9
During the operation the device controller creates and sends
voltage impulses with set parameters to the scanner. These parameters
correspond to the type of the connected scanner and the selected
operating mode. Moreover, the controller carries out self-diagnostic,
controls ACC charge and provides its additional charge (if the ACC
charging device is connected).
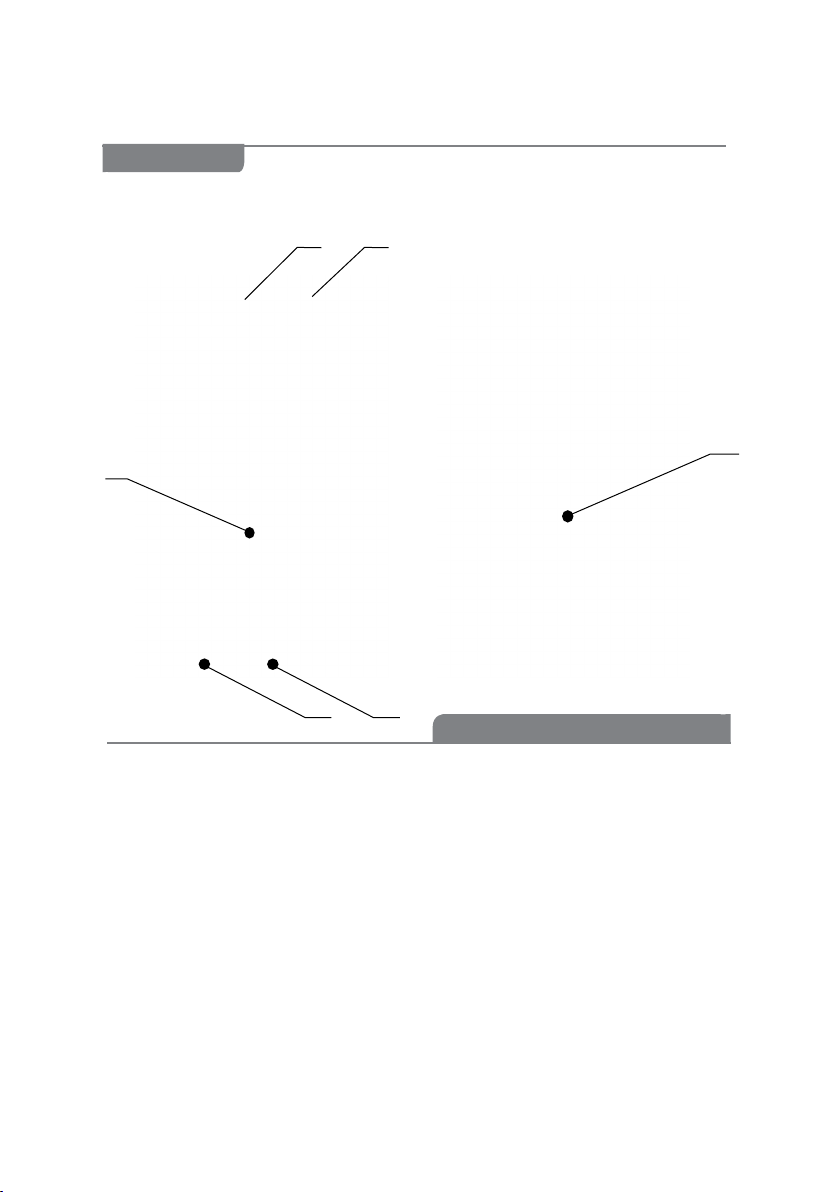
After the scanner socket (pos. 2) is connected and power supply
of the controller device is activated with the button (pos. 3),
the indicators may have the following states:
Only the green indicator glows – controller state and ACC
charge are normal; the scanner is activated – it receives
voltage impulses necessary for magnetographing;
The green indicator glows and the red indicator blinks
impulsively – ACC charge is needed;
The green indicator blinks impulsively – the current
operating mode. The indicator blinks one time when
switching on the controller and changing its operating
modes. The numbers of ashes correspond to the power
level of Fe-scanner (see paragraph 2.3 for the power levels);
None of LEDs glows – ACCs are absent or are fully
discharged, the device controller malfunction;
The controller switches off automatically one minute after
its activation to save energy and protect the scanner from
overheating.
To save energy and protect the scanner from overheating, the
controller is switched off automatically in a minute after activation.
When the ACC charging device is connected to the controller device
(socket – pos. 6) and its power supply is connected to the mains
220V, the yellow indicator (pos. 4) may glow. The glowing means
the presence of external power supply (=24V) at the controller
input, which provides additional ACC charge of the ACC including
the ACC charge during the device operation process.
The access to ACC for their charge and replacement is carried
out by unscrewing 4 screws and removing the cover of the ACC cells
(pos. 5).
External view of AL-scanner is given in Fig. 4.
The Al-scanner is intended for examination of non-ferromagnetic
materials. The scanner is shown in Fig. 4. It is designed in a plastic
body (pos. 1). The eddy-current inductor (pos. 2) is inserted into
the groove in the lower part of the scanner and xed with screws
(pos. 3) on the pads.