, compressor, safety
valve and 2 or more pressure sensors. This chapter describes these components by giving an image of each device and
by numbering the most important parts. The compressor is not described because different brands and types can be
applied and it is delivered with its own manual.
2.1 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY A
N2 system
N2i system
Figure 1. N2 ECONOMY A system
Figure 2. N2i ECONOMY A system
3.
3.
5.A
4.
6.
8.
10.
7.
9.
2.
11.
1.
1. 2.
3.1
3.1
4.
3. 3.
5.A
6.
8.
10.
7.
9.
1.
11.
1.
3.1 3.1

12
2.2 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY B
N2 system
N2i system
Figure 3. N2 ECONOMY B system
Figure 4. N2i ECONOMY B system
3. 3.
5.B
6.
8.
10.
7.
9.
2.
4.
11.
1.
1. 2.
3.1
3.1
4.
3. 3.
5.B
6.
8.
10.
7.
9.
1.
11.
1.
3.1 3.1

13
2.3 Nitrogen generator type ECONOMY DUO
N2 system
N2i system
Figure 5. N2 ECONOMY DUO system
Figure 6. N2i ECONOMY DUO system
3. 3.
8.
10.
7.
9.
1.B
2
4.
5.A
6.
1.A
11.
1A. 2. 1B.
3.1 3.1
4.
3. 3.
8.
10.
7.
9.
1.B
5.A
6.
1.A
11.
1B.
1A.
3.1 3.1

14
Legend
Legend for the nitrogen generator of the types: ECONOMY A, ECONOMY B, ECONOMY DUO.
Ref.
No.
Description
Function
1.
Nitrogen output connection
Tube which puts out the nitrogen mixture that is produced by the nitrogen
generator. This outlet will be connected to the piping that runs to the buffer tank.
Please note that this connection is located differently when comparing the N2 and
N2i systems. Also note that the N2 and DUO systems have solenoid valves in the
tubing while the N2i systems do not.
1.A/B
Nitrogen inlet tank 1 and tank 2
Same connection as the standard Nitrogen output connection. Connection 1.A is
used for supplying nitrogen to tank 1 and connection 1.B is used for supplying
nitrogen to tank 2.
2.
Nitrogen HP vessel connection
Tube which puts out the nitrogen mixture that is produced by the nitrogen
generator. This outlet is specially fitted for connecting a nitrogen HP vessel.
3.
PSA vessels
High pressure vessels with active carbon inside. The Pressure Swing Adsorption
process takes place within these vessels. The ST BASIC systems also uses the
nitrogen HP vessel for the Pressure Swing Adsorption process.
3.1
PSA pressure gauges
0 – 10 bar (0,0 – 1,0 MPa) pressure gauges that indicate the pressure within the
PSA vessels. The left pressure gauge is for the left PSA vessel and the right
pressure gauge is for the right pressure vessel.
4.
Digital nitrogen HP vessel
pressure regulator.
Digital pressure switch with a start and stop setting. At default, the pressure
regulator will generate a start signal below 4.0 Bar. At 6.5 Bar, the signal will turn
off and the text on the display will turn green. If the pressure then drops below 4.0
Bar, the text on the display will turn red and a new start signal is generated.
5.A
Touchscreen
Standard for ECONOMY A and ECONOMY DUO systems. This is the most
important monitoring device for reading the statuses and values of the system. The
touchscreen is used to navigate and adjust the settings.
5.B
PRESS-display
LCD display with buttons. Standard for ECONOMY B systems. This is the most
important monitoring device for reading the statuses and values of the system. The
buttons are used to navigate and adjust the settings.
6.
Control cabinet
Control cabinet containing all the electronic components needed to manage the
nitrogen generator, compressor and sensor measurements of 1 buffer tank. This
type of control cabinet has enough space for all standard components and
additional components required for any further expansion of the control cabinet.
7.
Compressed air regulator and
pressure switch.
Composition of pressure control valve and pressure switch. The maximum air
pressure for the nitrogen generator is manually setup by adjusting the pressure
control valve. The pressure switch notifies the system if there is a pressure drop.
8.
Compressed air inlet
Push-in connection that is used for connecting the compressor to the nitrogen
generator. This is commonly done with a 16mm nylon air hose.
9.
PSA control manifold
A pneumatically controlled manifold block that regulates the flow of air and nitrogen
during the Pressure Swing Adsorption process.
10.
Compressed air filters
2 filters that filter out dirt and moisture that comes with the compressed air.
11.
Nitrogen inlet manifold
A pneumatically controlled manifold block that regulates the flow of nitrogen to the
nitrogen storage vessel and one or two buffer tanks.

15
2.4 Vacuum- overpressure safety valve and vacuum safety valve
Figure 7. PV 80/25/20-2, PV 150/25/20-2, PV 200/25/20-2 (VERNIT
systems)
Figure 8. PV 50-2F, PV 80-2F, PV 100-
2F.(HORNIT systems)
Legend
Legend for the safety valves of the types: PV 80/25/20-2, PV 150/25/20-2, PV 200/25/20-2, PV 50-2F, PV 80-2F, PV
100-2F.
Ref.
No.
Description
Function
1.
Maximum overpressure valve
A mechanically operating valve plate with calibrated lead slices that relieves
nitrogen at the maximum allowed pressure. It is protected with an additional
cover.
2.
Operating overpressure valve
A mechanically operating valve plate with calibrated lead slices that relieves
nitrogen at the maximum operating pressure. It is protected with an
additional cover.
3.
Safety valve housing
Assembly housing that holds the vacuum valve and overpressure valves.
4.
Vacuum pressure valve
A mechanically operating valve plate without lead slices that is lifted when a
vacuum occurs.

16
2.5 Vacuum- overpressure safety valve with tracing band
For cold environments it is possible to install tracing ribbon around the vacuum- overpressure safety valve to prevent it
from freezing. Although the safety valve is designed to withstand a certain level of frost, the additional tracing ribbon is an
optional feature that is advisable for environments with long periods of frost.
Figure 9. Vacuum- overpressure safety valve
Legend
Ref.
No.
Description
Function
5.
Tracing band
Band that is heated when powered with electricity.
6.
Thermostat
Thermostat that monitors the surrounding temperature at the sensor and
activates the tracing ribbon when the temperature becomes too low.
7.
Insulation material
Insulation material that prevents the loss of heat that is generated by the
tracing band. By preventing loss of heat to the surrounding, more heat is
induced into the safety valve.
8.
Finishing plating
Plating that keeps the tracing band and insulation material in place and
protects them against external influence.

17
2.6 Pressure sensor
Figure 10. Sensor 0-600mBar, 0-1000mBar, 0-1500mBar, 0-1600mBar, 0-2500mBar.
Legend
Legend for the pressure sensors of the types: 0-600mBar, 0-1000mBar, 0-1600mBar, 0-2500mBar,
Ref.
No.
Description
Function
1.
Protection cap cover
Plastic cover that slides over the pressure sensor. It clamps onto the
protection cap sensor holder.
2.
Pressure sensor
Electrical transmitter that translates a pressure measurement into a
readable 4…20mA signal over a 2 wire connection.
3.
Rubber ring
Rubber ring that seals leakage from air and water between the pressor
sensor and protection cap of the sensor.
4.
Protection cap sensor holder
Plastic isolated holder with tubing that holds the pressure sensor. The
sensor holder functions as additional protection against heat and moisture.
It also allows the pressure sensor to be easily exchanged.
5.
Threaded end of sensor cap
1/2” threaded end through which the protection cap is fitted onto the
buffertank.
6.
Welded threaded socket
1/2” Socket that is welded onto the buffertank and in which the pressure
sensor protection cap is fitted. (fitted by a third party company)
2.7 Pressure sensor with tracing ribbon
For cold environments it is possible to install tracing ribbon around the sensor to prevent it from freezing. Although the
protection cap of the sensor can protect the sensor against freezing to a certain level, the additional tracing ribbon is an
optional feature that is advisable for environments with long periods of frost.
4.
2.
1.
6.
5.
3.

18
Figure 11. Sensor with tracing ribbon
Legend
Ref.
No.
Description
Function
7.
Tracing ribbon
Ribbon that is heated when powered with electricity.
8.
Thermostat
Thermostat that monitors the surrounding temperature at the sensor and
activates the tracing ribbon when the temperature becomes too low.
8.
7.

19
3 General operation
3.1 Operation of the expansion system
The expansion systems can be applied in two different ways. The VERNIT type systems take care of regulating the
pressure of the nitrogen blanket and monitor the water level in the vertical buffer tank. It also has the capability to
regulate the water level if so desired. The HORNIT type systems take care of regulating the total system pressure and
monitor the water level in the horizontal buffer tank. To further explain the operation and functionality of the expansion
systems, the following steps describe how these systems work.
3.1.1 Compressed air supply
Step 1. The compressor takes the air from the surrounding and compresses it to a pressure of 10 Bar. The compressor
has a compressed air HP vessel that holds the compressed air and will continuously maintain the pressure.
From the HP vessel, the air is fed to the nitrogen generator through a hose. At the nitrogen generator, the water
and oil residue is filtered from the compressed air by two filters. This process is the same for all type of nitrogen
generators that are described in this manual.
3.1.2 Nitrogen production
Step 1. The pressure sensors on the buffer tank measure the pressure of the nitrogen blanket and the height of the
water level. This data is sent to the nitrogen generator control cabinet and is displayed on the Touchscreen or
the PRESS-display. The VERNIT systems monitor the pressure of the nitrogen blanket, when it is too low a start
command is generated and nitrogen production starts. The HORNIT systems monitor the total system pressure,
which consists of both the water pressure and the nitrogen pressure. If this is too low, a start command is
generated and nitrogen production starts.
Step 2. Nitrogen production starts with drawing in compressed air from the compressor. The compressed air is
transported to the PSA tubes where the Pressure Swing Adsorption process takes place. The ECONOMY -A -B
and - DUO systems have 2 PSA tubes for this process. Any remaining nitrogen from the Pressure Swing
Adsorption process is blown back into the immediate environment. The remaining mix of oxygen and nitrogen
has a purity of 99.0 vol. % N2. The nitrogen mix is fed to the vertical or horizontal buffer tank and the pressure of
the nitrogen blanket or total system pressure is increased. The nitrogen mix can be sent directly to the buffer
tank if necessary. But it is also possible to first store the nitrogen in the nitrogen storage tank after which it is
sent from here to the buffer tank.
Step 3. The pressure sensors on the buffer tank measure the increased pressure of the nitrogen blanket in the VERNIT
system. In the case of a HORNIT system, the increased system pressure is measured. When the pressure is at
the desired level according to the settings in the Touchscreen or PRESS-Display, the nitrogen production is
stopped. The compressor will continuously keep the air pressure constant. When no more air pressure is being
used by the nitrogen generator, the compressor will also stop.
3.1.3 Water monitoring
Step 1. The pressure sensors on the buffer tank measure the pressure of the nitrogen blanket and the height of the
water level. This data is transferred to the control box of the nitrogen generator and is displayed on the
Touchscreen or the PRESS-display. The water level sensor also measures the pressure of the nitrogen blanket
because the blanket is on top of the water column. The measurement of the nitrogen blanket pressure is
therefore used to calculate a correct water level. To monitor the water level correctly, the VERNIT HORNIT
expansion system is set with multiple error and alarm limits.
Step 2. When the water in the buffer tank is heated or cooled down, the water level will increase or decrease. Under
normal circumstances, the VERNIT HORNIT expansion system will do nothing and only show the
corresponding water level. The error- and alarm limits are set in such a way that they are not triggered under
normal circumstances.
Step 3. When the water level in the buffer tank becomes higher or lower than desired, the VERNIT HORNIT expansion
system will report an error. A pre-alert is generated on the Touchscreen or PRESS-display indicating that the
water level is higher or lower than it should be but that it is not yet problematic. The error message also
indicates whether water should be added or released to remedy the situation.

20
It is important to note that these pre-alerts could indicate that the buffer tank is overfilled or that water is leaking
from the system.
If the water level in the buffer tank continues to fall or rise after the pre-warning is given, the VERNIT HORNIT expansion
system will sound an alarm for a too high or too low water level. This indicates that the water level has risen or fallen to a
problematic level and should not be allowed to rise or fall any further. If it were to rise or fall further, the buffer tank could
be damaged or air could enter the supply spray tube of the central heating network. The VERNIT HORNIT expansion
system will now stop nitrogen production and also generate a stop signal for all relevant devices such as the boiler.
Please note that the relevant devices connected to the stop signal are different in each individual system and depend on
the preferences of the system owner.
3.1.4 Systems that also regulate the water level (optional)
The PRESSCON expansion system of the ECONOMY –A and –DUO types has the possibility to regulate the water level
automatically. This is an optional function that can be used to automatically replenish or drain water from the buffer tank
when needed.
Step 1. The pressure sensors on the buffer tank measure the height of the water level. This data is sent to the control
box of the nitrogen generator and is displayed on the Touchscreen or the PRESS-display. When the water level
is below the minimum height, an electric start signal is generated that turns on an external water pump.
Step 2. The water pump adds water directly to the buffer tank, increasing the water level.
Step 3. The pressure sensors on the buffer tank measure the increased water level. When the water has reached the
minimum height, in accordance with the settings of the Touch Screen or the PRESS-display, the water pump
stops.
The water level regulate function can disguise a water leakage in the central heating
system. This should always be considered when this function is applied.
3.1.5 Protection against overpressure and vacuum with VERNIT systems
These steps only apply to the VERNIT type systems. These systems operate on a pressure of 10 mBar to 28 mBar at
which the overpressure protection can be regulated with a mechanical safety valve.
Step 1. If the pressure of the nitrogen blanket in the buffer tank is at the desired nominal pressure, the nitrogen
generator stops and the vacuum- overpressure safety valve is closed. Under influence of heat, water expands
and the pressure of the nitrogen blanket increases. When the pressure of the nitrogen blanket is at its maximum
operating pressure, the operating overpressure valve will open. The nitrogen is relieved until the water in the
storage tank is not heated any more.
Step 2. If the pressure of the nitrogen blanket is at its maximum operating pressure it is still possible that the pressure
can further increase under special circumstances. It can increase to the maximum allowed pressure. If this
happens, the maximum overpressure valve will open in addition to the operating overpressure valve. With both
valves open, the pressure is relieved with the maximum flow that the safety valve can handle. This will prevent
that the pressure increases any further.
Step 3. If water in the buffer tank is not heated anymore and cools then the pressure of the nitrogen blanket also drops.
It is possible that the pressure drops below 0 Bar and turns into a vacuum. The vacuum pressure valve will
open and will let surrounding air into the tank. This will undo the vacuum.
This manual suits for next models
3
Table of contents
Other PRESSCON Control System manuals
Popular Control System manuals by other brands

SAI
SAI Connect Operation manual

Kessler
Kessler SECOND SHOOTER quick start guide

Airzone
Airzone iQ Zone installation manual

Dormakaba
Dormakaba BEST Wi-Q ONGUARD Interface User Guide

CNC-Step
CNC-Step RaptorX-SL1200-S15 operating instructions

ASCO POWER TECHNOLOGIES
ASCO POWER TECHNOLOGIES 5010 Operator's manual