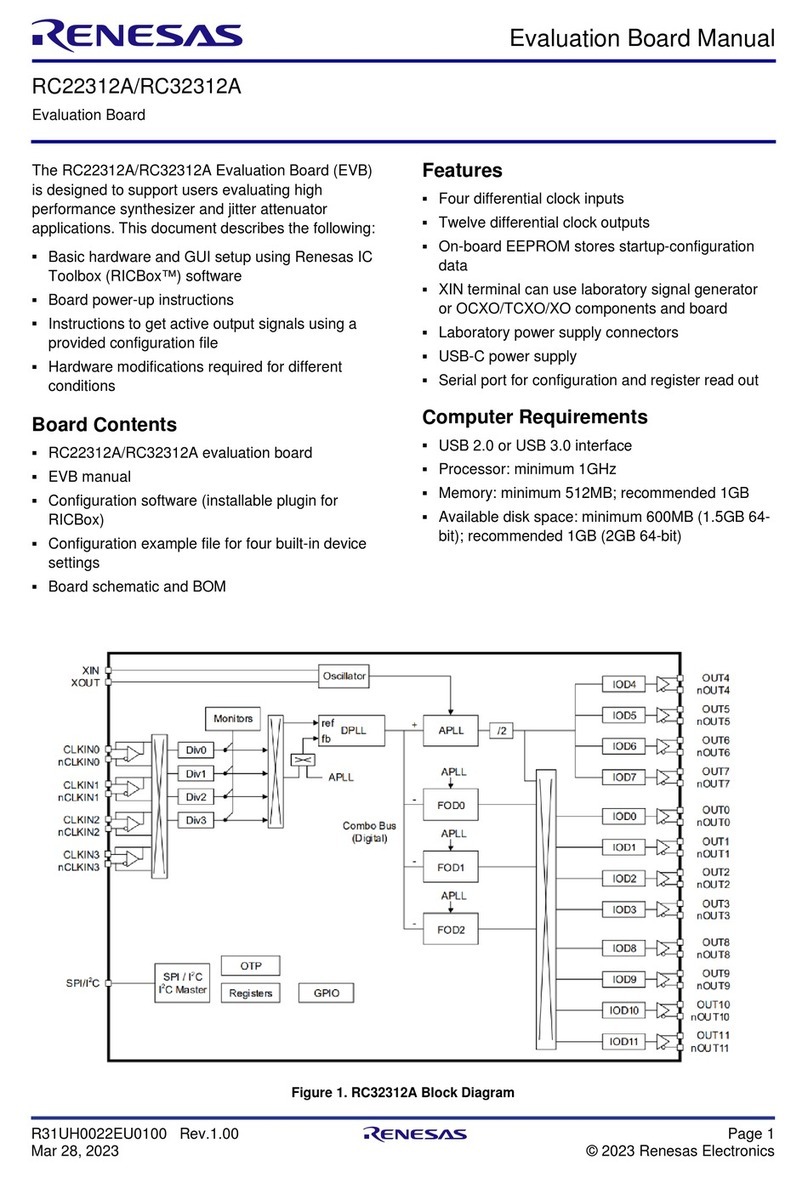
ISL94203EVKIT1Z 4. Using the GUI
AN1952 Rev.3.00 Page 8 of 43
May.9.19
4. Using the GUI
4.1 Common Screen
The right side of the GUI shows the status of the ISL94203. At the top are voltage, current, and temperature
readings. The bottom shows the status bits.
At the bottom of the screen are several controls for temperature settings and memory access.
4.1.1 CELL Voltage Scans
The voltage readouts (Figure 5) show the values for each cell, plus CELLMAX and CELLMIN values. The
CELLMAX and CELLMIN values are returned from the ISL94203 registers. To properly implement this operation,
the GUI stops the internal voltage scan of the ISL94203 (using the µCSCAN bit). It reads the cell voltages and
CELLMAX and CELLMIN values and restarts the automatic scan of the device. The values are read
asynchronously, so without stopping the scan there is not sufficient time to read all the values prior to the next
internal scan. For this reason, the CELLMIN and CELLMAX values are often reported from a different scan than
the rest of the cell voltages. Also, during the scan, the cell balance operation is stopped. The operation stops so
that the cell balance currents do not cause false readings of the cell voltages, due to external voltage drops.
To the right of the cell voltages, there is a graphic indication of the capacity of the cell. This is based on the voltage
of the cell. In this graphic depiction, the scale shows no bar when the voltage is less than or equal to the
undervoltage threshold. It shows 100%, or maximum, when the cell voltage is equal to or greater than the
overvoltage threshold. See the overvoltage and undervoltage thresholds in the Pack settings tab on the left of the
screen.
The GUI highlights the specific cells that equal the CELLMAX and CELLMIN voltages. This helps to identify which
cells are high or low on quick inspection.
When any cell voltage is lower than the undervoltage level, or higher than the overvoltage level, the background
color of that voltage readout changes to red. When the voltage rises above the UV recovery voltage or drops
below the OV recovery voltage the background color returns to white. These color changes are GUI
representations of the cell voltage conditions, the actual indication from the device is shown by the UV and OV
status indicators (bottom right of the screen). These indicators come directly from the device status bits.
Below the CellMIN and CellMAX readings are three boxes that show additional voltage values. The top box
contains the sum of the individual cell readings. The middle box shows the voltage reading of the total battery
pack as derived from an internal divide by 16 voltage divider and converted by the ADC. Comparing these two
values allows a gross determination if there is a cell voltage failure.
The bottom box shows the voltage of the 2.5V regulator. The regulator voltage is internally divided by 2, converted
by the ADC, and multiplied by 2 prior to display.
Figure 5. Voltage Readouts