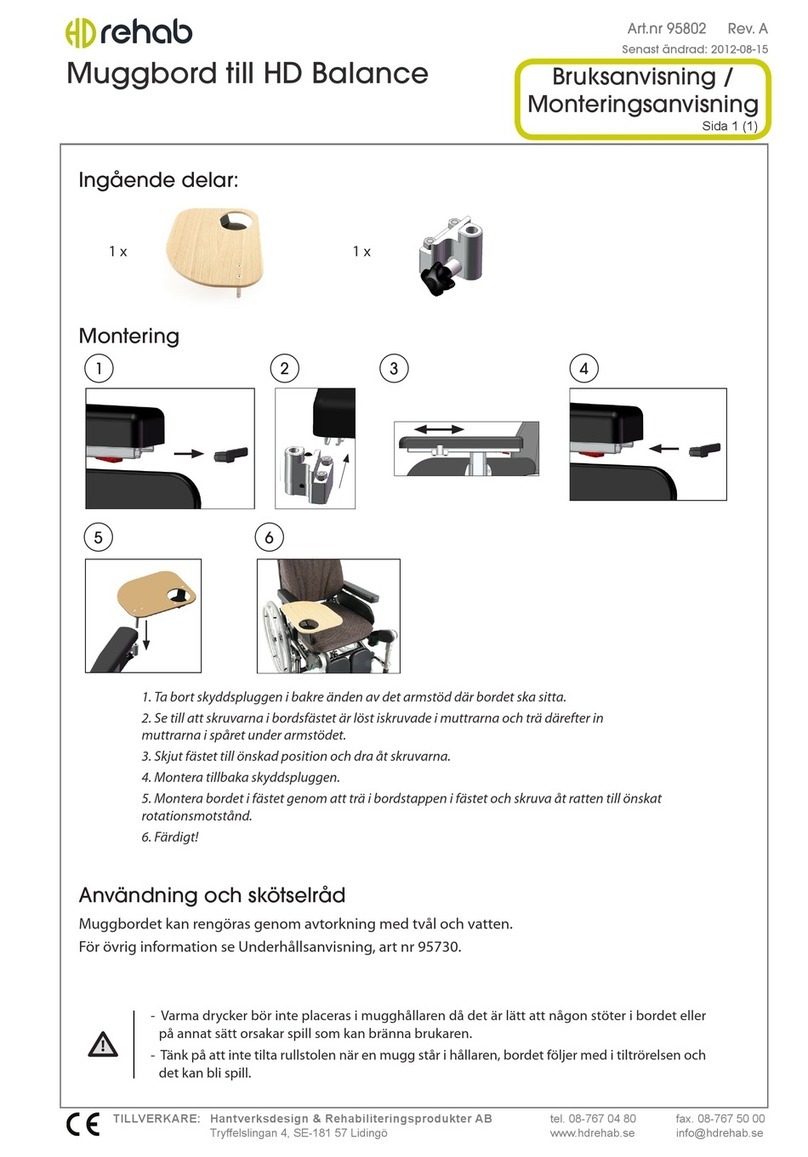
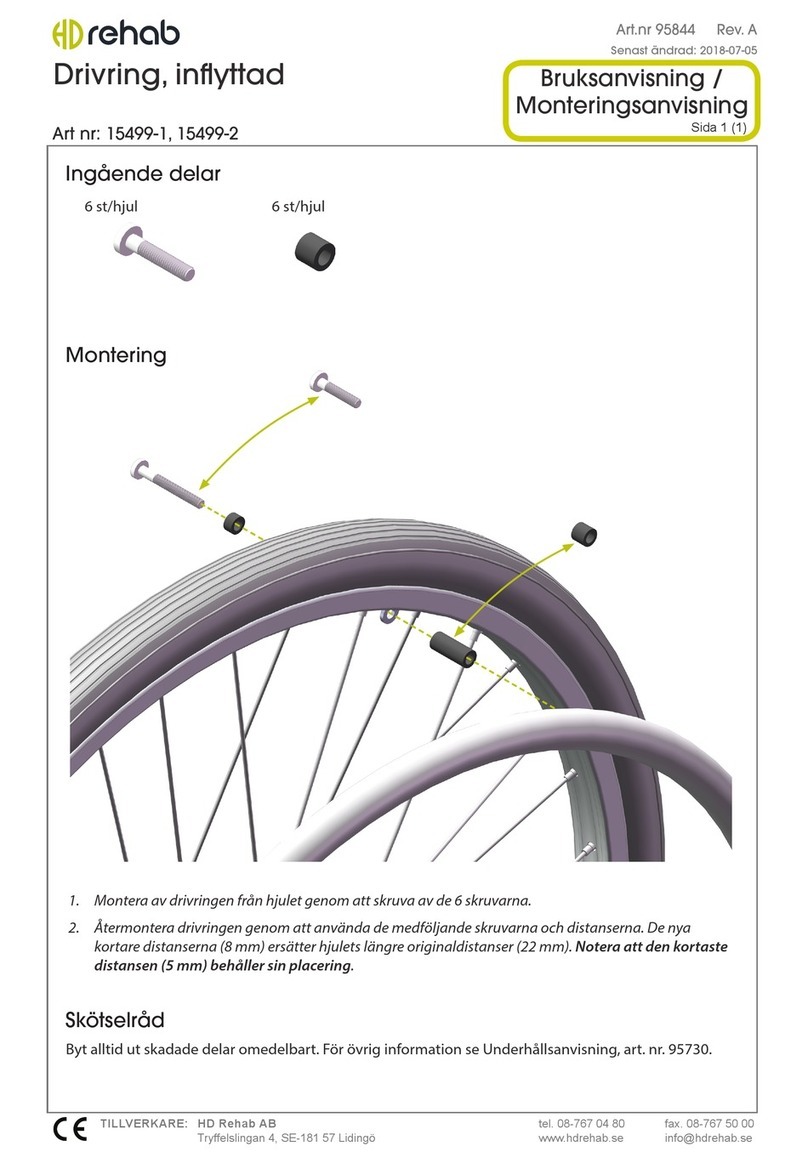
5
HD BALANCE | Technical Information
2. Chassis Construction
The HD Balance chassis is constructed of three interacting frames; wheel frame, seat frame, and
back frame. These are attached to each other at a number of points such that desired geometry
for balance, recline, and seat tilt can be achieved. The wheel frame and seat frame are connected
by balance plates. The balance plates are critical to the characteristics of the wheelchair.
The two models, 16 and 24, have identical chassis with the exception of the wheel frame, where
the plates for wheel attachment have different designs.
2.1 Chassis conguration options
The HD Balance chassis can be modied to change the wheelchair characteristics. The standard
conguration is the reference point for any given data in terms of characteristics, function,
measurements, and tests against existing standards. Changes to the chassis conguration come
with both positive and negative consequences. Therefore the standard conguration should be
used wherever possible.
The following modications can be made:
- Change of balancing plates. Provides raised seat height, lowered seat height, or moving
the balance point forward or backward. Described in section 2.4.
- Lengthened seat frame. Provides increased seat depth. Must be selected with initial
wheelchair order, cannot be changed after assembly.
- Increased / Limited tilt. Described in section 2.5.
- Change of tilt rod. Eects tilt range per document 95758-1. Described in section 2.6.
- Change to rod in place of gas spring. Provides a xed back angle between 90 and105
degrees. Described in section 2.7.
- Moving wheel mounting point 50 mm backward. Makes the wheelchair more stable but
with somewhat poorer handling. Described in section 2.9.
2.2 Change of back frame
1. Remove the push handle by pulling it competely out of the back
frame. Be careful with the cables!
2. Remove the back cushion and disassemble back system (Flexi-
back or Fixed back).
3. Release the rear bracket of the gas spring by pulling out the pin
so that the gas spring can be gently removed.
4. Remove the retaining rings on the inside of the back system
attachment points (A, g1). Tap the pins so that the back frame
can be lifted o. NOTE! It is not necessary to remove the pins
completely in order to release the back frame.
5. Remove the back frame and replace it with the new frame.
6. Assemble the new frame by repeating the same steps in reverse
order. Be careful not to damage the retaining rings, replace
them with new rings if necessary!
2.3 Change of seat frame
1. Remove the back frame per section 2.2 steps 1-4.
2. Remove seat cushion, seat board, leg rests and armrests.
3. Remove tilt rod and gas spring per section 2.6 steps 1-5.
4. Remove the screws from both balance plates (A, g 2).
5. Carefully press one balance plate outwards (B) so that
the seat frame can be lifted o. Be careful when the seat
frame comes free as there can be a pinching hazard and
cables can be damaged.
A
Fig 1
B
A